Java ConcurrentSkipListSet与实例
Java中的 ConcurrentSkipListSet 类是Java集合框架的一部分,实现了 集合接口 和 AbstractSet类。 它为Java中的NavigableSet提供了一个可扩展和并发的版本。ConcurrentSkipListSet的实现是基于 ConcurrentSkipListMap的。 ConcurrentSkipListSet中的元素默认是按自然顺序排序的,或者按集合创建时提供的比较器排序,这取决于使用哪个构造函数。
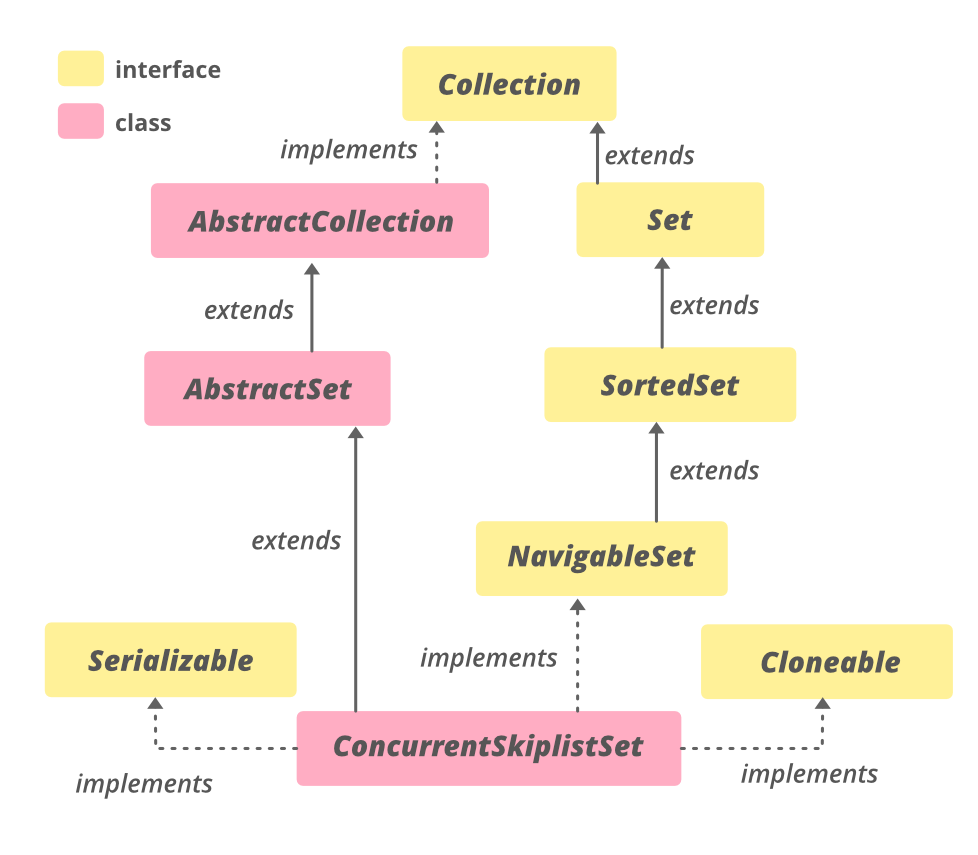
因为它实现了 **SortedSet
类的层次结构
声明
public class ConcurrentSkipListSet<E>
extends AbstractSet<E>
implements NavigableSet<E>, Cloneable, Serializable
Where **E** is the type of elements maintained by this collection
ConcurrentSkipListSet的一些要点
- 它实现了 Serializable , Cloneable , **Iterable
**, **Collection **, NavigableSet , Set , SortedSet 接口。 - 它不允许空元素,因为空参数和返回值不能与没有元素的情况可靠地区分开。
- 它的实现为包含、添加和删除操作及其变体提供了平均对数(n)的时间成本。
- 它是线程安全的。
- 当需要对集合进行并发修改时,它应该比实现Set接口更受欢迎。
构造函数
1.ConcurrentSkipListSet() : 这个构造函数用来构造一个空集合。
ConcurrentSkipListSet<E> set = new ConcurrentSkipListSet<E>()
**2.ConcurrentSkipListSet(Collection
ConcurrentSkipListSet<E> set = new ConcurrentSkipListSet<E>(Collection<E> c)
**3.ConcurrentSkipListSet(Comparator
ConcurrentSkipListSet<E> set = new ConcurrentSkipListSet<E>(Comparator<E> comparator)
**4.ConcurrentSkipListSet(SortedSet
ConcurrentSkipListSet<E> set = new ConcurrentSkipListSet<E>(SortedSet<E> s)
例1 :
// Java program to demonstrate ConcurrentSkipListSet
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentSkipListSet;
class ConcurrentSkipListSetLastExample1 {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Initializing the set using
// ConcurrentSkipListSet()
ConcurrentSkipListSet<Integer> set
= new ConcurrentSkipListSet<Integer>();
// Adding elements to this set
set.add(78);
set.add(64);
set.add(12);
set.add(45);
set.add(8);
// Printing the ConcurrentSkipListSet
System.out.println("ConcurrentSkipListSet: " + set);
// Initializing the set using
// ConcurrentSkipListSet(Collection)
ConcurrentSkipListSet<Integer> set1
= new ConcurrentSkipListSet<Integer>(set);
// Printing the ConcurrentSkipListSet1
System.out.println("ConcurrentSkipListSet1: "
+ set1);
// Initializing the set using
// ConcurrentSkipListSet()
ConcurrentSkipListSet<String> set2
= new ConcurrentSkipListSet<>();
// Adding elements to this set
set2.add("Apple");
set2.add("Lemon");
set2.add("Banana");
set2.add("Apple");
// creating an iterator
Iterator<String> itr = set2.iterator();
System.out.print("Fruits Set: ");
while (itr.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(itr.next() + " ");
}
}
}
输出
ConcurrentSkipListSet: [8, 12, 45, 64, 78]
ConcurrentSkipListSet1: [8, 12, 45, 64, 78]
Fruits Set: Apple Banana Lemon
例2 :
// Java program to demonstrate ConcurrentSkipListSet
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentSkipListSet;
class ConcurrentSkipListSetLastExample1 {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Initializing the set using ConcurrentSkipListSet()
ConcurrentSkipListSet<Integer>
set = new ConcurrentSkipListSet<Integer>();
// Adding elements to this set
// using add() method
set.add(78);
set.add(64);
set.add(12);
set.add(45);
set.add(8);
// Printing the ConcurrentSkipListSet
System.out.println("ConcurrentSkipListSet: "
+ set);
// Printing the highest element of the set
// using last() method
System.out.println("The highest element of the set: "
+ set.last());
// Retrieving and removing first element of the set
System.out.println("The first element of the set: "
+ set.pollFirst());
// Checks if 9 is present in the set
// using contains() method
if (set.contains(9))
System.out.println("9 is present in the set.");
else
System.out.println("9 is not present in the set.");
// Printing the size of the set
// using size() method
System.out.println("Number of elements in the set = "
+ set.size());
}
}
输出
ConcurrentSkipListSet: [8, 12, 45, 64, 78]
The highest element of the set: 78
The first element of the set: 8
9 is not present in the set.
Number of elements in the set = 4
ConcurrentSkipListSet的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| add(E e) | 如果指定的元素还没有出现,则将其添加到这个集合中。 |
| ceiling(E e) | 返回这个集合中大于或等于给定元素的最小元素,如果没有这样的元素,则返回空。 |
| clear() | 移除这个集合中的所有元素。 |
| clone() | 返回这个ConcurrentSkipListSet实例的一个浅层拷贝。 |
| 比较器() | 返回用于对这个集合中的元素进行排序的比较器,如果这个集合使用其元素的自然排序,则返回空。 |
| contains(Object o) | 如果这个集合包含指定的元素,则返回true。 |
| descendingIterator() | 返回这个集合中的元素按降序排列的迭代器。 |
| descendingSet() | 返回这个集合中所包含的元素的反向顺序视图。 |
| equals(Object o) | 将指定的对象与这个集合进行比较,看是否相等。 |
| first() | 返回当前在这个集合中的第一个(最低)元素。 |
| floor(E e) | 返回这个集合中小于或等于给定元素的最大元素,如果没有这样的元素,则返回空。 |
| headSet(E toElement) | 返回这个集合中元素严格小于toElement的部分的视图。 |
| headSet(E toElement, boolean inclusive) | 返回这个集合中元素小于(或等于,如果包容性为真)toElement的部分的视图。 |
| higher(E e) | 返回这个集合中严格大于给定元素的最小元素,如果没有这样的元素,则返回空。 |
| isEmpty() | 返回这个集合中的元素的迭代器,以升序排列。 |
| last() | 返回当前在这个集合中的最后一个(最高)元素。 |
| lower(E e) | 返回这个集合中严格小于给定元素的最大元素,如果没有这样的元素,则返回空。 |
| pollFirst() | 检索并删除第一个(最低)元素,如果这个集合是空的,则返回null。 |
| pollLast() | 检索并删除最后一个(最高)元素,如果这个集合是空的,则返回null。 |
| remove(Object o) | 从这个集合中删除指定的元素,如果它存在的话。 |
| removeAll(Collection c) | 从这个集合中移除包含在指定集合中的所有元素。 size() | 返回这个集合中元素的数量。 spliterator() | 返回这个集合中的元素的Spliterator。 subSet(E fromElement, boolean fromInclusive, E toElement, boolean toInclusive) | 返回这个集合中元素范围从fromElement到toElement的部分的视图。 subSet(E fromElement, E toElement) | 返回这个集合中元素范围从fromElement(包括)到toElement(不包括)的部分的视图。 tailSet(E fromElement) | 返回这个集合中元素大于或等于fromElement的部分的视图。 tailSet(E fromElement, boolean inclusive) | 返回这个集合中元素大于(或等于,如果包容性为真)fromElement的部分的视图。 ### 从java.util.AbstractSet类继承的方法 方法 | 描述 ### 从java.util.AbstractCollection类继承的方法 方法 | 描述 |
如果这个集合包含了指定集合中的所有元素,返回true。 |
| retainAll(Collection c) | 只保留本集合中包含在指定集合中的元素(可选操作)。 toArray() | 返回一个包含此集合中所有元素的数组。 toArray(T[] a) | 返回一个包含此集合中所有元素的数组;返回的数组的运行时类型是指定数组的类型。 toString() | 返回这个集合的字符串表示。 ### 从java.util.Set接口继承的方法 方法 | 描述 |
如果这个集合包含了指定集合中的所有元素,则返回true。 |
| 哈希代码() | 返回这个集合的哈希代码值。 |
| retainAll(Collection<?> c) | 只保留这个集合中包含在指定集合中的元素(可选操作)。 |
| toArray() | 返回一个包含这个集合中所有元素的数组。 |
| toArray(T[] a) | 返回一个包含此集合中所有元素的数组;返回的数组的运行时类型是指定数组的类型。 |
从java.util.Collection接口继承的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| parallelStream() | 返回一个以该集合为源的可能的并行流。 |
| removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) | 删除这个集合中满足给定谓词的所有元素。 |
| stream() | 返回一个以该集合为源的顺序流。 |
从java.lang.Iterable接口继承的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| forEach(Consumer<? super T> action) | 对Iterable中的每个元素执行给定的动作,直到所有元素都被处理完或者该动作抛出一个异常。 |
 极客教程
极客教程