Java 数组asList()方法及示例
java.util.Arrays 类的 asList() 方法是用来返回一个由指定数组支持的固定大小的列表。这个方法作为 基于数组和基于集合的API之间的桥梁 ,与Collection.toArray()结合使用。返回的列表是可序列化的,并且实现了RandomAccess。
提示: 该方法在O(1)时间内运行。
语法
public static List asList(T... a)
参数: 该方法接收需要转换为List的 数组a 。 这里……被称为 varargs ,它是一个参数数组,工作原理类似于对象数组参数。
特别注意: 如果是原始数据类型(int, float,等),数组的类型必须是一个封装类(Integer,Float,等),即你不能传递int a[],但你可以传递Integer a[]。如果你传递int a[],这个函数将返回一个List <int a[]>,而不是List <Integer>,因为在这种情况下 “autoboxing “不会发生,int a[]本身被识别为一个对象,并且返回一个int数组的List,而不是整数的List,这将在各种Collection函数中引起错误。
返回值: 该方法返回一个指定数组的 列表视图 。
例1 :
// Java program to Demonstrate asList() method
// of Arrays class for a string value
// Importing utility classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception
{
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
// Creating Arrays of String type
String a[]
= new String[] { "A", "B", "C", "D" };
// Getting the list view of Array
List<String> list = Arrays.asList(a);
// Printing all the elements in list object
System.out.println("The list is: " + list);
}
// Catch block to handle exceptions
catch (NullPointerException e) {
// Print statement
System.out.println("Exception thrown : " + e);
}
}
}
输出
The list is: [A, B, C, D]
例2 :
// Java program to Demonstrate asList() method
// of Arrays class For an integer value
// Importing utility classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception
{
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
// Creating Arrays of Integer type
Integer a[] = new Integer[] { 10, 20, 30, 40 };
// Getting the list view of Array
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(a);
// Printing all the elements inside list object
System.out.println("The list is: " + list);
}
// Catch block to handle exceptions
catch (NullPointerException e) {
// Print statements
System.out.println("Exception thrown : " + e);
}
}
}
输出
The list is: [10, 20, 30, 40]
例3 :
// Java Program to demonstrate asList() method
// Which returns fixed size list and
// throws UnsupportedOperationException
// if any element is added using add() method
// Importing required classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception
{
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
// Creating Arrays of Integer type
Integer a[] = new Integer[] { 10, 20, 30, 40 };
// Getting the list view of Array
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(a);
// Adding another int to the list
// As Arrays.asList() returns fixed size
// list, we'll get
// java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException
list.add(50);
// Printing all the elements of list
System.out.println("The list is: " + list);
}
// Catch block to handle exceptions
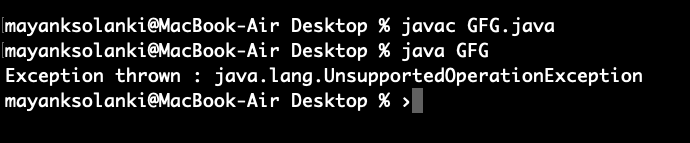
catch (UnsupportedOperationException e) {
// Display message when exception occurs
System.out.println("Exception thrown : " + e);
}
}
}
输出
 极客教程
极客教程