Java中的ArrayList和LinkedList
数组是存储在连续内存位置的项的集合。其思想是将相同类型的多个项存储在一起。但是,数组的限制是数组的大小是预定义的和固定的。有多种方法可以解决这个问题。在本文中,讨论了解决这个问题的两个类ArrayList和LinkedList的区别。
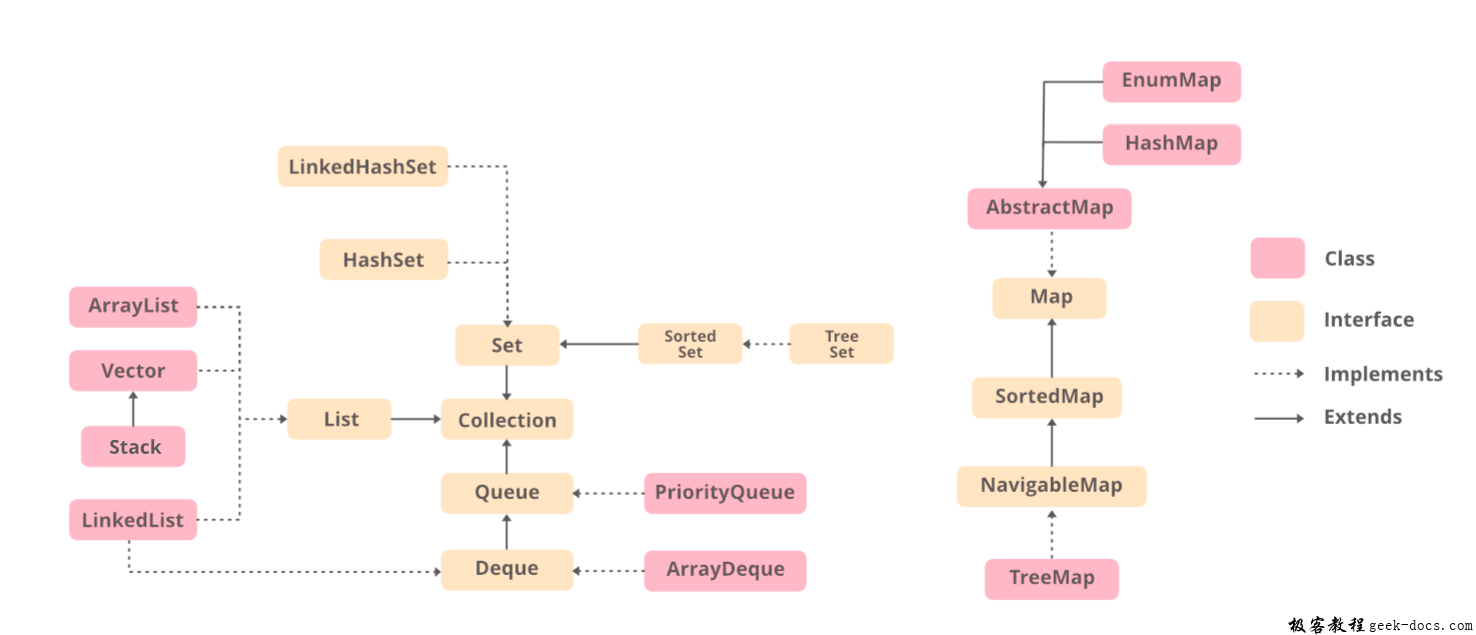
ArrayList是集合框架的一部分。它存在于java.util包中,并为我们提供java中的动态数组。虽然,它可能比标准数组慢,但在需要对数组进行大量操作的程序中很有帮助。我们可以动态地添加和删除条目。它会自动调整大小。下面是一个演示ArrayList实现的示例。
示例:
// Java program to Illustrate Working of an ArrayList
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an ArrayList of Integer type
ArrayList<Integer> arrli
= new ArrayList<Integer>();
// Appending the new elements
// at the end of the list
// using add () method via for loops
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++)
arrli.add(i);
// Printing the ArrayList
System.out.println(arrli);
// Removing an element at index 3
// from the ArrayList
// using remove() method
arrli.remove(3);
// Printing the ArrayList after
// removing the element
System.out.println(arrli);
}
}
输出:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
[1, 2, 3, 5]
LinkedList是一种线性数据结构,其中元素不是存储在连续的位置,每个元素都是一个单独的对象,具有数据部分和地址部分。元素使用指针和地址链接。每个元素被称为一个节点。由于插入和删除的动态性和易用性,它们比数组更受欢迎。下面是演示LinkedList实现的示例。
注意:这个类实现了LinkedList数据结构。
示例:
// Java program to Demonstrate Working of a LinkedList
// Importing required classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating an object of the
// class linked list
LinkedList<String> object
= new LinkedList<String>();
// Adding the elements to the object created
// using add() and addLast() method
// Custom input elements
object.add("A");
object.add("B");
object.addLast("C");
// Print the current LinkedList
System.out.println(object);
// Removing elements from the List object
// using remove() and removeFirst() method
object.remove("B");
object.removeFirst();
System.out.println("Linked list after "
+ "deletion: " + object);
}
}
输出:
[A, B, C]
Linked list after deletion: [C]
现在,在充分理解了它们之后,让我们来讨论一下Java中ArrayList和LinkedList的区别
| ArrayList | LinkedList |
|---|---|
| 这个类使用动态数组来存储其中的元素。随着泛型的引入,这个类支持存储所有类型的对象。 | 这个类使用一个双向链表来存储其中的元素。与ArrayList类似,这个类也支持存储所有类型的对象。 |
| 由于内部实现的原因,操作ArrayList需要更多的时间。无论何时删除一个元素,都会在内部遍历数组并移位内存位。 | 与ArrayList相比,操作LinkedList花费的时间更少,因为在双向链表中,没有移动内存位的概念。遍历列表并更改引用链接。 |
| 这个类实现了一个List接口。因此,它充当一个列表。 | 这个类实现了List接口和Deque接口。因此,它可以作为list和deque。 |
| 当应用程序要求存储和访问数据时,这个类工作得更好。 | 当应用程序需要操作存储的数据时,这个类可以更好地工作。 |
 极客教程
极客教程