C语言 break语句
C语言中的break是一个循环控制语句,当遇到一个循环时就会终止。它可以在循环或开关语句中使用,以使控制权离开块。break语句每次只能从一个循环中断开。
语法:
break;
以下三种类型的循环将与break语句一起使用。
- 简单的循环
- 嵌套循环
- 无限循环
使用简单循环的中断声明
C++中的break语句可以用于简单的循环,即for循环、while循环和do-while循环。
例1:带有for循环的break语句
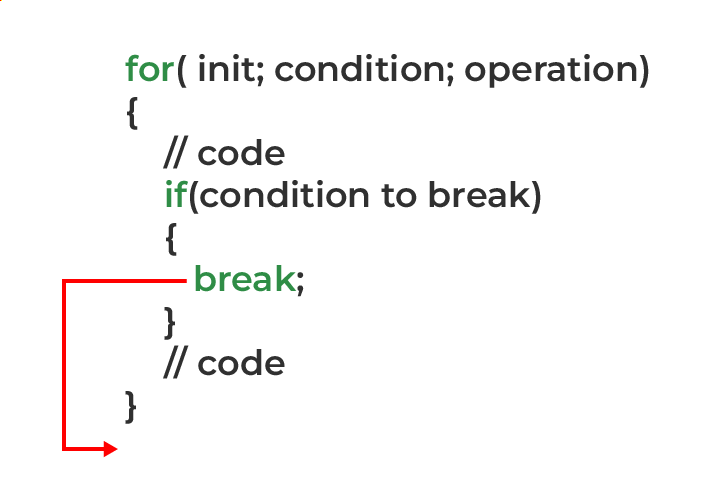
在for循环中的break语句的工作
// C Program to demonstrate break statement with for loop
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
for (int i = 1; i < 5; i++) {
if (i == 3) {
break;
}
else {
printf("%d ", i);
}
}
return 0;
}
输出
1 2
例2:带有while循环的break语句

在while循环中的中断工作
// C Program to demonstrate break statement with while loop
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i = 1;
while (i <= 5) {
if (i == 3) {
break;
}
else {
printf("%d ", i);
}
i++;
}
return 0;
}
输出
1 2
例3:带有Do-while循环的break语句
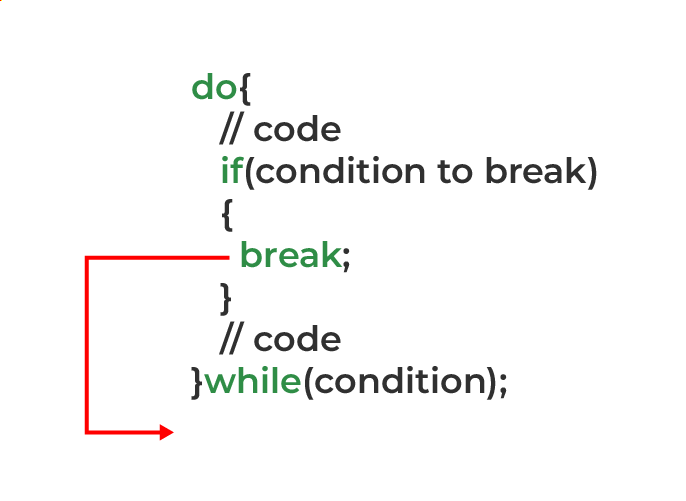
在do-while循环中的中断工作
// C Program to demonstrate break statement with do-while
// loop
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i = 1;
do {
if (i == 3) {
break;
}
else {
printf("%d ", i);
}
i++;
} while (i <= 5);
return 0;
}
输出
1 2
嵌套循环的break语句
在处理嵌套循环时,也可以使用break语句。控制将只从使用中断语句的那个循环中出来。
示例:
// C program to illustrate
// using break statement
// in Nested loops
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
// nested for loops with break statement
// at inner loop
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; ++j) {
if (i <= 4) {
printf("%d ", j);
}
else {
// if i > 4 then this innermost loop will
// break
break;
}
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
输出
1
1 2
1 2 3
1 2 3 4
注意:Break语句一次只能跳出一个循环。因此,如果在嵌套循环中,我们在内循环中使用了break语句,那么控制权将进入外循环,而不是一次脱离所有的循环。如果我们想跳出所有的循环,我们必须使用多个break语句。
无限循环的中断语句
无限循环可以用break语句作为条件的一部分来终止。
// C Program to demonstrate infinite loop without using
// break statement
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i = 0;
// while loop which will always be true
while (1) {
printf("%d ", i);
i++;
}
return 0;
}
输出:
Execution timed out
注意 : 请不要在你的编译器中运行上述程序,因为它是一个无限循环,所以你可能不得不强行退出编译器来终止程序。
在上述程序中,循环条件总是为真,这将导致循环无限期地执行。这可以通过使用break语句来纠正,如下图所示。
示例:
// C Program to demonstrate infinite loop using
// break statement
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i = 0;
// while loop which will always be true
while (1) {
if (i > 8) {
// if i will be greater than 8 then program
// control will be outside the while loop
break;
}
printf("%d ", i);
i++;
}
return 0;
}
输出
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
在上述代码中,借助于break语句,循环的迭代被限制为8次。
带有Switch case的break语句
一般来说,Switch case 语句会评估一个表达式,并根据表达式的值,执行与该值相关的语句。不仅如此,在匹配的case之后的所有case也将被执行。为了防止这种情况,我们可以在switch case中使用break语句,如图所示。
语法:
switch(expression)
{
case value1: statement_1; break;
case value2: statement_2; break;
.....
......
......
case value_n: statement_n; break;
default: default statement;
}
示例:
// C Program to demonstrate working of break with switch
// case
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
char c;
float x, y;
while (1) {
printf("Enter an operator (+, -), if want to exit "
"press x: ");
scanf(" %c", &c);
// to exit
if (c == 'x')
exit(0);
printf("Enter Two Values:\n ");
scanf("%f %f", &x, &y);
switch (c) {
// For Addition
case '+':
printf("%.1f + %.1f = %.1f\n", x, y, x + y);
break;
// For Subtraction
case '-':
printf("%.1f - %.1f = %.1f\n", x, y, x - y);
break;
default:
printf(
"Error! please write a valid operator\n");
}
}
}
输出:
Enter an operator (+, -), if want to exit press x: +
Enter Two Values:
10
20
10.0 + 20.0 = 30.0
 极客教程
极客教程