Python – tensorflow.math.tan()
TensorFlow是谷歌设计的开源python库,用于开发机器学习模型和深度学习神经网络。
tan()是用来寻找x的元素正切。
语法: tf.math.tan(x, name)
参数:
- x:它是输入的张量。这个张量允许的dtype是bfloat16, half, float32, float64。
- name(可选):它定义了操作的名称。
返回:它返回一个与x具有相同dtype的张量。
示例 1:
# Importing the library
import tensorflow as tf
# Initializing the input tensor
a = tf.constant([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], dtype = tf.float64)
# Printing the input tensor
print('Input: ', a)
# Calculating tangent
res = tf.math.tan(x = a)
# Printing the result
print('Result: ', res)
输出:
Input: tf.Tensor([1. 2. 3. 4. 5.], shape=(5, ), dtype=float64)
Result: tf.Tensor([ 1.55740772 -2.18503986 -0.14254654 1.15782128 -3.38051501], shape=(5, ), dtype=float64)
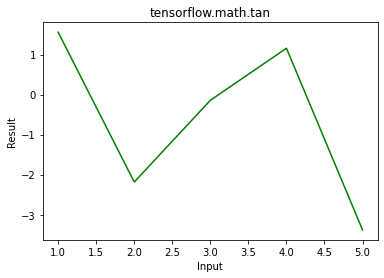
例子2:视觉化
# importing the library
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Initializing the input tensor
a = tf.constant([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], dtype = tf.float64)
# Calculating tangent
res = tf.math.tan(x = a)
# Plotting the graph
plt.plot(a, res, color ='green')
plt.title('tensorflow.math.tan')
plt.xlabel('Input')
plt.ylabel('Result')
plt.show()
输出:
 极客教程
极客教程