Scala Reduce、Fold和Scan
在本教程中,我们将学习Scala中的Reduce、Fold和Scan函数。
- Reduce : Reduce函数适用于scala中的集合数据结构,其中包含列表、集合、地图、序列和图元。Reduce函数的参数是一个二进制操作,它合并了集合中的所有元素并返回一个单一的值。前两个值被二进制操作合并,该操作的结果与集合的下一个值合并,最后得到一个单一的值。
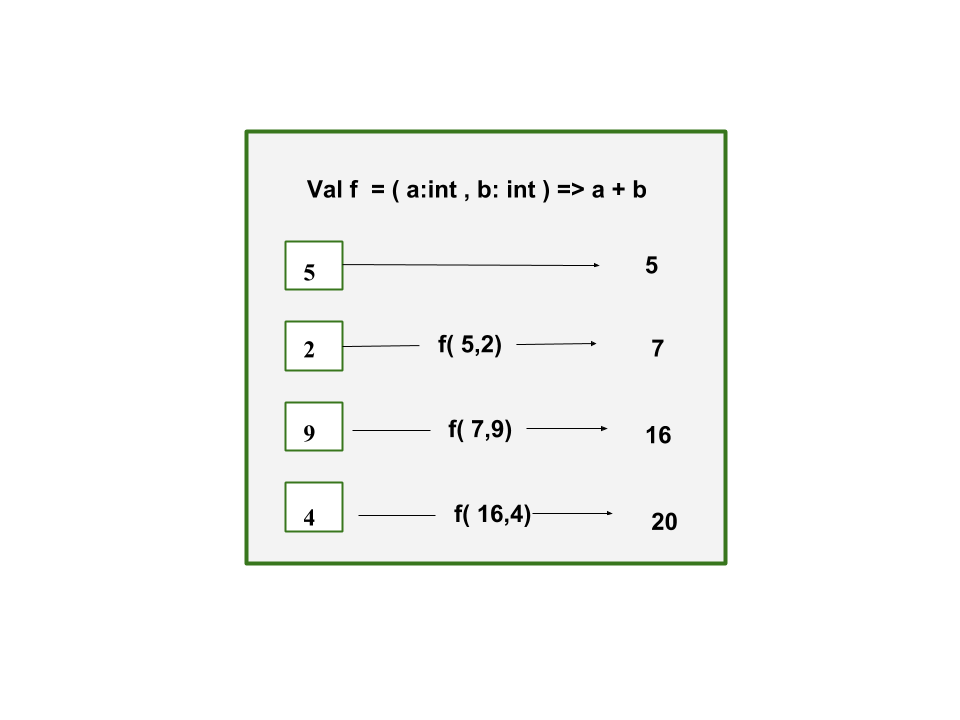
这段代码使用reduce函数实现了一个序列中元素的总和。
示例 :
// Scala program sum of elements
// using reduce function
// Creating object
object geeks
{
// Main method
def main(arg:Array[String])
{
// initialize a sequence of elements
val seq_elements: Seq[Double] = Seq(3.5, 5.0, 1.5)
println(s"Elements = seq_elements")
// find the sum of the elements
// using reduce function
val sum: Double = seq_elements.reduce((a, b) => a + b)
println(s"Sum of elements =sum")
}
}
输出:
Elements = List(3.5, 5.0, 1.5)
Sum of elements = 10.0
这段代码使用还原函数找到序列中的最大和最小元素.
示例 :
// Scala program to find maximum and minimum
// using reduce function
// Creating object
object geeks
{
// Main method
def main(arg:Array[String])
{
// initialize a sequence of elements
val seq_elements : Seq[Double] = Seq(3.5, 5.0, 1.5)
println(s"Elements = seq_elements")
// find the maximum element using reduce function
val maximum : Double = seq_elements.reduce(_ max _)
println(s"Maximum element =maximum")
// find the minimum element using reduce function
val minimum : Double = seq_elements.reduce(_ min _)
println(s"Minimum element = $minimum")
}
}
输出:
Elements = List(3.5, 5.0, 1.5)
Maximum element = 5.0
Minimum element = 1.5
- Fold : 和reduce一样,fold也是采取二进制操作,合并集合中的所有元素并返回一个单一的值。不同的是,fold允许我们定义一个初始值。由于这个属性,fold也可以管理空集合。如果集合是空的,初始化的值就成为最终的答案。由于这个原因,我们也可以使用其他数据类型的初始值从集合中返回一个不同的值。Reduce只能返回相同类型的值,因为其初始值是集合中的第一个值。

这段代码使用fold函数实现了一个序列中的元素之和。这里的初始值是0.0,因为序列的数据类型是Double。
示例 :
// Scala program sum of elements
// using fold function
// Creating object
object geeks
{
// Main method
def main(arg:Array[String])
{
// initialize a sequence of elements
val seq_elements: Seq[Double] = Seq(3.5, 5.0, 1.5)
println(s"Elements = seq_elements")
// find the sum of the elements using fold function
val sum: Double = seq_elements.fold(0.0)((a, b) => a + b)
println(s"Sum of elements =sum")
}
}
输出:
Elements = List(3.5, 5.0, 1.5)
Sum of elements = 10.0
这段代码用连字符连接字符串。我们使用初始值为空字符串。所以我们的折叠方法也会在空字符串上应用运算符,而在减少方法中,我们不会在集合的第一个值之前得到连字符。
示例 :
// Scala program concatenate string
// using fold function
// Creating object
object geeks
{
// Main method
def main(arg:Array[String])
{
// initialize a sequence of strings
val str_elements: Seq[String] = Seq("hello",
"Geeks", "For", "Geeks")
println(s"Elements = str_elements")
// Concatenate strings with fold function
val concat: String = str_elements.fold("")(
(a, b) => a + "-" + b)
println(s"After concatenation =concat")
}
}
输出:
Elements = List(hello, Geeks, For, Geeks)
After concatenation = -hello-Geeks-For-Geeks
- Scan : Scan函数以二进制操作为参数,并返回该操作在集合中每个元素的值。它返回该二进制操作在集合中的每个迭代。在扫描中我们也可以定义初始值。
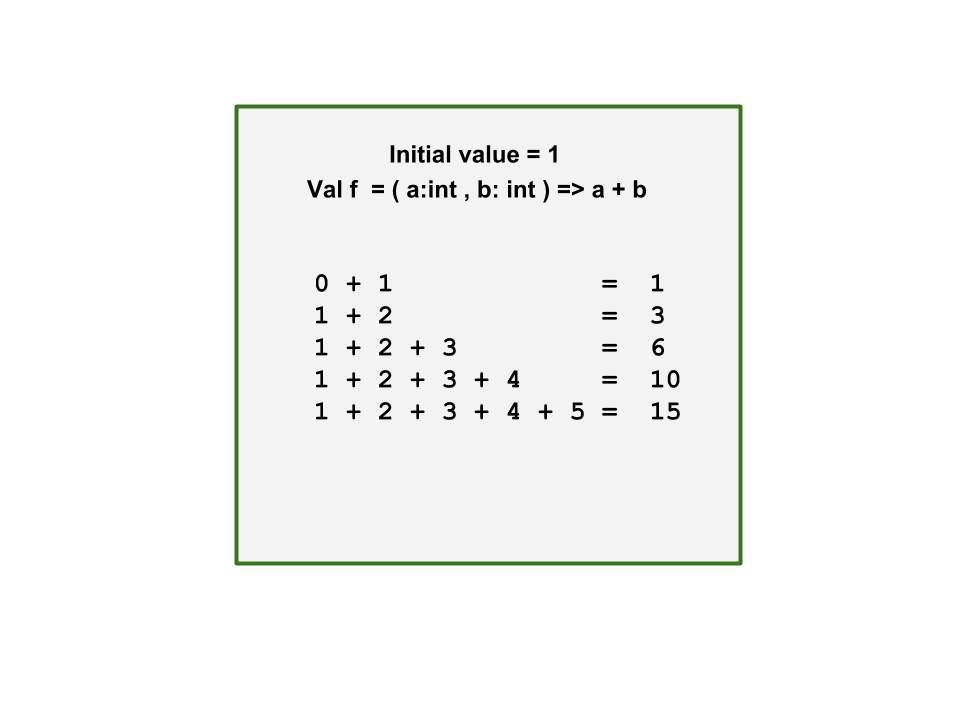
这段代码使用scan函数实现了所有元素之和的迭代。
示例 :
// Scala program sum of elements
// using scan function
// Creating object
object geeks
{
// Main method
def main(arg:Array[String])
{
//initialize a sequence of numbers
val numbers: Seq[Int] = Seq(4, 2, 1, 6, 9)
println(s"Elements of numbers = numbers")
//find the sum of the elements using scan function
val iterations: Seq[Int] = numbers.scan(0)(_ + _)
println("Running total of all elements" +
s"in the collection =iterations")
}
}
输出:
Elements of numbers = List(4, 2, 1, 6, 9)
Running total of all elements in the collection = List(0, 4, 6, 7, 13, 22)
这是带连字符的字符串连接的实现,显示了迭代的情况。
示例 :
// Scala program concatenate string
// using scan function
// Creating object
object geeks
{
// Main method
def main(arg:Array[String])
{
// initialize a sequence of strings
val str_elements : Seq[String] = Seq("hello",
"Geeks", "For", "Geeks")
println(s"Elements = str_elements")
// Concatenate strings with scan function
val concat : Seq[String]
= str_elements.scan("")((a, b) => a + "-" + b)
println(s"After concatenation =concat")
}
}
输出:
Elements = List(hello, Geeks, For, Geeks)
After concatenation = List(, -hello, -hello-Geeks, -hello-Geeks-For, -hello-Geeks-For-Geeks)
 极客教程
极客教程