在 Python 中查找二叉树中第二个最深的结点的程序
假设有一个二叉树,我们需要找到第二深的叶节点。如果有多个最深的叶节点,则第二深的叶结点将是下一个最高的叶节点。我们知道根节点的深度为0。
因此,如果输入如下所示:
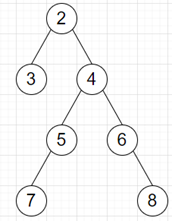
则输出将为1,因为第二深的结点是3。
为了解决这个问题,我们将遵循以下步骤:
- 如果根为空,则
- 返回null
- nodes:=新列表
- 将根插入 nodes 的末尾
- 计数:= 0,上一个结点:= 0,现在结点:= 0
- while 列表 nodes 不为空, do
- new:=新列表
- flag:= True
- for each node in nodes, do
- 如果 flag 为 true 并且(节点左侧为 null)并且(节点右侧为 null),则
- prev:= now
- now:= count
- flag:= False
- 如果节点的左侧不为 null,则
- 将节点的左侧插入 new 的末尾
- 如果节点右侧不为 null,则
- 将节点的右侧插入 new 的末尾
- nodes:= new
- count:= count + 1
- 返回 prev
为了更好地理解,请看以下实现:
例子
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, data, left = None, right = None):
self.data = data
self.left = left
self.right = right
class Solution:
def solve(self, root):
if root is None:
return None
nodes = []
nodes.append(root)
count = 0
prev = 0
now = 0
while nodes:
new = []
flag = True
for node in nodes:
if flag and (not node.left) and (not node.right):
prev = now
now = count
flag = False
if node.left:
new.append(node.left)
if node.right:
new.append(node.right)
nodes = new
count += 1
return prev
ob = Solution()
root = TreeNode(2)
root.left = TreeNode(3)
root.right = TreeNode(4)
root.right.left = TreeNode(5)
root.right.right = TreeNode(6)
root.right.left.left = TreeNode(7)
root.right.right.right = TreeNode(8)
print(ob.solve(root))
输入
root = TreeNode(2)
root.left = TreeNode(3)
root.right = TreeNode(4)
root.right.left = TreeNode(5)
root.right.right = TreeNode(6)
root.right.left.left = TreeNode(7)
root.right.right.right = TreeNode(8)
输出
1
 极客教程
极客教程