Java 抽象类和接口的区别
我们知道,抽象是指隐藏功能的内部实现,只向用户展示功能,即它是什么(展示),如何工作(隐藏)。抽象类和接口都是用于抽象的,因此,接口和抽象类是必要的先决条件。
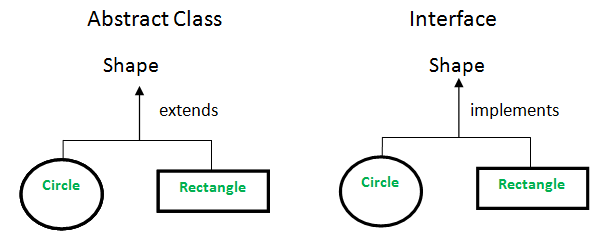
抽象类与接口
- 方法的类型: 接口只能有抽象的方法。一个抽象类可以有抽象和非抽象的方法。从Java 8开始,它也可以有默认和静态方法。从Java 9开始,它也可以有私有的具体方法。
- 最终变量: 在Java接口中声明的变量默认为最终变量。一个抽象类可以包含非最终变量。
- 变量的类型: 抽象类可以有最终变量、非最终变量、静态变量和非静态变量。接口只有静态和最终变量。
- 实现: 抽象类可以提供接口的实现。接口不能提供抽象类的实现。
- 继承与抽象: 一个Java接口可以用关键词 “实现 “来实现,一个抽象类可以用关键词 “扩展 “来扩展。
- 多重实现: 一个接口可以扩展一个或多个Java接口;一个抽象类可以扩展另一个Java类并实现多个Java接口。
- 多重继承: 接口支持多重继承;抽象类不支持多重继承。
- 数据成员的可访问性: 一个Java接口的成员默认是公开的。一个Java抽象类可以有私有、保护等类成员。
例1-A:抽象类
abstract class sunstar {
abstract void printInfo();
}
class employee extends sunstar {
void printInfo() {
String name = "avinash";
int age = 21;
float salary = 222.2F;
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(age);
System.out.println(salary);
}
}
class base {
public static void main(String args[]) {
sunstar s = new employee();
s.printInfo();
}
}
输出
avinash
21
222.2
示例2:抽象类
// Java Program to Illustrate Concept of
// Abstract Class
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
// Class 1
// Helper abstract class
abstract class Shape {
// Declare fields
String objectName = " ";
// Constructor of this class
Shape(String name) { this.objectName = name; }
// Method
// Non-abstract methods
// Having as default implementation
public void moveTo(int x, int y)
{
System.out.println(this.objectName + " "
+ "has been moved to"
+ " x = " + x + " and y = " + y);
}
// Method 2
// Abstract methods which will be
// implemented by its subclass(es)
abstract public double area();
abstract public void draw();
}
// Class 2
// Helper class extending Class 1
class Rectangle extends Shape {
// Attributes of rectangle
int length, width;
// Constructor
Rectangle(int length, int width, String name)
{
// Super keyword refers to current instance itself
super(name);
// this keyword refers to current instance itself
this.length = length;
this.width = width;
}
// Method 1
// To draw rectangle
@Override public void draw()
{
System.out.println("Rectangle has been drawn ");
}
// Method 2
// To compute rectangle area
@Override public double area()
{
// Length * Breadth
return (double)(length * width);
}
}
// Class 3
// Helper class extending Class 1
class Circle extends Shape {
// Attributes of a Circle
double pi = 3.14;
int radius;
// Constructor
Circle(int radius, String name)
{
// Super keyword refers to parent class
super(name);
// This keyword refers to current instance itself
this.radius = radius;
}
// Method 1
// To draw circle
@Override public void draw()
{
// Print statement
System.out.println("Circle has been drawn ");
}
// Method 2
// To compute circle area
@Override public double area()
{
return (double)((pi * radius * radius));
}
}
// Class 4
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating the Object of Rectangle class
// and using shape class reference.
Shape rect = new Rectangle(2, 3, "Rectangle");
System.out.println("Area of rectangle: "
+ rect.area());
rect.moveTo(1, 2);
System.out.println(" ");
// Creating the Objects of circle class
Shape circle = new Circle(2, "Circle");
System.out.println("Area of circle: "
+ circle.area());
circle.moveTo(2, 4);
}
}
输出
Area of rectangle: 6.0
Rectangle has been moved to x = 1 and y = 2
Area of circle: 12.56
Circle has been moved to x = 2 and y = 4
如果我们在矩形和圆形之间没有任何共同的代码,那么就使用接口。
接口:
例子 1- :
// Java Program to Illustrate Concept of Interface
// Importing I/O classes
import java.io.*;
// Interface
interface Shape {
// Abstract method
void draw();
double area();
}
// Class 1
// Helper class
class Rectangle implements Shape {
int length, width;
// constructor
Rectangle(int length, int width)
{
this.length = length;
this.width = width;
}
@Override public void draw()
{
System.out.println("Rectangle has been drawn ");
}
@Override public double area()
{
return (double)(length * width);
}
}
// Class 2
// Helper class
class Circle implements Shape {
double pi = 3.14;
int radius;
// constructor
Circle(int radius) { this.radius = radius; }
@Override public void draw()
{
System.out.println("Circle has been drawn ");
}
@Override public double area()
{
return (double)((pi * radius * radius));
}
}
// Class 3
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating the Object of Rectangle class
// and using shape interface reference.
Shape rect = new Rectangle(2, 3);
System.out.println("Area of rectangle: "
+ rect.area());
// Creating the Objects of circle class
Shape circle = new Circle(2);
System.out.println("Area of circle: "
+ circle.area());
}
}
输出
Area of rectangle: 6.0
Area of circle: 12.56
例2 :
interface student
{
void printInfo();
}
class avi implements student
{
public void printInfo()
{
String name= "avi";
int age=23;
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(age);
}
}
class interfacesss
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
avi s = new avi();
s.printInfo();
}
}
输出
avi
23
什么时候使用什么 ?
如果这些说法中的任何一个适用于你的情况,就考虑使用抽象类。
- 在java应用程序中,有一些相关的类需要共享一些代码行,那么你可以把这些代码行放在抽象类中,这个抽象类应该被所有这些相关的类所扩展。
- 你可以在抽象类中定义非静态或非最终的字段,这样你就可以通过一个方法访问和修改它们所属对象的状态。
- 你可以预期扩展一个抽象类的类有许多共同的方法或字段,或者需要除public以外的访问修饰符(如protected和private)。
如果这些说法中的任何一条适用于你的情况,请考虑使用接口。
- 它是一种完全的抽象,在一个接口中声明的所有方法都必须由实现这个接口的类来实现。
- 一个类可以实现一个以上的接口。这就是所谓的多重继承。
- 你想指定一个特定数据类型的行为,但并不关心谁实现了它的行为。
 极客教程
极客教程