Java java.math 类和方法
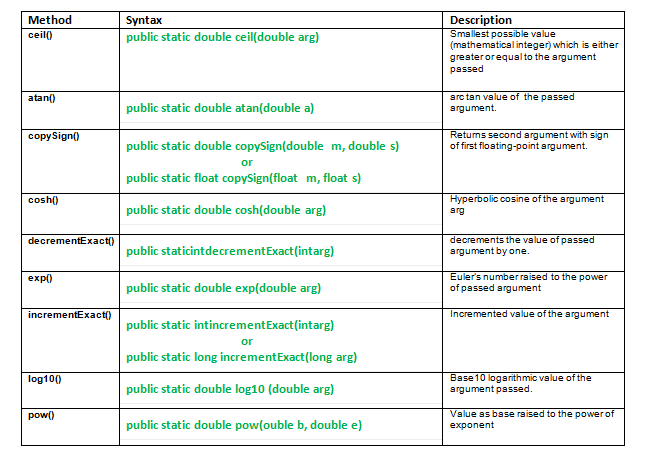
- ceil() : java.math.ceil(double a) 方法返回大于或等于所传参数的最小可能值。返回的值是一个数学上的整数。 特殊情况。
- 如果返回值已经是一个数学整数,则结果相同。
- 如果传递的参数是NaN或无限或零,则结果相同。
- 如果传递的参数小于零但大于-1.0,则结果为负零。
语法
public static double ceil(double arg)
- atan() : java.math.atan() 方法返回方法参数值的弧正切。返回的角度范围是-pi/2到pi/2。
arc tan是所传参数的反tan。
atan(arg) = tan inverse of arg
特殊情况
- 如果传递的参数是NaN或其绝对值>1,则结果为NaN。
- 如果参数为零,则结果为零。
语法
public static double atan(double a)
- copySign() : java.math.copySign() 方法返回第一个浮点参数,但有第二个参数的符号。
语法
public static double copySign(double m, double s)
or
public static float copySign(float m, float s)
解释数学类中atan(), ceil(), copySign()方法的Java代码。
// Java program explaining Math class methods
// atan(), ceil(), copySign()
import java.math.*;
public class NewClass
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Use of atan() method
double Atani = Math.atan(0);
System.out.println("atan value of Atani : "+Atani);
double x = Math.PI/2;
// Use of toRadian() method
x = Math.toRadians(x);
double Atanj = Math.atan(x);
System.out.println("atan value of Atanj : "+Atanj);
System.out.println("");
// Use of ceil() method
double val = 15.34 ,ceilval;
ceilval = Math.ceil(val);
System.out.println("ceil value of val : "+ceilval);
System.out.println("");
double dblMag = val;
double dblSign1 = 3;
double dblSign2 = -3;
// Use of copySign() method
double result1 = Math.copySign(dblMag,dblSign1);
System.out.println("copySign1 : "+result1);
double result2 = Math.copySign(dblMag,dblSign2);
System.out.println("copySign2 : "+result2);
}
}
输出:
atan value of Atani : 0.0
atan value of Atanj : 0.0274087022410345
ceil value of val : 16.0
copySign1 : 15.34
copySign2 : -15.34
- cosh() : java.math.cosh() 方法返回所传参数的双曲余弦。
特殊情况
- 如果参数是NaN,则结果为NaN。
- 如果参数为零,结果为1.0。
- 如果参数是无限的,结果是+ve infinity。
语法
public static double cosh(double arg)
- decrementExact() : java.math.decrementExact() 方法将传递的参数值递减1。
语法
public static int decrementExact(int arg)
or
public static long decrementExact(long arg)
- exp() : java.math.exp(double arg) 方法将欧拉数提高到双倍参数的幂。
重要情况- 如果参数是NaN,则结果为NaN。
- 结果是+ve infinity,如果参数是+ve infinity。
- 如果参数为-ve infinity,则结果为+ve zero。
语法
public static double exp(double arg)
解释数学类中exp(), decrementExact(), cosh()方法的Java代码。
// Java program explaining Math class methods
// exp(), decrementExact(), cosh()
import java.math.*;
public class NewClass
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Use of cosh() method
double value = 2;
double coshValue = Math.cosh(value);
System.out.println("Hyperbolic Cosine of " + coshValue);
System.out.println("");
// Use of decrementExact() method
int result = Math.decrementExact(3051);
System.out.println("Use of decrementExact() : " + result);
System.out.println("");
// Use of exp() method
// declare the exponent to be used
double exponent = 34;
// raise e to exponent declared
double expVal = Math.exp(exponent);
System.out.println("Value of exp : "+ expVal);
}
}
输出:
Using addExact() : 9
acos value of Asini : NaN
acos value of Asinj : 0.054858647341251204
cube root : 6.0
- incrementExact() : java.math.incrementExact() 方法通过增加参数的值返回参数。
public static int incrementExact(int arg)
or
public static long incrementExact(long arg)
- log10() : java.math.log10() 方法返回所传参数的10进制对数值。
public static double log(double arg)
- pow() : java.math.pow(double b, double e) 方法返回值为 **b e **。
public static double pow(double b,double e)
JAVA代码解释Math类中的incrementExact(), log10(), pow()方法。
// Java program explaining MATH class methods
// incrementExact(), log10(), pow()
import java.lang.*;
public class NewClass
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Use of incrementExact() method
int f1 = 30, f2 = -56;
f1 =Math.incrementExact(f1);
System.out.println("Incremented value of f1 : "+f1);
f2 =Math.incrementExact(f2);
System.out.println("Incremented value of f2 : "+f2);
System.out.println("");
// Use of log10() method
double value = 10;
double logValue = Math.log10(value);
System.out.println("Log10 value of 10 : "+logValue);
System.out.println("");
// Use of pow() method
double b = 10, e = 2;
double power = Math.pow(b,e);
System.out.println("Use of pow() : "+power);
}
}
输出:
Incremented value of f1 : 31
Incremented value of f2 : -55
Log10 value of 10 : 1.0
Use of pow() : 100.0
注意: 不需要创建一个新对象来调用这些方法,因为上面讨论的数学类方法是静态的。
 极客教程
极客教程