Java Floats类
Floats 是原始类型float的一个实用类。它提供了Float或Arrays中没有的与Float基元相关的 静态实用方法 。
声明 :
@GwtCompatible(emulated=true)
public final class Floats
extends Object
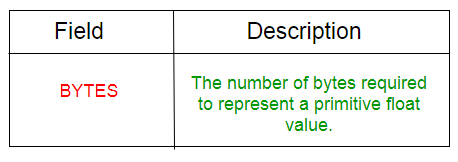
下表显示了Guava Floats类的字段总结。
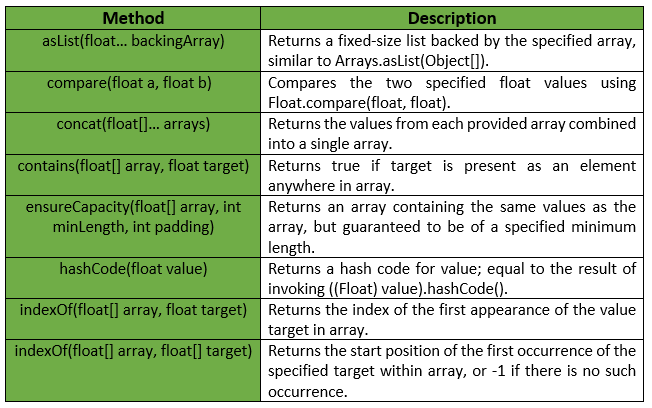
Guava Floats类提供的一些方法有:
异常。
- min : 如果数组为空,会出现IllegalArgumentException。
- max : 如果数组是空的,会出现IllegalArgumentException。
- ensureCapacity : 如果minLength或padding为负数,则出现IllegalArgumentException。
- toArray : 如果集合或其任何元素为空,则出现NullPointerException。
下表显示了Guava Floats Class提供的一些其他方法:

下面给出了一些例子,显示了Guava Floats Class的方法的实现:
例子1 :
// Java code to show implementation
// of Guava Floats.asList() method
import com.google.common.primitives.Floats;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
float arr[] = { 2.6f, 4.6f, 1.2f, 2.4f, 1.5f };
// Using Floats.asList() method which
// converts array of primitives to array of objects
List<Float> myList = Floats.asList(arr);
// Displaying the elements
System.out.println(myList);
}
}
输出:
[2.6, 4.6, 1.2, 2.4, 1.5]
例2 :
// Java code to show implementation
// of Guava Floats.toArray() method
import com.google.common.primitives.Floats;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
List<Float> myList = Arrays.asList(2.6f, 4.6f, 1.2f, 2.4f, 1.5f);
// Using Floats.toArray() method which
// converts a List of Floats to an
// array of float
float[] arr = Floats.toArray(myList);
// Displaying the elements
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
输出:
[2.6, 4.6, 1.2, 2.4, 1.5]
例3 :
// Java code to show implementation
// of Guava Floats.concat() method
import com.google.common.primitives.Floats;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
float[] arr1 = { 2.6f, 4.6f, 1.2f };
float[] arr2 = { 2.4f, 1.5f };
// Using Floats.concat() method which
// combines arrays from specified
// arrays into a single array
float[] arr = Floats.concat(arr1, arr2);
// Displaying the elements
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
输出:
[2.6, 4.6, 1.2, 2.4, 1.5]
例4 :
// Java code to show implementation
// of Guava Floats.contains() method
import com.google.common.primitives.Floats;
class GFG {
// Driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
float[] arr = { 2.6f, 4.6f, 1.2f, 2.4f, 1.5f };
// Using Floats.contains() method which
// checks if element is present in array
// or not
System.out.println(Floats.contains(arr, 2.5f));
System.out.println(Floats.contains(arr, 1.5f));
}
}
产出 :
false
true
例5 :
// Java code to show implementation
// of Guava Floats.min() method
import com.google.common.primitives.Floats;
class GFG {
// Driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
float[] arr = { 2.6f, 4.6f, 1.2f, 2.4f, 1.5f };
// Using Floats.min() method
System.out.println(Floats.min(arr));
}
}
输出:
1.2
例6 :
// Java code to show implementation
// of Guava Floats.max() method
import com.google.common.primitives.Floats;
class GFG {
// Driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
float[] arr = { 2.6f, 4.6f, 1.2f, 2.4f, 1.5f };
// Using Floats.max() method
System.out.println(Floats.max(arr));
}
}
输出:
4.6
 极客教程
极客教程