Java Stack类
Java集合框架提供了一个Stack类,它模拟和实现了一个 Stack数据结构 该类是基于后进先出的基本原则。除了基本的push和pop操作外,该类还提供了empty、search和peek三种功能。该类也可以说是对Vector的扩展,并将该类作为一个具有上述五个功能的堆栈。该类也可以被称为Vector的子类。
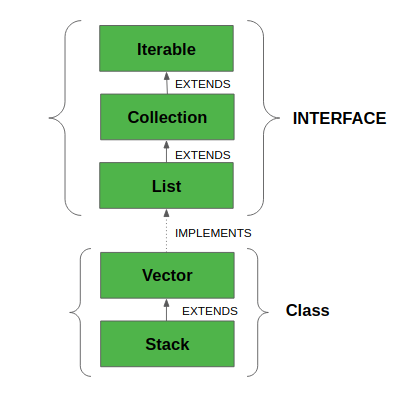
下图显示了 Stack类的层次结构
该类支持一个默认的构造函数 Stack() ,用于创建一个空栈。
声明
public class Stack<E> extends Vector<E>
所有实现的接口 。
- 可序列化(Serializable): 这是一个标记性的接口,如果类要被序列化和反序列化,就必须实现它。
- Cloneable: 这是Java中的一个接口,需要由一个类来实现,以使其对象可以被克隆。
Iterable <E>:这个接口表示一个可迭代的对象集合,意思是可以迭代。Collection <E>:一个集合代表了一组被称为其元素的对象。在需要最大限度的通用性时,Collection接口被用来传递对象的集合。List <E>:List接口提供了一种存储有序集合的方法。它是Collection的一个子接口。- RandomAccess: 这是一个标记接口,由List实现使用,表示它们支持快速(一般是恒定时间)的随机访问。
如何创建一个堆栈
为了创建一个堆栈,我们必须导入 java.util.stack 包并使用该类的Stack()构造函数。下面的例子创建了一个空的堆栈。
Stack<E> stack = new Stack<E>()
这里E是对象的类型。
例子
// Java code for stack implementation
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Test
{
// Pushing element on the top of the stack
static void stack_push(Stack<Integer> stack)
{
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
stack.push(i);
}
}
// Popping element from the top of the stack
static void stack_pop(Stack<Integer> stack)
{
System.out.println("Pop Operation:");
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Integer y = (Integer) stack.pop();
System.out.println(y);
}
}
// Displaying element on the top of the stack
static void stack_peek(Stack<Integer> stack)
{
Integer element = (Integer) stack.peek();
System.out.println("Element on stack top: " + element);
}
// Searching element in the stack
static void stack_search(Stack<Integer> stack, int element)
{
Integer pos = (Integer) stack.search(element);
if(pos == -1)
System.out.println("Element not found");
else
System.out.println("Element is found at position: " + pos);
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
stack_push(stack);
stack_pop(stack);
stack_push(stack);
stack_peek(stack);
stack_search(stack, 2);
stack_search(stack, 6);
}
}
输出
Pop Operation:
4
3
2
1
0
Element on stack top: 4
Element is found at position: 3
Element not found
对堆栈类进行各种操作
1.添加元素: 为了添加一个元素到堆栈,我们可以使用push()方法。这个 push() 操作将元素放在堆栈的顶部。
// Java program to add the
// elements in the stack
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class StackDemo {
// Main Method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Default initialization of Stack
Stack stack1 = new Stack();
// Initialization of Stack
// using Generics
Stack<String> stack2 = new Stack<String>();
// pushing the elements
stack1.push(4);
stack1.push("All");
stack1.push("Geeks");
stack2.push("Geeks");
stack2.push("For");
stack2.push("Geeks");
// Printing the Stack Elements
System.out.println(stack1);
System.out.println(stack2);
}
}
输出
[4, All, Geeks]
[Geeks, For, Geeks]
2.访问元素: 为了检索或获取堆栈的第一个元素或存在于堆栈顶部的元素,我们可以使用 peek() 方法。取回的元素不会被删除或从堆栈中删除。
// Java program to demonstrate the accessing
// of the elements from the stack
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class StackDemo {
// Main Method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating an empty Stack
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>();
// Use push() to add elements into the Stack
stack.push("Welcome");
stack.push("To");
stack.push("Geeks");
stack.push("For");
stack.push("Geeks");
// Displaying the Stack
System.out.println("Initial Stack: " + stack);
// Fetching the element at the head of the Stack
System.out.println("The element at the top of the"
+ " stack is: " + stack.peek());
// Displaying the Stack after the Operation
System.out.println("Final Stack: " + stack);
}
}
输出
Initial Stack: [Welcome, To, Geeks, For, Geeks]
The element at the top of the stack is: Geeks
Final Stack: [Welcome, To, Geeks, For, Geeks]
3.删除元素: 要从堆栈中取出一个元素,我们可以使用 pop() 方法。该元素从堆栈的顶部被弹出,并从相同的地方被删除。
// Java program to demonstrate the removing
// of the elements from the stack
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class StackDemo {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating an empty Stack
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
// Use add() method to add elements
stack.push(10);
stack.push(15);
stack.push(30);
stack.push(20);
stack.push(5);
// Displaying the Stack
System.out.println("Initial Stack: " + stack);
// Removing elements using pop() method
System.out.println("Popped element: "
+ stack.pop());
System.out.println("Popped element: "
+ stack.pop());
// Displaying the Stack after pop operation
System.out.println("Stack after pop operation "
+ stack);
}
}
输出
Initial Stack: [10, 15, 30, 20, 5]
Popped element: 5
Popped element: 20
Stack after pop operation [10, 15, 30]
堆栈类中的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| empty() | 如果堆栈的顶部没有任何东西,则返回true。否则,返回false。 |
| peek() | 返回堆栈顶部的元素,但不删除它。 |
| pop() | 删除并返回堆栈顶部的元素。如果我们在调用pop()时,调用的堆栈是空的,就会抛出一个’EmptyStackException’异常。 |
| push(Object element) | 将一个元素推到堆栈的顶部。 |
| search(Object element) | 它确定一个对象是否存在于堆栈中。如果找到该元素,它返回该元素在堆栈顶部的位置。否则,它返回-1。 |
从java.util.Vector类继承的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| add(Object obj) | 将指定的元素添加到这个Vector的末尾。 |
| add(int index, Object obj) | 在这个Vector中的指定位置插入指定的元素。 |
| addAll(Collection c) | 将指定的Collection中的所有元素添加到这个Vector的末尾,顺序是由指定的Collection的Iterator返回。 |
| addAll(int index, Collection c) | 在指定的位置将指定集合中的所有元素插入到这个向量中。 |
| addElement(Object o) | 将指定的组件添加到这个向量的末端,使其大小增加一个。 |
| capacity() | 返回这个向量的当前容量。 |
| clear() | 移除此向量的所有元素。 |
| clone() | 返回这个向量的一个克隆。 |
| contains(Object o) | 如果这个向量包含指定的元素,返回true。 |
| containsAll(Collection c) | 如果此Vector包含指定Collection中的所有元素,则返回true。 |
| copyInto(Object []array) | 将此向量的元素复制到指定的数组中。 |
| elementAt(int index) | 返回指定索引处的组件。 |
| elements() | 返回这个向量的组件的枚举值。 |
| ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) | 如果需要的话,增加这个向量的容量,以确保它至少能容纳最小容量参数所指定的组件数量。 |
| equals() | 将指定的对象与这个向量进行比较,看是否相等。 |
| firstElement() | 返回这个向量的第一个分量(索引为0的项目)。 |
| get(int index) | 返回此Vector中指定位置的元素。 |
| hashCode() | 返回此Vector的哈希代码值。 |
| indexOf(Object o) | 返回指定元素在这个向量中第一次出现的索引,如果这个向量不包含该元素,则返回-1。 |
| indexOf(Object o, int index) | 返回指定元素在这个向量中第一次出现的索引,从该索引开始向前搜索,如果没有找到该元素,则返回-1。 |
| insertElementAt(Object o, int index) | 在这个向量中的指定索引处插入指定的对象作为一个组件。 |
| isEmpty() | 测试这个向量是否没有组件。 |
| iterator() | 返回这个列表中的元素的迭代器,顺序正确。 |
| LastElement() | 返回向量的最后一个组件。 |
| LastIndexOf(Object o) | 返回指定元素在此向量中最后出现的索引,如果此向量不包含该元素,则返回-1。 |
| LastIndexOf(Object o, int index) | 返回指定元素在这个向量中最后出现的索引,从索引开始向后搜索,如果没有找到该元素,则返回-1。 |
| listIterator() | 返回此列表中元素的列表迭代器(按照适当的顺序)。 |
| listIterator(int index) | 返回一个列表中的元素的迭代器(按适当的顺序),从列表中的指定位置开始。 |
| remove(int index) | 移除这个Vector中指定位置的元素。 |
| remove(Object o) | 移除此Vector中第一次出现的指定元素 如果Vector中不包含该元素,那么它就不会被改变。 |
| removeAll(Collection c) | 从这个向量中移除所有包含在指定Collection中的元素。 |
| removeAllElements() | 从这个向量中移除所有元素,并将其大小设置为零。 |
| removeElement(Object o) | 从这个向量中移除第一个(最低索引)出现的参数。 |
| removeElementAt(int index) | 删除指定索引处的组件。 |
| removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) | 从这个列表中删除所有索引在fromIndex(含)和toIndex(不含)之间的元素。 |
| retainAll(Collection c) | 只保留这个Vector中包含在指定Collection中的元素。 |
| set(int index, Object o) | 用指定的元素替换这个Vector中指定位置的元素。 |
| setElementAt(Object o, int index) | 将此Vector中指定索引处的元素设定为指定的对象。 |
| setSize(int newSize) | 设置此向量的大小。 |
| size() | 返回此向量中的组件数量。 |
| subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) | 返回列表中从Index(含)到toIndex(不含)之间的部分的视图。 |
| toArray() | 返回一个包含向量中所有元素的数组,顺序正确。 |
| toArray(Object []array) | 返回一个数组,包含这个Vector中的所有元素,并以正确的顺序排列;返回的数组的运行时类型是指定的数组的类型。 |
| toString() | 返回此Vector的字符串表示,包含每个元素的字符串表示。 |
| trimToSize() | 将此向量的容量修剪为向量的当前大小。 |
注意: 请注意,Java中的Stack类是一个遗留类,继承自 Java中的Vector。 它是一个线程安全类,因此当我们不需要线程安全时,就会产生开销。建议使用 ArrayDeque 来实现堆栈,因为它在单线程环境下更有效率。
// A Java Program to show implementation
// of Stack using ArrayDeque
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main (String[] args) {
Deque<Character> stack = new ArrayDeque<Character>();
stack.push('A');
stack.push('B');
System.out.println(stack.peek());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
}
}
输出
B
B
 极客教程
极客教程