Java 集合
Set接口存在于java.util包中,并扩展了Collection接口。它是一个无序的对象集合,其中不能存储重复的值。它是一个实现了数学集合的接口。这个接口包含了从Collection接口继承的方法,并增加了一个限制重复元素插入的功能。有两个接口可以扩展集合的实现,即SortedSet和NavigableSet。
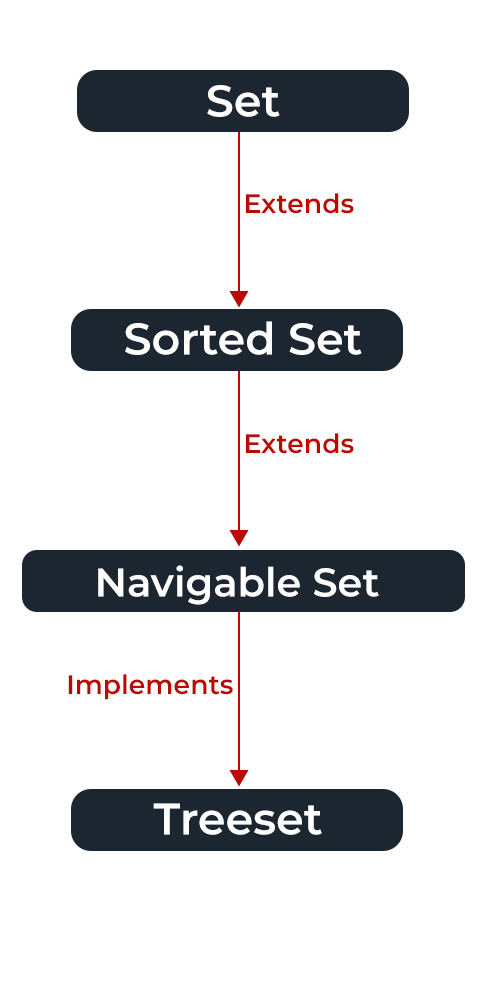
在上图中,可导航集扩展了排序集的接口。由于集合并不保留插入顺序,可导航集合接口提供了在集合中导航的实现。实现可导航集合的类是TreeSet,它是自平衡树的一个实现。因此,这个接口为我们提供了一种在这棵树上导航的方法。
声明: Set接口被声明为。
public interface Set extends Collection
创建Set对象
由于Set是一个接口,所以不能创建类型化的对象。我们总是需要一个扩展这个列表的类来创建一个对象。而且,在Java 1.5引入泛型之后,我们可以限制可以存储在Set中的对象的类型。这个类型安全的集合可以定义为。
// Obj is the type of the object to be stored in Set
Set<Obj> set = new HashSet<Obj> ();
让我们以表格的形式讨论下面提供的Set接口中的方法,如下所示。
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| add(element) | 这个方法用来向集合中添加一个特定的元素。只有当指定的元素还没有出现在集合中时,该函数才会添加该元素,否则,如果该元素已经出现在集合中,该函数会返回False。 |
| addAll(collection) | 这个方法用于将所述集合中的所有元素追加到现有的集合中。这些元素是随机添加的,不遵循任何特定的顺序。 |
| clear() | 这个方法用来从集合中移除所有的元素,但不是删除集合。该集合的引用仍然存在。 |
| contains(element) | 这个方法用来检查一个特定的元素是否存在于集合中。 |
| containsAll(collection) | 这个方法用来检查集合是否包含了给定集合中的所有元素。如果集合包含了所有的元素,该方法返回true;如果有任何元素丢失,则返回false。 |
| hashCode() | 这个方法用来获取这个Set实例的hashCode值。它返回一个整数,这个整数就是这个Set实例的hashCode值。 |
| isEmpty() | 该方法用于检查该集合是否为空。 |
| iterator() | 这个方法用来返回集合的迭代器。集合中的元素将以随机顺序返回。 |
| remove(element) | 这个方法用来从集合中移除给定的元素。如果指定的元素存在于集合中,该方法返回True,否则返回False。 |
| removeAll(collection) | 该方法用于从集合中删除所有存在于集合中的元素。如果这个集合因调用而改变,该方法返回真。 |
| retainAll(collection) | 这个方法用于保留集合中的所有元素,这些元素在给定的集合中被提及。如果这个集合在调用后发生了变化,该方法将返回true。 |
| size() | 这个方法用来获取集合的大小。它返回一个整数值,表示元素的数量。 |
| toArray() | 这个方法用来形成一个与集合相同元素的数组。 |
示例: 说明集合界面的示例程序
// Java program Illustrating Set Interface
// Importing utility classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Demonstrating Set using HashSet
// Declaring object of type String
Set<String> hash_Set = new HashSet<String>();
// Adding elements to the Set
// using add() method
hash_Set.add("Geeks");
hash_Set.add("For");
hash_Set.add("Geeks");
hash_Set.add("Example");
hash_Set.add("Set");
// Printing elements of HashSet object
System.out.println(hash_Set);
}
}
输出
[Set, Example, Geeks, For]
对集合界面的操作
集合界面允许用户对集合进行基本的数学运算。让我们拿两个数组来理解这些基本操作。让set1 = [1, 3, 2, 4, 8, 9, 0] 和set2 = [1, 3, 7, 5, 4, 0, 7, 5]。那么对这两个集合的可能操作是
1.相交: 该操作返回给定两个集合的所有共同元素。对于上述两个集合,交集将是。
Intersection = [0, 1, 3, 4]
2.联合: 这个操作是将一个集合中的所有元素与另一个集合相加。对于上述两个集合,并集将是。
Union = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9]
3. 差值: 该操作将一个集合中的所有数值从另一个集合中删除。对于上述两个集合,差值将是。
Difference = [2, 8, 9]
现在,让我们按照上面的定义实现以下操作,具体如下。
例子
// Java Program Demonstrating Operations on the Set
// such as Union, Intersection and Difference operations
// Importing all utility classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
public class SetExample {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating an object of Set class
// Declaring object of Integer type
Set<Integer> a = new HashSet<Integer>();
// Adding all elements to List
a.addAll(Arrays.asList(
new Integer[] { 1, 3, 2, 4, 8, 9, 0 }));
// Again declaring object of Set class
// with reference to HashSet
Set<Integer> b = new HashSet<Integer>();
b.addAll(Arrays.asList(
new Integer[] { 1, 3, 7, 5, 4, 0, 7, 5 }));
// To find union
Set<Integer> union = new HashSet<Integer>(a);
union.addAll(b);
System.out.print("Union of the two Set");
System.out.println(union);
// To find intersection
Set<Integer> intersection = new HashSet<Integer>(a);
intersection.retainAll(b);
System.out.print("Intersection of the two Set");
System.out.println(intersection);
// To find the symmetric difference
Set<Integer> difference = new HashSet<Integer>(a);
difference.removeAll(b);
System.out.print("Difference of the two Set");
System.out.println(difference);
}
}
输出
Union of the two Set[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9]
Intersection of the two Set[0, 1, 3, 4]
Difference of the two Set[2, 8, 9]
对排序的集合进行各种操作
在Java 1.5中引入泛型后,可以限制可以存储在Set中的对象的类型。由于Set是一个接口,它只能与实现该接口的类一起使用。HashSet是其中一个广泛使用的实现Set接口的类。现在,让我们看看如何在HashSet上执行一些常用的操作。我们将执行以下的操作,如下。
- 添加元素
- 访问元素
- 删除元素
- 迭代元素
- 遍历集合
现在让我们单独讨论这些操作,如下所示。
操作1: 添加元素
为了向集合添加一个元素,我们可以使用add()方法。然而,插入的顺序在集合中没有被保留。在内部,对于每一个元素,都会生成一个哈希值,并根据生成的哈希值来存储。这些值会被比较并按升序排序。我们需要注意的是,重复的元素是不允许的,所有重复的元素都会被忽略。而且,Set也接受空值。
例子
// Java Program Demonstrating Working of Set by
// Adding elements using add() method
// Importing all utility classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an object of Set and
// declaring object of type String
Set<String> hs = new HashSet<String>();
// Adding elements to above object
// using add() method
hs.add("B");
hs.add("B");
hs.add("C");
hs.add("A");
// Printing the elements inside the Set object
System.out.println(hs);
}
}
输出
[A, B, C]
操作2: 访问元素
添加完元素后,如果我们想访问这些元素,我们可以使用内置的方法,如contains()。
例子
// Java code to demonstrate Working of Set by
// Accessing the Elements of the Set object
// Importing all utility classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an object of Set and
// declaring object of type String
Set<String> hs = new HashSet<String>();
// Elements are added using add() method
// Later onwards we will show accessing the same
// Custom input elements
hs.add("A");
hs.add("B");
hs.add("C");
hs.add("A");
// Print the Set object elements
System.out.println("Set is " + hs);
// Declaring a string
String check = "D";
// Check if the above string exists in
// the SortedSet or not
// using contains() method
System.out.println("Contains " + check + " "
+ hs.contains(check));
}
}
输出
Set is [A, B, C]
Contains D false
操作3: 移除数值
可以使用remove()方法从集合中移除这些值。
例子
// Java Program Demonstrating Working of Set by
// Removing Element/s from the Set
// Importing all utility classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Declaring object of Set of type String
Set<String> hs = new HashSet<String>();
// Elements are added
// using add() method
// Custom input elements
hs.add("A");
hs.add("B");
hs.add("C");
hs.add("B");
hs.add("D");
hs.add("E");
// Printing initial Set elements
System.out.println("Initial HashSet " + hs);
// Removing custom element
// using remove() method
hs.remove("B");
// Printing Set elements after removing an element
// and printing updated Set elements
System.out.println("After removing element " + hs);
}
}
输出
Initial HashSet [A, B, C, D, E]
After removing element [A, C, D, E]
操作4: 遍历集合
有各种方法来迭代集合。最著名的方法是使用增强的for循环。
例子
// Java Program to Demonstrate Working of Set by
// Iterating through the Elements
// Importing utility classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating object of Set and declaring String type
Set<String> hs = new HashSet<String>();
// Adding elements to Set
// using add() method
// Custom input elements
hs.add("A");
hs.add("B");
hs.add("C");
hs.add("B");
hs.add("D");
hs.add("E");
// Iterating through the Set
// via for-each loop
for (String value : hs)
// Printing all the values inside the object
System.out.print(value + ", ");
System.out.println();
}
}
输出
A, B, C, D, E,
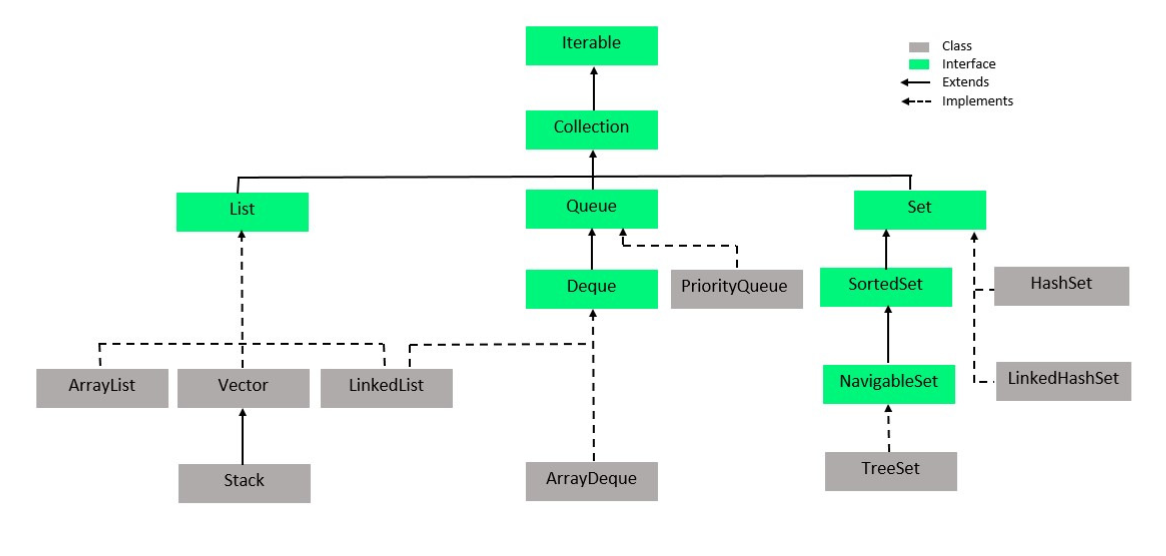
在Java集合中实现Set接口的类,从下面的图片中可以很容易地感知到,并列举如下。
- HashSet
- EnumSet
- LinkedHashSet
- 树形集合
Class 1: HashSet ****
在集合框架中实现的HashSet类是哈希表数据结构的一个固有的实现。我们插入到HashSet中的对象并不保证以相同的顺序插入。这些对象是根据它们的哈希码插入的。这个类也允许插入NULL元素。让我们看看如何使用这个类来创建一个集合对象。
例子
// Java program Demonstrating Creation of Set object
// Using the Hashset class
// Importing utility classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating object of Set of type String
Set<String> h = new HashSet<String>();
// Adding elements into the HashSet
// using add() method
// Custom input elements
h.add("India");
h.add("Australia");
h.add("South Africa");
// Adding the duplicate element
h.add("India");
// Displaying the HashSet
System.out.println(h);
// Removing items from HashSet
// using remove() method
h.remove("Australia");
System.out.println("Set after removing "
+ "Australia:" + h);
// Iterating over hash set items
System.out.println("Iterating over set:");
// Iterating through iterators
Iterator<String> i = h.iterator();
// It holds true till there is a single element
// remaining in the object
while (i.hasNext())
System.out.println(i.next());
}
}
输出
[South Africa, Australia, India]
Set after removing Australia:[South Africa, India]
Iterating over set:
South Africa
India
类2: EnumSet
EnumSet类是在集合框架中实现的,是Set接口的专门实现之一,用于枚举类型。它是一个高性能的集合实现,比HashSet快得多。枚举集合中的所有元素都必须来自一个枚举类型,这个枚举类型在创建集合时被明确或隐含地指定。让我们看看如何使用这个类来创建一个集合对象。
例子
// Java program to demonstrate the
// creation of the set object
// using the EnumSet class
import java.util.*;
enum Gfg { CODE, LEARN, CONTRIBUTE, QUIZ, MCQ }
;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating a set
Set<Gfg> set1;
// Adding the elements
set1 = EnumSet.of(Gfg.QUIZ, Gfg.CONTRIBUTE,
Gfg.LEARN, Gfg.CODE);
System.out.println("Set 1: " + set1);
}
}
输出
Set 1: [CODE, LEARN, CONTRIBUTE, QUIZ]
类3: LinkedHashSet
在集合框架中实现的LinkedHashSet类是HashSet的一个有序版本,它在所有的元素中保持了一个双链接的List。当需要维护迭代顺序时,可以使用这个类。当在HashSet中迭代时,顺序是不可预测的,而LinkedHashSet可以让我们按照元素插入的顺序来迭代它们。让我们看看如何使用这个类来创建一个集合对象。
例子
// Java program to demonstrate the
// creation of Set object using
// the LinkedHashset class
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Set<String> lh = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
// Adding elements into the LinkedHashSet
// using add()
lh.add("India");
lh.add("Australia");
lh.add("South Africa");
// Adding the duplicate
// element
lh.add("India");
// Displaying the LinkedHashSet
System.out.println(lh);
// Removing items from LinkedHashSet
// using remove()
lh.remove("Australia");
System.out.println("Set after removing "
+ "Australia:" + lh);
// Iterating over linked hash set items
System.out.println("Iterating over set:");
Iterator<String> i = lh.iterator();
while (i.hasNext())
System.out.println(i.next());
}
}
输出
[India, Australia, South Africa]
Set after removing Australia:[India, South Africa]
Iterating over set:
India
South Africa
类4:TreeSet
TreeSet类是在集合框架中实现的,它实现了SortedSet接口和SortedSet扩展Set接口。它的行为就像一个简单的集合,例外的是它以排序的形式存储元素。TreeSet使用树形数据结构进行存储。对象是以排序后的升序存储的。但是我们可以使用TreeSet.descendingIterator()方法以降序进行迭代。让我们看看如何使用这个类来创建一个集合对象。
例子
// Java Program Demonstrating Creation of Set object
// Using the TreeSet class
// Importing utility classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating a Set object and declaring it of String
// type
// with reference to TreeSet
Set<String> ts = new TreeSet<String>();
// Adding elements into the TreeSet
// using add()
ts.add("India");
ts.add("Australia");
ts.add("South Africa");
// Adding the duplicate
// element
ts.add("India");
// Displaying the TreeSet
System.out.println(ts);
// Removing items from TreeSet
// using remove()
ts.remove("Australia");
System.out.println("Set after removing "
+ "Australia:" + ts);
// Iterating over Tree set items
System.out.println("Iterating over set:");
Iterator<String> i = ts.iterator();
while (i.hasNext())
System.out.println(i.next());
}
}
输出
[Australia, India, South Africa]
Set after removing Australia:[India, South Africa]
Iterating over set:
India
South Africa
 极客教程
极客教程