Java Map 接口
map接口存在于java.util包中,表示一个键和一个值之间的映射。Map接口不是Collection接口的一个子类型。因此,它的行为与其他的集合类型有些不同。一个Map包含唯一的键。
极客们,脑力激荡者应该是 为什么以及何时使用Maps ?
Map非常适合用于键值关联映射,如字典。Map被用来按键进行查找,或者当有人想按键检索和更新元素时。一些常见的情况如下。
- 一个错误代码及其描述的Map。
- 一个邮编和城市的Map。
- 经理和雇员的Map。每个经理(键)与他所管理的雇员(值)的列表相关。
- 一个班级和学生的Map。每个班级(键)都与一个学生(值)的列表相关联。
创建Map对象
由于Map是一个接口,所以不能创建map类型的对象。我们总是需要一个扩展了这个Map的类来创建一个对象。而且,在Java 1.5引入泛型之后,我们可以限制可以存储在Map中的对象的类型。
语法: 定义类型安全的Map
Map hm = new HashMap();
// Obj is the type of the object to be stored in Map
Map接口的特点
- Map不能包含重复的键,每个键最多可以映射到一个值。有些实现允许空键和空值,如HashMap和LinkedHashMap,但有些不允许,如TreeMap。
- Map的顺序取决于具体的实现。例如,TreeMap和LinkedHashMap有可预测的顺序,而HashMap则没有。
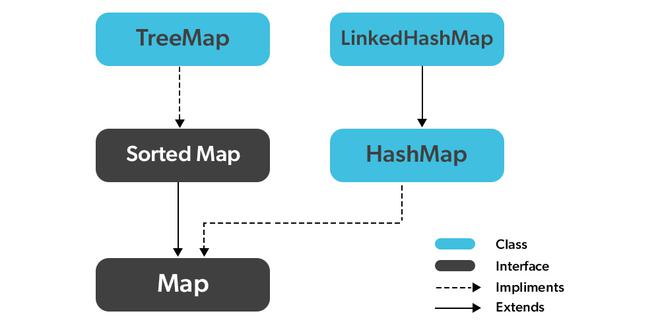
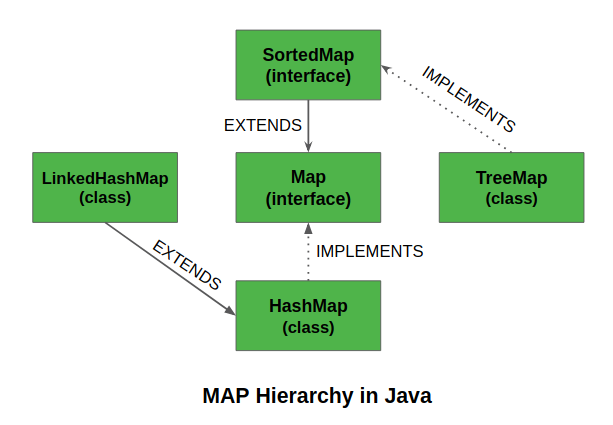
- 在java中,有两个接口用于实现Map。它们是Map和SortedMap,以及三个类。HashMap, TreeMap, 和 LinkedHashMap.
Map接口中的方法
| 方法名称 | 执行的动作 |
|---|---|
| clear() | 该方法用于清除和删除指定Map集合中的所有元素或映射。 |
| containsKey(Object) | 这个方法用来检查一个特定的键是否被映射到Map中。它以键元素为参数,如果该元素在Map中被映射,则返回True。 |
| containsValue(Object) | 该方法用于检查一个特定的值是否被Map中的一个或多个键所映射。它以值为参数,如果该值被Map中的任何一个键所映射,则返回True。 |
| entrySet() | 该方法用于创建一个由Map中包含的相同元素组成的集合。它基本上返回一个Map的集合视图,或者我们可以创建一个新的集合并将Map元素存储到其中。 |
| equals(Object) | 这个方法用于检查两个Map之间是否相等。它验证作为参数传递的一个Map的元素是否与这个Map的元素相等。 |
| get(Object) | 该方法用于检索或获取由参数中提到的特定键映射的值。当Map不包含该键的映射时,它返回NULL。 |
| hashCode() | 该方法用于为包含键和值的给定Map生成一个hashCode。 |
| isEmpty() | 这个方法用来检查一个Map是否有任何键和值对的条目。如果没有映射存在,那么该方法返回true。 |
| keySet() | 该方法用于返回该Map中包含的键的Set视图。这个集合是由Map支持的,所以Map的变化会反映在这个集合中,反之亦然。 |
| put(Object, Object) | 这个方法用来把指定的值和这个Map中指定的键联系起来。 |
| putAll(Map) | 该方法用于将指定Map中的所有映射复制到该Map中。 |
| remove(Object) | 如果Map中存在某个键的映射,该方法用于从该Map中删除该键的映射。 |
| size() | 该方法用于返回Map中可用的键/值对的数量。 |
| values() | 这个方法用来从Map的值中创建一个集合。它基本上返回HashMap中数值的一个集合视图。 |
| getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) | 返回指定键所映射的值,如果该Map不包含键的映射,则返回defaultValue。 |
| merge(K key, V value, BiFunction<? super V,? super V,? extends V> remappingFunction) | 如果指定的键还没有与一个值关联,或者与空值关联,那么将其与给定的非空值关联。 |
| putIfAbsent(K key, V value) | 如果指定的键还没有与一个值关联(或被映射为null),则将其与给定的值关联并返回null,否则返回当前关联的值。 |
例子
// Java Program to Demonstrate
// Working of Map interface
// Importing required classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating an empty HashMap
Map<String, Integer> hm
= new HashMap<String, Integer>();
// Inserting pairs in above Map
// using put() method
hm.put("a", new Integer(100));
hm.put("b", new Integer(200));
hm.put("c", new Integer(300));
hm.put("d", new Integer(400));
// Traversing through Map using for-each loop
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> me :
hm.entrySet()) {
// Printing keys
System.out.print(me.getKey() + ":");
System.out.println(me.getValue());
}
}
}
输出
a:100
b:200
c:300
d:400
实现Map接口的类在下面的媒体中被描绘出来,后面的描述如下。
类1:HashMap
从Java 1.2开始,HashMap是Java集合的一部分。它提供了Java的Map接口的基本实现。它以(Key, Value)对的形式存储数据。要访问一个值,必须知道它的键。这个类使用了一种叫做Hashing的技术。Hashing是一种将大的字符串转换为代表相同字符串的小字符串的技术。一个较短的值有助于索引和快速搜索。让我们看看如何使用这个类来创建一个map对象。
例子
// Java Program to illustrate the Hashmap Class
// Importing required classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an empty HashMap
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
// Inserting entries in the Map
// using put() method
map.put("vishal", 10);
map.put("sachin", 30);
map.put("vaibhav", 20);
// Iterating over Map
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> e : map.entrySet())
// Printing key-value pairs
System.out.println(e.getKey() + " "
+ e.getValue());
}
}
输出
vaibhav 20
vishal 10
sachin 30
第2类:LinkedHashMap
LinkedHashMap就像HashMap一样,有一个额外的功能,即维护插入其中的元素的顺序。HashMap提供了快速插入、搜索和删除的优势,但是它从来没有保持插入的轨迹和顺序,而LinkedHashMap提供了元素可以按照插入的顺序被访问。让我们看看如何使用这个类来创建一个Map对象。
例子
// Java Program to Illustrate the LinkedHashmap Class
// Importing required classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an empty LinkedHashMap
Map<String, Integer> map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
// Inserting pair entries in above Map
// using put() method
map.put("vishal", 10);
map.put("sachin", 30);
map.put("vaibhav", 20);
// Iterating over Map
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> e : map.entrySet())
// Printing key-value pairs
System.out.println(e.getKey() + " "
+ e.getValue());
}
}
输出
vishal 10
sachin 30
vaibhav 20
类3:TreeMap
Java中的TreeMap与抽象类一起用于实现Map接口和NavigableMap。Map根据其键的自然顺序进行排序,或者根据Map创建时提供的比较器进行排序,这取决于使用哪个构造函数。这被证明是对键值对进行排序和存储的一种有效方式。由treemap维护的存储顺序必须与等价物一致,就像其他排序的Map一样,与显式比较器无关。让我们看看如何使用这个类来创建一个Map对象。
例子
// Java Program to Illustrate TreeMap Class
// Importing required classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an empty TreeMap
Map<String, Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
// Inserting custom elements in the Map
// using put() method
map.put("vishal", 10);
map.put("sachin", 30);
map.put("vaibhav", 20);
// Iterating over Map using for each loop
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> e : map.entrySet())
// Printing key-value pairs
System.out.println(e.getKey() + " "
+ e.getValue());
}
}
输出
sachin 30
vaibhav 20
vishal 10
使用Map接口和HashMap类执行各种操作
由于Map是一个接口,它只能与实现这个接口的类一起使用。现在,让我们看看如何使用广泛使用的HashMap类对Map进行一些常用的操作。还有,在Java 1.5中引入泛型后,可以限制可以存储在Map中的对象的类型。
操作1: 添加元素
为了向Map添加一个元素,我们可以使用put()方法。然而,插入的顺序并没有保留在hashmap中。在内部,对于每一个元素,都会产生一个单独的哈希值,元素的索引是基于这个哈希值的,以使其更有效率。
例子
// Java program to demonstrate
// the working of Map interface
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Default Initialization of a
// Map
Map<Integer, String> hm1 = new HashMap<>();
// Initialization of a Map
// using Generics
Map<Integer, String> hm2
= new HashMap<Integer, String>();
// Inserting the Elements
hm1.put(1, "Geeks");
hm1.put(2, "For");
hm1.put(3, "Geeks");
hm2.put(new Integer(1), "Geeks");
hm2.put(new Integer(2), "For");
hm2.put(new Integer(3), "Geeks");
System.out.println(hm1);
System.out.println(hm2);
}
}
输出
{1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}
{1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}
操作2: 改变元素
在添加完元素后,如果我们想改变元素,可以通过put()方法再次添加元素来完成。由于Map中的元素是用键来索引的,所以键的值可以通过简单地插入我们想改变的键的更新值来改变。
例子
// Java program to demonstrate
// the working of Map interface
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Initialization of a Map
// using Generics
Map<Integer, String> hm1
= new HashMap<Integer, String>();
// Inserting the Elements
hm1.put(new Integer(1), "Geeks");
hm1.put(new Integer(2), "Geeks");
hm1.put(new Integer(3), "Geeks");
System.out.println("Initial Map " + hm1);
hm1.put(new Integer(2), "For");
System.out.println("Updated Map " + hm1);
}
}
输出
Initial Map {1=Geeks, 2=Geeks, 3=Geeks}
Updated Map {1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}
操作3: 删除元素
为了从Map中删除一个元素,我们可以使用remove()方法。这个方法接收键值,如果一个键存在于Map中,就从这个Map中删除它的映射。
例子
// Java program to demonstrate
// the working of Map interface
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Initialization of a Map
// using Generics
Map<Integer, String> hm1
= new HashMap<Integer, String>();
// Inserting the Elements
hm1.put(new Integer(1), "Geeks");
hm1.put(new Integer(2), "For");
hm1.put(new Integer(3), "Geeks");
hm1.put(new Integer(4), "For");
// Initial Map
System.out.println(hm1);
hm1.remove(new Integer(4));
// Final Map
System.out.println(hm1);
}
}
输出
{1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks, 4=For}
{1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}
操作4: 在Map中迭代
有多种方法来迭代Map。最著名的方法是使用for-each循环并获得键。通过使用getValue()方法可以找到键的值。
例子
// Java program to demonstrate
// the working of Map interface
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Initialization of a Map
// using Generics
Map<Integer, String> hm1
= new HashMap<Integer, String>();
// Inserting the Elements
hm1.put(new Integer(1), "Geeks");
hm1.put(new Integer(2), "For");
hm1.put(new Integer(3), "Geeks");
for (Map.Entry mapElement : hm1.entrySet()) {
int key
= (int)mapElement.getKey();
// Finding the value
String value
= (String)mapElement.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " : "
+ value);
}
}
}
输出
1 : Geeks
2 : For
3 : Geeks
 极客教程
极客教程