Java LinkedList
链接列表是集合框架的一部分,存在于java.util包中。该类是LinkedList数据结构的实现,LinkedList是一种线性数据结构,其中的元素不是存储在连续的位置,每个元素都是一个独立的对象,有数据部分和地址部分。这些元素使用指针和地址进行链接。每个元素被称为一个节点。
由于其动态性和易于插入和删除,它们比数组更受欢迎。它也有一些缺点,比如节点不能被直接访问,而我们需要从头部开始,通过链接到达我们想要访问的节点。
链接表是如何在内部工作的
由于LinkedList是一个动态数组,我们在创建它时不需要指定大小,当我们动态添加和删除项目时,列表的大小会自动增加。而且,这些元素也不是以连续的方式存储的。因此,没有必要增加大小。在内部,LinkedList是使用双链表数据结构实现的。
普通的链接列表和双链接列表的主要区别在于,双链接列表包含一个额外的指针,通常称为上一个指针,以及下一个指针和单链接列表中的数据。
链接列表中的构造器
为了创建一个LinkedList,我们需要创建一个LinkedList类的对象。LinkedList类由各种构造函数组成,允许创建列表。以下是该类中可用的构造函数:
- LinkedList(): 这个构造函数用于创建一个空的链接列表。如果我们希望创建一个名字为ll的空LinkedList,那么,可以这样创建。
LinkedList ll = new LinkedList()
- LinkedList(Collection C): 该构造函数用于创建一个有序的列表,包含指定集合的所有元素,由集合的迭代器返回。如果我们希望创建一个名字为ll的LinkedList,那么,可以这样创建。
LinkedList ll = new LinkedList(C)
Java LinkedList的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| add(int index, E element) | 此方法在这个列表的指定位置插入指定的元素。 |
| add(E e) | 此方法将指定的元素添加到这个列表的最后。 |
| addAll(int index, Collection |
此方法将指定集合中的所有元素插入此列表,从指定位置开始。 |
| addAll(Collection |
此方法将指定集合中的所有元素按照指定集合的迭代器返回的顺序追加到此列表的末尾。 |
| addFirst(E e) | 此方法将指定的元素插入此列表的开头。 |
| addLast(E e) | 此方法将指定的元素添加到这个列表的末尾。 |
| clear() | 此方法将所有的元素从这个列表中移除。 |
| clone() | 该方法返回该LinkedList的浅层拷贝。 |
| contains(Object o) | 如果该列表包含指定的元素,该方法返回true。 |
| descendingIterator() | 该方法返回该deque中元素的反向顺序的迭代器。 |
| element() | 此方法检索但不删除此列表的头部(第一个元素)。 |
| get(int index) | 该方法返回列表中指定位置的元素。 |
| getFirst() | 此方法返回列表中的第一个元素。 |
| getLast() | 此方法返回此列表中的最后一个元素。 |
| indexOf(Object o) | 此方法返回指定元素在此列表中第一次出现的索引,如果此列表不包含该元素,则返回-1。 |
| lastIndexOf(Object o) | 该方法返回指定元素在此列表中最后出现的索引,如果此列表不包含该元素,则返回-1。 |
| listIterator(int index) | 此方法返回此列表中的元素的列表迭代器(按适当的顺序),从列表中的指定位置开始。 |
| offer(E e) | 此方法将指定的元素添加到这个列表的尾部(最后一个元素)。 |
| offerFirst(E e) | 此方法在这个列表的前面插入指定的元素。 |
| offerLast(E e) | 此方法将指定的元素插入此列表的末尾。 |
| peek() | 这个方法检索但不删除这个列表的头部(第一个元素)。 |
| peekFirst() | 此方法获取但不删除此列表的第一个元素,如果此列表为空,则返回null。 |
| peekLast() | 此方法检索但不删除此列表的最后一个元素,如果此列表为空,则返回null。 |
| poll() | 这个方法检索并删除这个列表的头部(第一个元素)。 |
| pollFirst() | 此方法检索并删除此列表中的第一个元素,如果此列表为空,则返回null。 |
| pollLast() | 此方法检索并删除此列表的最后一个元素,如果此列表是空的,则返回null。 |
| pop() | 这个方法从这个列表的堆栈中弹出一个元素。 |
| push(E e) | 这个方法将一个元素推到这个列表所代表的堆栈中。 |
| remove() | 此方法检索并删除此列表的头部(第一个元素)。 |
| remove(int index) | 这个方法删除这个列表中指定位置的元素。 |
| remove(Object o) | 如果指定的元素存在,该方法将从这个列表中移除其第一次出现的元素。 |
| removeFirst() | 此方法删除并返回此列表中的第一个元素。 |
| removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) | 这个方法删除列表中第一次出现的指定元素(当从头到尾遍历列表时)。 |
| removeLast() | 此方法删除并返回此列表中的最后一个元素。 |
| removeLastOccurrence(Object o) | 这个方法删除这个列表中最后出现的指定元素(当从头到尾遍历这个列表时)。 |
| set(int index, E element) | 这个方法用指定的元素替换这个列表中指定位置的元素。 |
| size() | 这个方法返回这个列表中的元素数量。 |
| spliterator() | 这个方法在这个列表中的元素上创建一个晚期绑定的、故障快速的Spliterator。 |
| toArray() | 这个方法返回一个数组,包含这个列表中的所有元素,并以适当的顺序(从第一个元素到最后一个元素)。 |
| toArray(T[] a) | 本方法返回一个数组,包含这个列表中的所有元素,并以适当的顺序(从第一个元素到最后一个元素);返回的数组的运行时间类型是指定的数组的类型。 |
| toString() | 该方法返回一个字符串,包含这个列表中的所有元素,以适当的顺序(从第一个元素到最后一个元素),每个元素用逗号分隔,字符串用方括号括起来。 |
下面是上述操作的实现。
// Java Program to Demonstrate
// Implementation of LinkedList
// class
// Importing required classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating object of the
// class linked list
LinkedList<String> ll = new LinkedList<String>();
// Adding elements to the linked list
ll.add("A");
ll.add("B");
ll.addLast("C");
ll.addFirst("D");
ll.add(2, "E");
System.out.println(ll);
ll.remove("B");
ll.remove(3);
ll.removeFirst();
ll.removeLast();
System.out.println(ll);
}
}
输出
[D, A, E, B, C]
[A]
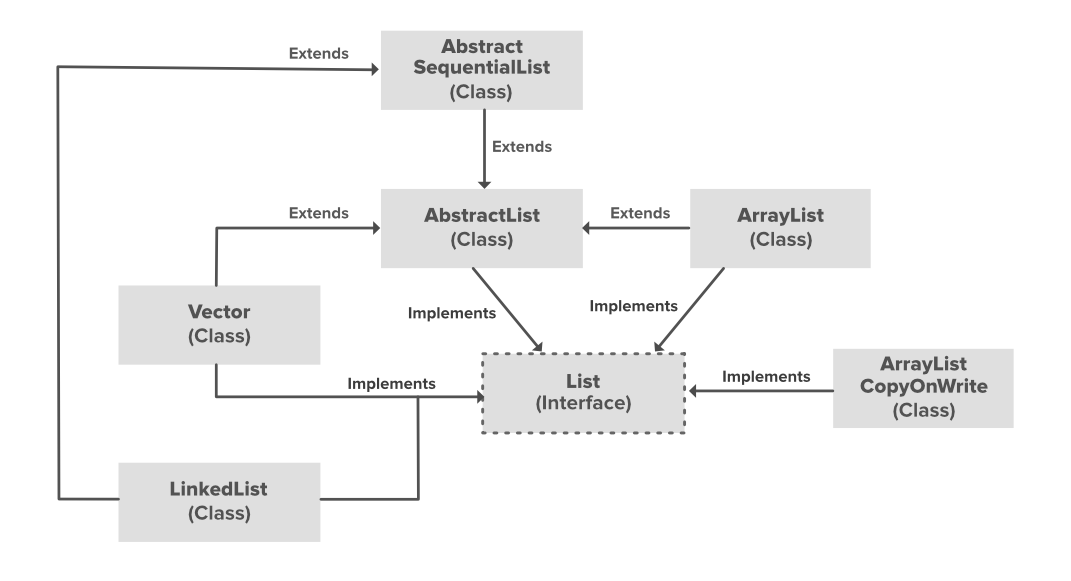
在上面的示例中,AbstractList、CopyOnWriteArrayList和AbstractSequentialList是实现列表接口的类。每一个提到的类都实现了一个单独的功能。它们是
- AbstractList: 这个类用来实现一个不可修改的列表,为此只需要扩展这个AbstractList类,并只实现get()和size()方法。
- CopyOnWriteArrayList: 该类实现了列表接口。它是ArrayList的一个增强版本,其中所有的修改(添加、设置、删除等)都是通过对列表进行新的复制来实现的。
对LinkedList进行各种操作
- 添加元素
- 更新元素
- 删除元素
- 遍历元素
- 对数组()。
- Size();
- 删除 First();
- 删除last()。
操作1:添加元素
为了向ArrayList添加一个元素,我们可以使用add()方法。这个方法被重载,可以根据不同的参数进行多种操作。它们是
- add(Object): 该方法用于在LinkedList的末端添加一个元素。
- add(int index, Object): 该方法用于在LinkedList的特定索引处添加一个元素。
下面是上述操作的实现。
// Java program to add elements
// to a LinkedList
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
LinkedList<String> ll = new LinkedList<>();
ll.add("Geeks");
ll.add("Geeks");
ll.add(1, "For");
System.out.println(ll);
}
}
输出
[Geeks, For, Geeks]
操作2:改变元素
在添加完元素后,如果我们想改变元素,可以使用set()方法来完成。由于LinkedList是有索引的,我们想要改变的元素是通过元素的索引来引用的。因此,该方法需要一个索引和需要在该索引处插入的更新元素。
下面是上述操作的实现。
// Java program to change elements
// in a LinkedList
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
LinkedList<String> ll = new LinkedList<>();
ll.add("Geeks");
ll.add("Geeks");
ll.add(1, "Geeks");
System.out.println("Initial LinkedList " + ll);
ll.set(1, "For");
System.out.println("Updated LinkedList " + ll);
}
}
输出
Initial LinkedList [Geeks, Geeks, Geeks]
Updated LinkedList [Geeks, For, Geeks]
操作3:删除元素
为了从LinkedList中删除一个元素,我们可以使用remove()方法。该方法被重载,可以根据不同的参数执行多种操作。它们是
- remove(Object): 该方法用于简单地从LinkedList中删除一个对象。如果有多个这样的对象,那么第一个出现的对象被删除。
- remove(int index): 由于LinkedList是有索引的,该方法需要一个整数值,它可以简单的删除LinkedList中存在于该特定索引的元素。在删除元素后,元素的索引会被更新,因此在删除元素后,LinkedList的对象也会被更新,产生一个新的List。
下面是上述操作的实现。
// Java program to remove elements
// in a LinkedList
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
LinkedList<String> ll = new LinkedList<>();
ll.add("Geeks");
ll.add("Geeks");
ll.add(1, "For");
System.out.println("Initial LinkedList " + ll);
// Function call
ll.remove(1);
System.out.println("After the Index Removal " + ll);
ll.remove("Geeks");
System.out.println("After the Object Removal "
+ ll);
}
}
输出
Initial LinkedList [Geeks, For, Geeks]
After the Index Removal [Geeks, Geeks]
After the Object Removal [Geeks]
操作4:迭代LinkedList
有多种方法可以对LinkedList进行迭代。最著名的方法是通过使用基本的for循环,结合get()方法来获取特定索引的元素,以及使用高级的for-loop。
下面是上述操作的实现。
// Java program to iterate the elements
// in an LinkedList
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
LinkedList<String> ll
= new LinkedList<>();
ll.add("Geeks");
ll.add("Geeks");
ll.add(1, "For");
// Using the Get method and the
// for loop
for (int i = 0; i < ll.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(ll.get(i) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
// Using the for each loop
for (String str : ll)
System.out.print(str + " ");
}
}
输出
Geeks For Geeks
Geeks For Geeks
操作4:通过使用toArray()将列表链接到数组
import java.util.*;
public class GFG2 {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList<Integer> list= new LinkedList<Integer>();
list.add(123);
list.add(12);
list.add(11);
list.add(1134);
System.out.println("LinkedList: "+ list);
Object[] a = list.toArray();
System.out.print("After converted LinkedList to Array: ");
for(Object element : a)
System.out.print(element+" ");
}
}
输出
LinkedList: [123, 12, 11, 1134]
After converted LinkedList to Array: 123 12 11 1134
操作5-size()
import java.io.*;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class GFG2 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
LinkedList<String> list = new LinkedList<String>();
list.add("Geeks for Geeks ");
list.add("is best ");
// Displaying the size of the list
System.out.println("The size of the linked list is: " + list.size());
}
}
输出
The size of the linked list is: 2
操作7 – removeFirst()
import java.io.*;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class GFG2 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<Integer>();
list.add(10);
list.add(20);
list.add(30);
System.out.println("LinkedList:" + list);
System.out.println("The remove first element is: " + list.removeFirst());
// Displaying the final list
System.out.println("Final LinkedList:" + list);
}
}
输出
LinkedList:[10, 20, 30]
The remove first element is: 10
Final LinkedList:[20, 30]
操作8- removelast()
import java.io.*;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class GFG2 {
public static void main(String args[])
{
LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<Integer>();
list.add(10);
list.add(20);
list.add(30);
System.out.println("LinkedList:" + list);
// Remove the tail using removeLast()
System.out.println("The last element is removed: " + list.removeLast());
// Displaying the final list
System.out.println("Final LinkedList:" + list);
// Remove the tail using removeLast()
System.out.println("The last element is removed: " + list.removeLast());
// Displaying the final list
System.out.println("Final LinkedList:" + list);
}
}
输出
LinkedList:[10, 20, 30]
The last element is removed: 30
Final LinkedList:[10, 20]
The last element is removed: 20
Final LinkedList:[10]
 极客教程
极客教程