Java HashMap及实例
HashMap <K, V> **是Java 1.2版本中的一个集合。这个类在 **java.util 包中找到。它提供了Java的Map接口的基本实现。它以(Key, Value)对的形式存储数据,你可以通过另一种类型的索引(例如,整数)来访问它们。一个对象被用作另一个对象(值)的键(索引)。如果你试图插入重复的键,它将替换相应键的元素。
HashMap 类似于HashTable,但它是不同步的。它也允许存储空键,但应该只有一个空键对象,可以有任意数量的空值。 这个类对Map的顺序没有任何保证。要使用这个类和它的方法,你需要导入 java.util.HashMap 包或其超类。
// Java program to illustrate HashMap class of java.util
// package
// Importing HashMap class
import java.util.HashMap;
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create an empty hash map by declaring object
// of string and integer type
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
// Adding elements to the Map
// using standard put() method
map.put("vishal", 10);
map.put("sachin", 30);
map.put("vaibhav", 20);
// Print size and content of the Map
System.out.println("Size of map is:- "
+ map.size());
// Printing elements in object of Map
System.out.println(map);
// Checking if a key is present and if
// present, print value by passing
// random element
if (map.containsKey("vishal")) {
// Mapping
Integer a = map.get("vishal");
// Printing value for the corresponding key
System.out.println("value for key"
+ " \"vishal\" is:- " + a);
}
}
}
输出
Size of map is:- 3
{vaibhav=20, vishal=10, sachin=30}
value for key "vishal" is:- 10
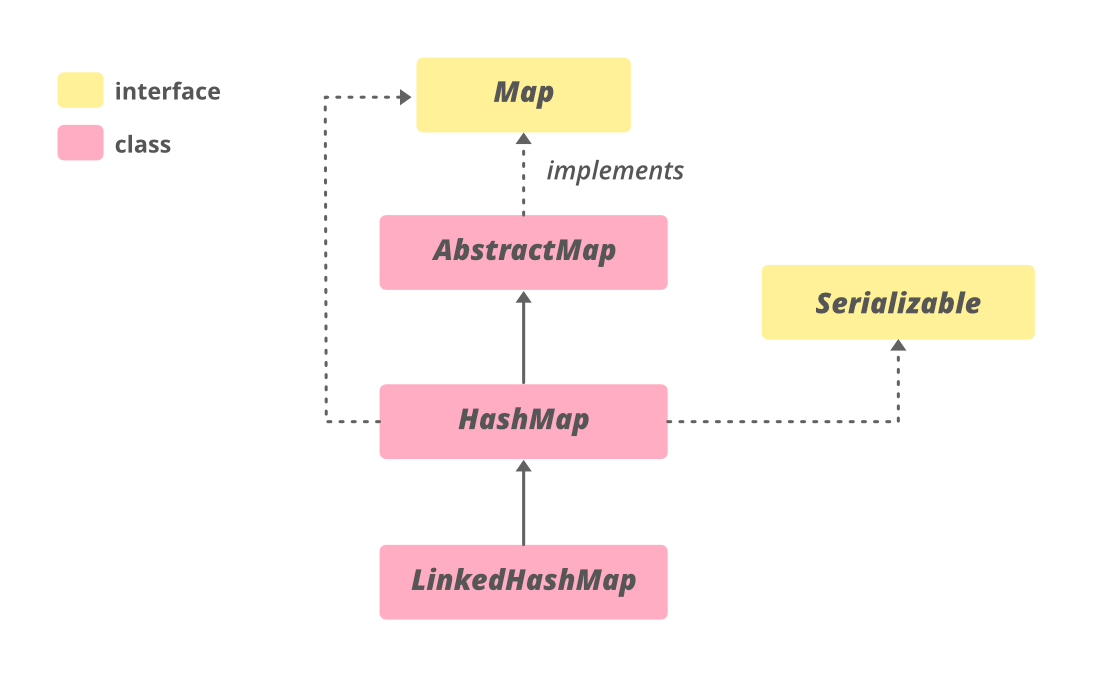
HashMap的层次结构如下。
语法: 声明
public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable
参数: 它需要两个参数,即如下。
- 该Map所维护的键的类型
- 映射值的类型
HashMap实现了 Serializable , Cloneable , Map<K, V>接口。HashMap扩展了 AbstractMap <K, V> **类。直接的子类是LinkedHashMap , **PrinterStateReasons
HashMap的构造函数如下
HashMap提供了4个构造函数,每个构造函数的访问修饰符都是public,如下所示。
- HashMap()
- HashMap(int initialCapacity)
- HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor)
- HashMap(Map map)
现在逐一讨论上述构造函数,并在干净的java程序的帮助下实现这些构造函数。
构造函数1: HashMap()
这是一个默认的构造函数,它创建了一个初始容量为16、负载因子为0.75的HashMap实例。
语法
HashMap<K, V> hm = new HashMap<K, V>();
例子
// Java program to Demonstrate the HashMap() constructor
// Importing basic required classes
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Main class
// To add elements to HashMap
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// No need to mention the
// Generic type twice
HashMap<Integer, String> hm1 = new HashMap<>();
// Initialization of a HashMap using Generics
HashMap<Integer, String> hm2
= new HashMap<Integer, String>();
// Adding elements using put method
// Custom input elements
hm1.put(1, "one");
hm1.put(2, "two");
hm1.put(3, "three");
hm2.put(4, "four");
hm2.put(5, "five");
hm2.put(6, "six");
// Print and display mapping of HashMap 1
System.out.println("Mappings of HashMap hm1 are : "
+ hm1);
// Print and display mapping of HashMap 2
System.out.println("Mapping of HashMap hm2 are : "
+ hm2);
}
}
输出
Mappings of HashMap hm1 are : {1=one, 2=two, 3=three}
Mapping of HashMap hm2 are : {4=four, 5=five, 6=six}
构造函数2: HashMap(int initialCapacity)
它创建一个HashMap实例,其初始容量为 ,负载系数为 0.75。
语法
HashMap<K, V> hm = new HashMap<K, V>(int initialCapacity);
例子
// Java program to Demonstrate
// HashMap(int initialCapacity) Constructor
// Importing basic classes
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Main class
// To add elements to HashMap
class AddElementsToHashMap {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// No need to mention the
// Generic type twice
HashMap<Integer, String> hm1 = new HashMap<>(10);
// Initialization of a HashMap using Generics
HashMap<Integer, String> hm2
= new HashMap<Integer, String>(2);
// Adding elements to object of HashMap
// using put method
// HashMap 1
hm1.put(1, "one");
hm1.put(2, "two");
hm1.put(3, "three");
// HashMap 2
hm2.put(4, "four");
hm2.put(5, "five");
hm2.put(6, "six");
// Printing elements of HashMap 1
System.out.println("Mappings of HashMap hm1 are : "
+ hm1);
// Printing elements of HashMap 2
System.out.println("Mapping of HashMap hm2 are : "
+ hm2);
}
}
输出
Mappings of HashMap hm1 are : {1=one, 2=two, 3=three}
Mapping of HashMap hm2 are : {4=four, 5=five, 6=six}
构造函数3: HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor)
它创建一个具有指定初始容量和指定负载因子的HashMap实例。
语法
HashMap<K, V> hm = new HashMap<K, V>(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor);
例子
// Java program to Demonstrate
// HashMap(int initialCapacity,float loadFactor) Constructor
// Importing basic classes
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Main class
// To add elements to HashMap
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// No need to mention the generic type twice
HashMap<Integer, String> hm1
= new HashMap<>(5, 0.75f);
// Initialization of a HashMap using Generics
HashMap<Integer, String> hm2
= new HashMap<Integer, String>(3, 0.5f);
// Add Elements using put() method
// Custom input elements
hm1.put(1, "one");
hm1.put(2, "two");
hm1.put(3, "three");
hm2.put(4, "four");
hm2.put(5, "five");
hm2.put(6, "six");
// Print and display elements in object of hashMap 1
System.out.println("Mappings of HashMap hm1 are : "
+ hm1);
// Print and display elements in object of hashMap 2
System.out.println("Mapping of HashMap hm2 are : "
+ hm2);
}
}
输出
Mappings of HashMap hm1 are : {1=one, 2=two, 3=three}
Mapping of HashMap hm2 are : {4=four, 5=five, 6=six}
4.HashMap(Map map): 它创建了一个HashMap的实例,其映射与指定Map相同。
HashMap<K, V> hm = new HashMap<K, V>(Map map)
// Java program to demonstrate the
// HashMap(Map map) Constructor
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class AddElementsToHashMap {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// No need to mention the
// Generic type twice
Map<Integer, String> hm1 = new HashMap<>();
// Add Elements using put method
hm1.put(1, "one");
hm1.put(2, "two");
hm1.put(3, "three");
// Initialization of a HashMap
// using Generics
HashMap<Integer, String> hm2
= new HashMap<Integer, String>(hm1);
System.out.println("Mappings of HashMap hm1 are : "
+ hm1);
System.out.println("Mapping of HashMap hm2 are : "
+ hm2);
}
}
输出
Mappings of HashMap hm1 are : {1=one, 2=two, 3=three}
Mapping of HashMap hm2 are : {1=one, 2=two, 3=three}
对HashMap进行各种操作
1.添加元素: 为了向Map添加一个元素,我们可以使用put()方法。然而,在Hashmap中不保留插入顺序。在内部,对于每一个元素,都会产生一个单独的哈希值,并且基于这个哈希值对元素进行索引,以使其更有效率。
// Java program to add elements
// to the HashMap
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class AddElementsToHashMap {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// No need to mention the
// Generic type twice
HashMap<Integer, String> hm1 = new HashMap<>();
// Initialization of a HashMap
// using Generics
HashMap<Integer, String> hm2
= new HashMap<Integer, String>();
// Add Elements using put method
hm1.put(1, "Geeks");
hm1.put(2, "For");
hm1.put(3, "Geeks");
hm2.put(1, "Geeks");
hm2.put(2, "For");
hm2.put(3, "Geeks");
System.out.println("Mappings of HashMap hm1 are : "
+ hm1);
System.out.println("Mapping of HashMap hm2 are : "
+ hm2);
}
}
输出
Mappings of HashMap hm1 are : {1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}
Mapping of HashMap hm2 are : {1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}
2.改变元素: 在添加元素后,如果我们想改变元素,可以通过put()方法再次添加元素来完成。由于Map中的元素是用键来索引的,所以键的值可以通过简单地插入我们想改变的键的更新值来改变。
// Java program to change
// elements of HashMap
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class ChangeElementsOfHashMap {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Initialization of a HashMap
HashMap<Integer, String> hm
= new HashMap<Integer, String>();
// Change Value using put method
hm.put(1, "Geeks");
hm.put(2, "Geeks");
hm.put(3, "Geeks");
System.out.println("Initial Map " + hm);
hm.put(2, "For");
System.out.println("Updated Map " + hm);
}
}
输出
Initial Map {1=Geeks, 2=Geeks, 3=Geeks}
Updated Map {1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}
3.删除元素: 为了从Map中删除一个元素,我们可以使用remove()方法。这个方法接收键值,如果一个键存在于Map中,就从这个Map中删除它的映射。
// Java program to remove
// elements from HashMap
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class RemoveElementsOfHashMap{
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Initialization of a HashMap
Map<Integer, String> hm
= new HashMap<Integer, String>();
// Add elements using put method
hm.put(1, "Geeks");
hm.put(2, "For");
hm.put(3, "Geeks");
hm.put(4, "For");
// Initial HashMap
System.out.println("Mappings of HashMap are : "
+ hm);
// remove element with a key
// using remove method
hm.remove(4);
// Final HashMap
System.out.println("Mappings after removal are : "
+ hm);
}
}
输出
Mappings of HashMap are : {1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks, 4=For}
Mappings after removal are : {1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}
4.HashMap的遍历
我们可以使用Iterator接口来遍历集合框架的任何结构。由于迭代器只处理一种类型的数据,我们使用Entry< ?, ? >来将两种不同的类型解析成一种兼容的格式。然后使用next()方法来打印HashMap的条目。
// Java program to traversal a
// Java.util.HashMap
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class TraversalTheHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// initialize a HashMap
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
// Add elements using put method
map.put("vishal", 10);
map.put("sachin", 30);
map.put("vaibhav", 20);
// Iterate the map using
// for-each loop
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> e : map.entrySet())
System.out.println("Key: " + e.getKey()
+ " Value: " + e.getValue());
}
}
输出
Key: vaibhav Value: 20
Key: vishal Value: 10
Key: sachin Value: 30
HashMap的重要特征
要访问一个值,必须知道它的键。HashMap之所以被称为HashMap,是因为它使用了一种叫做Hashing的技术。散列是一种将大字符串转换为代表同一字符串的小字符串的技术。一个较短的值有助于索引和快速搜索。HashSet也在内部使用HashMap。
HashMap的几个重要特征是。
- HashMap是java.util包的一部分。
- HashMap扩展了一个抽象类AbstractMap,它也提供了Map接口的不完整实现。
- 它还实现了Cloneable和Serializable接口。上述定义中的K和V分别代表Key和Value。
- HashMap不允许重复的键,但允许重复的值。这意味着一个键不能包含一个以上的值,但一个以上的键可以包含一个值。
- HashMap也允许空键,但只允许一次和多个空值。
- 这个类不保证Map的顺序;特别是不保证顺序会随着时间的推移保持不变。它与HashTable大致相似,但不是同步的。
HashMap的内部结构
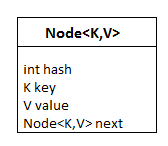
在内部,HashMap包含一个Node数组,一个节点被表示为一个包含4个字段的类。
- int hash
- K键
- V值
- Node next
可以看出,节点包含对其自身对象的引用。所以它是一个链接列表。
HashMap:
节点:
HashMap的性能
HashMap的性能取决于两个参数,它们的名称如下。
- 初始容量
- 负载系数
1.初始容量 - 它是HashMap在创建时的容量(它是HashMap实例化时可以容纳的桶的数量)。在java中,它最初是2^4=16,意味着它可以容纳16个键值对。
2. 负载因子 - 它是Hashmap容量的百分比值,之后Hashmap的容量将被增加(它是桶的填充百分比,之后会发生重新洗牌)。在java中,它默认为0.75f,这意味着在填满75%的容量后就会进行重新洗牌。
3.阈值 - 它是负载因子和初始容量的乘积。在java中,默认情况下,它是(16*0.75=12)。也就是说,在向HashMap中插入12个键值对后,就会发生重新洗牌。
4. 重洗 - 是指在HashMap达到阈值后将其容量翻倍的过程。在java中,HashMap继续以下列顺序进行重洗(默认情况下)–2^4, 2^5, 2^6, 2^7, …. 等等。
如果初始容量保持在较高的水平上,那么重洗就永远不会被完成。但是保持较高的容量会增加迭代的时间复杂性。所以应该非常巧妙地选择它以提高性能。在设置初始容量时,应该考虑到预期的数值数量。一般来说,最受欢迎的负载因子值是0.75,它在时间和空间成本之间提供了一个良好的交易。负载因子的值在0和1之间变化。
注意: 从Java 8开始,Java已经开始使用自平衡BST而不是链式列表。自平衡BST的优点是,我们得到的最坏情况(当每个键映射到相同的槽时)搜索时间是O(Log n)。
同步的HashMap
正如我们所知,HashMap是非同步的,即多个线程可以同时访问它。如果多个线程同时访问这个类,并且至少有一个线程在结构上操作它,那么就有必要在外部使其同步化。这可以通过同步一些封装Map的对象来实现。如果没有这样的对象存在,那么可以将其包裹在Collections.synchronizedMap()中,使HashMap同步化,避免意外的非同步访问。如下面的例子:
Map m = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap(...));
现在Map m是同步的。 如果在创建迭代器之后,以任何方式对结构进行修改,除了通过迭代器的删除方法之外,该类的迭代器是快速失败的。如果迭代器失败,它会抛出ConcurrentModificationException。
HashMap的时间复杂度: 如果散列函数编写得当,并且在桶中正确分散了元素,那么HashMap为基本操作提供了恒定的时间复杂度,即get和put。HashMap的迭代取决于HashMap的容量和键值对的数量。基本上,它与容量+大小成正比。容量是指HashMap中的桶的数量。因此,最初在HashMap中保留大量的桶并不是一个好主意。
HashMap的应用: HashMap主要是散列的实现。当我们需要有效地实现搜索、插入和删除操作时,它就很有用。详情请参考散列的应用。
HashMap中的方法
- K – Map中键的类型。
- V – 在Map中映射的值的类型。
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| clear() | 删除该Map中的所有映射。 |
| clone() | 返回该HashMap实例的一个浅层拷贝:键和值本身没有被克隆。 |
| compute(K key, BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) | 试图为指定的键和其当前映射的值计算一个映射(如果没有当前映射,则为空)。 |
| computeIfAbsent(K key, Function<? super K,? extends V> mappingFunction) | 如果指定的键还没有与一个值相关联(或者被映射为null),则尝试使用给定的映射函数计算其值,并将其输入此映射中,除非为null。 |
| computeIfPresent(K key, BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) | 如果指定的键的值是存在的,并且不是空的,则尝试计算一个新的映射,给定键和它当前的映射值。 |
| containsKey(Object key) | 如果这个Map包含指定键的映射,返回true。 |
| containsValue(Object value) | 如果这个Map将一个或多个键映射到指定的值,则返回true。 |
| entrySet() | 返回该Map中包含的映射的Set视图。 |
| get(Object key) | 返回指定的键被映射到的值,如果这个Map不包含键的映射,则返回空。 |
| isEmpty() | 如果这个Map不包含键值映射,则返回true。 |
| keySet() | 返回该Map中包含的键的Set视图。 |
| merge(K key, V value, BiFunction<? super V, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) | 如果指定的键还没有与一个值相关联或者与空值相关联,那么将其与给定的非空值相关联。 |
| put(K key, V value) | 将指定的值与这个Map中的指定键关联起来。 |
| putAll(Map<? extends K,? extends V> m) | 将指定Map中的所有映射复制到此Map中。 |
| remove(Object key) | 如果存在的话,从这个Map中删除指定键的映射。 |
| size() | 返回这个Map中的键值映射的数量。 |
| values() | 返回该Map中包含的值的集合视图。 |
从java.util.AbstractMap类继承的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| equals() | 将指定的对象与该Map进行比较,看是否相等。 |
| hashCode() | 返回该Map的哈希代码值。 |
| toString() | 返回该Map的字符串表示。 |
从java.util.Map接口继承的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| equals() | 将指定的对象与该Map进行比较,看是否相等。 |
| forEach(BiConsumer<? super K, ? super V> action) | 对这个Map中的每个条目执行给定的动作,直到所有条目都被处理完或该动作抛出一个异常。 |
| getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) | 返回指定的键所映射的值,如果这个Map不包含键的映射,则返回默认值。 |
| hashCode() | 返回这个Map的哈希代码值。 |
| putIfAbsent(K key, V value) | 如果指定的键没有与一个值相关联(或者被映射为null),则将其与给定的值相关联并返回null,否则返回当前值。 |
| remove(Object key, Object value) | 只有当指定的键当前被映射到指定的值时,才会删除该键的条目。 |
| replace(K key, V value) | 只有当指定的键当前被映射到某个值时,才会替换该键的条目。 |
| replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) | 只在当前映射到指定值的情况下替换指定键的条目。 |
| replaceAll(BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> function) | 用对该条目调用给定函数的结果替换每个条目的值,直到所有条目都被处理或该函数抛出一个异常。 |
 极客教程
极客教程