Java程序 实现linkedlist API
链接列表是集合框架的一部分,存在于java.util包中。该类是LinkedList数据结构的一个实现,它是一个线性数据结构,其中的元素不存储在连续的位置,每个元素都是一个独立的对象,有数据部分和地址部分。
什么是linkedlist API?
- 链接列表API旨在实现链接列表集合,它是继承自java.util包的集合框架的一部分。
- 这个API是list和deque接口的双链接列表实现。
- 这个API实现了所有可选的列表操作,并允许所有元素(包括null)。
- 所有的操作都是对双链表的预期执行。对列表进行索引的操作将从列表的开头或结尾开始遍历,以更接近指定索引的为准。
- 下面是实现LinkedList Collection API的java程序的源代码。
示例:
// Java Program to Implement LinkedList API
// Importing utility classes from java.util package
import java.util.*;
import java.util.Collection;
// Class
// Main class consisting of all methods
public class LinkedListImpl<E> {
// Member variable of this class
private LinkedList<E> linkedList;
// Constructors of this class
// 1. Default constructor
public LinkedListImpl()
{
linkedList = new LinkedList<E>();
}
// 2. Parameterized constructor
public LinkedListImpl(Collection<? extends E> c)
{
linkedList = new LinkedList<E>(c);
}
// Method 1
// To append specified element to end of this List
public boolean add(E e)
{
// Returning the last element from the List
return linkedList.add(e);
}
// Method 2
// To insert specified element at
// the specified position in this List
public void add(int index, E element)
{
linkedList.add(index, element);
}
// Method 3
// To add all the elements in this List
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)
{
return linkedList.addAll(c);
}
// Method 4
// To add all the elements in this List
public boolean addAll(int index,
Collection<? extends E> c)
{
return linkedList.addAll(index, c);
}
// Method 5
// to inserts specified element at beginning of this
// List
public void addFirst(E e) { linkedList.addFirst(e); }
// Method 6
// To appends specified element to end of this List
public void addLast(E e) { linkedList.addLast(e); }
// Method 7
// Removes all of the elements from this list.
public void clear() { linkedList.clear(); }
// Method 8
// Returns a shallow copy of this ArrayList instance.
public Object clone() { return linkedList.clone(); }
// Method 9
// Returns true if this list contains the specified
// element.
public boolean contains(Object o)
{
return linkedList.contains(o);
}
// Method 10
// Returns an iterator over the elements in this
// deque(reverse order)
public Iterator<E> descendingIterator()
{
return linkedList.descendingIterator();
}
// Method 11
// Retrieves, but does not remove, the head (first
// element) of this list.
public E element() { return linkedList.element(); }
// Method 12
// Returns the element at the specified position in this
// list.
public E get(int index)
{
return linkedList.get(index);
}
// Method 13
// Returns the first element in this list.
public E getFirst() { return linkedList.getFirst(); }
// Method 14
// Returns the last element in this list.
public E getLast() { return linkedList.getLast(); }
// Method 15
// Returns the index of the first occurrence of the
// specified element
public int indexOf(Object o)
{
return linkedList.indexOf(o);
}
// Method 16
// Returns true if this list contains no elements.
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return linkedList.isEmpty();
}
// Method 17
// Returns an iterator over the elements
// in this list in proper sequence.
public Iterator<E> iterator()
{
return linkedList.iterator();
}
// Method 18
public int lastIndexOf(Object o)
{
return linkedList.lastIndexOf(o);
}
// Method 19
public ListIterator<E> listIterator()
{
return linkedList.listIterator();
}
// Method 20
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index)
{
return linkedList.listIterator(index);
}
// Method 21
// Adds the specified element as the tail (last element)
// of this list.
public boolean offer(E e)
{
return linkedList.offer(e);
}
// Method 22
// Inserts the specified element at the front of this
// list.
public boolean offerFirst(E e)
{
return linkedList.offerFirst(e);
}
// Method 23
// Inserts the specified element at the end of this
// list.
public boolean offerLast(E e)
{
return linkedList.offerLast(e);
}
// Method 24
// Retrieves, but does not remove, the head (first
// element) of this list.
public E peek() { return linkedList.peek(); }
// Method 25
public E peekFirst() { return linkedList.peekFirst(); }
// Method 26
// Retrieves, but does not remove, the last element of
// this list
public E peekLast() { return linkedList.peekLast(); }
// Method 27
// Retrieves and removes the head (first element) of
// this list.
public E poll() { return linkedList.poll(); }
// Method 28
// Retrieves and removes the first element of this list,
// or returns null
public E pollFirst() { return linkedList.pollFirst(); }
// Method 29
// Retrieves and removes the last element of this list,
// or returns null
public E pollLast() { return linkedList.peekLast(); }
// Method 30
// Pops an element from the stack represented by this
// list.
public E pop() { return linkedList.pop(); }
// Method 31
// Pushes an element onto the stack represented by this
// list.
public void push(E e) { linkedList.push(e); }
// Method 32
// Removes the element at the specified position in this
// list.
public E remove(int index)
{
return linkedList.remove(index);
}
// Method 33
// Removes the first occurrence of the specified element
// from this list(if present)
public boolean remove(Object o)
{
return linkedList.remove(o);
}
// Method 34
public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c)
{
return linkedList.removeAll(c);
}
// Method 35
// Removes and returns the first element from this list.
public E removeFirst()
{
return linkedList.removeFirst();
}
// Method 36
// To remove th first occurrences in this List
public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o)
{
return linkedList.removeFirstOccurrence(o);
}
// Method 37
// Removes and returns the last element from this list.
public E removeLast()
{
return linkedList.removeLast();
}
// Method 38
// Removes the last occurrence of the specified element
// in this list
public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o)
{
return linkedList.removeLastOccurrence(o);
}
// Method 39
// Retains only the elements in this list
// contained in specific position
public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c)
{
return linkedList.removeAll(c);
}
// Method 40
// Replaces the element at the specified position
public E set(int index, E element)
{
return linkedList.set(index, element);
}
// Method 41
// Returns the number of elements in this list.
public int size() { return linkedList.size(); }
// Method 42
// Returns a view of the portion of this list
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex)
{
return linkedList.subList(fromIndex, toIndex);
}
// Method 43
// Returns an array containing all of the elements
// in this list(proper sequence)
public Object[] toArray()
{
return linkedList.toArray();
}
// Method 44
// Returns an array containing all of the elements in
// this list
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a)
{
return linkedList.toArray(a);
}
// Method 45
// Main driver method
public static void main(String... arg)
{
// Creating an object of above class
// User-defined
LinkedListImpl<Integer> linkedList
= new LinkedListImpl<>();
// Adding custom elements to above object
// Custom input elements addition
// using add() and addAll() methods
linkedList.add(100);
linkedList.add(20);
linkedList.addFirst(101);
linkedList.addLast(200);
// Creating a Set class object of integer type
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
// Custom input elements addition
// using add() and addAll() methods
set.add(101);
set.add(30);
set.add(32);
linkedList.addAll(4, set);
if (linkedList.contains(300))
System.out.println(
"the linked list contains 300");
else
System.out.println(
"the linked list does not contain 300");
System.out.println(
"the elements in descending order is");
Iterator<Integer> descendingitr
= linkedList.descendingIterator();
while (descendingitr.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(descendingitr.next() + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("the head of this list is "
+ linkedList.element());
System.out.println("the element at index 2 is "
+ linkedList.get(2));
System.out.println("the element first pos is "
+ linkedList.getFirst());
System.out.println("the element at last pos is"
+ linkedList.getLast());
System.out.println("the index of element 200 is "
+ linkedList.indexOf(200));
System.out.println(
"the last index of element 101 is "
+ linkedList.lastIndexOf(101));
System.out.println("the elements of list are");
Iterator<Integer> itr = linkedList.iterator();
while (itr.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(itr.next() + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
linkedList.offer(45);
linkedList.offerFirst(32);
linkedList.offerLast(19);
System.out.println("the head of the linkedlist is "
+ linkedList.peek());
System.out.println(
"the first element of linkedList is "
+ linkedList.peekFirst());
System.out.println(
"the last element of linked List is "
+ linkedList.peekLast());
System.out.println("the elements of list are");
itr = linkedList.iterator();
while (itr.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(itr.next() + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println(
"the first element of linkedList is (poll) "
+ linkedList.poll());
System.out.println("the first element polled is "
+ linkedList.pollFirst());
System.out.println("the last element polled is "
+ linkedList.pollLast());
linkedList.push(36);
System.out.println(
"the element popped from linked List is "
+ linkedList.pop());
System.out.println(
"index 3 element removed from list "
+ linkedList.remove(3));
System.out.println(
"last occurrence of 101 removed "
+ linkedList.removeLastOccurrence(101));
linkedList.clear();
if (linkedList.isEmpty())
System.out.println("the linkedList is empty");
else
System.out.println(
"the linked list is not empty");
}
}
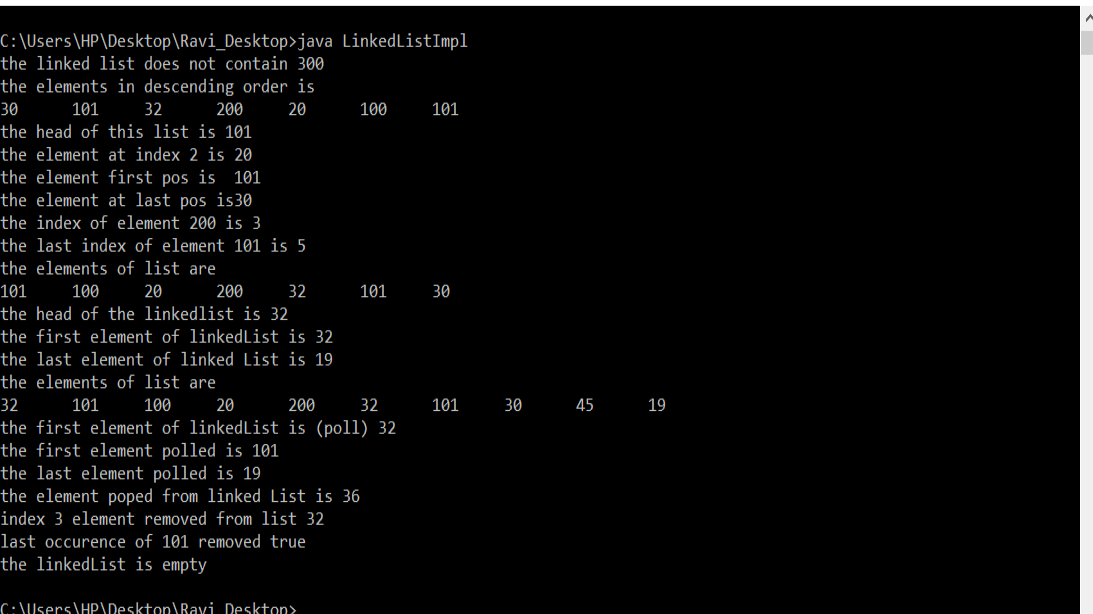
输出 :
代码解释:
1.我们创建了一个集合方法LinkedListImpl
2.我们创建一个布尔方法add(),将指定的元素追加到这个列表的结尾。
3.我们创建一个void add()方法,在这个列表的指定位置上插入指定的元素。
4.我们创建一个boolean addAll()方法,按照指定集合的迭代器返回的顺序,将指定集合中的所有元素附加到这个列表的末尾。
5.我们创建一个void addFirst()方法,在这个列表的开头插入指定的元素。
6.我们创建一个void addLast()方法,将指定的元素添加到这个列表的最后。
7.我们创建clear()方法来移除这个列表中的所有元素。
8.我们创建一个clone()方法,返回这个ArrayList实例的一个浅层拷贝。
9.我们创建一个contains()方法,如果这个列表包含指定的元素,则返回true。
10.我们创建一个descendingIterator(),它以相反的顺序返回这个deque中的元素的一个迭代器。
11.我们创建element()方法,检索但不删除这个列表的头部(第一个元素)。
12.我们创建getFirst()方法,该方法返回该列表中的第一个元素。
13.我们创建了getLast()方法,返回这个列表中的最后一个元素。
14.我们创建了以对象为参数的indexOf()方法,该方法返回指定元素在列表中第一次出现的索引,如果该列表不包含该元素则返回-1。
15.我们创建了isEmpty(),如果这个列表不包含任何元素,则返回真。
16.我们为arrayList创建了iterator()方法,该方法以适当的顺序返回该列表中的元素的迭代器。
17.我们创建lastIndexOf()来返回指定元素在此最后出现的索引,否则为-1。
18.我们为ArrayList创建了listIterator()方法,listIterator
19.我们写listIterator(int index)来返回这个列表中的元素的一个列表迭代器。
20.我们写offer()方法来添加指定的元素作为这个列表的尾部(最后一个元素)。
21.我们写offerFirst(E e)来插入指定的元素在这个列表的前面。
 极客教程
极客教程