Java程序 用双链接列表实现哈希表链
哈希表(类似于一般的表)提供了动态集合操作的一个子集。通常,一组键被映射到基于某些关系的一些值上。然而,可能会有这样的情况:不同的键映射到哈希函数提供的相同位置,这导致了碰撞。
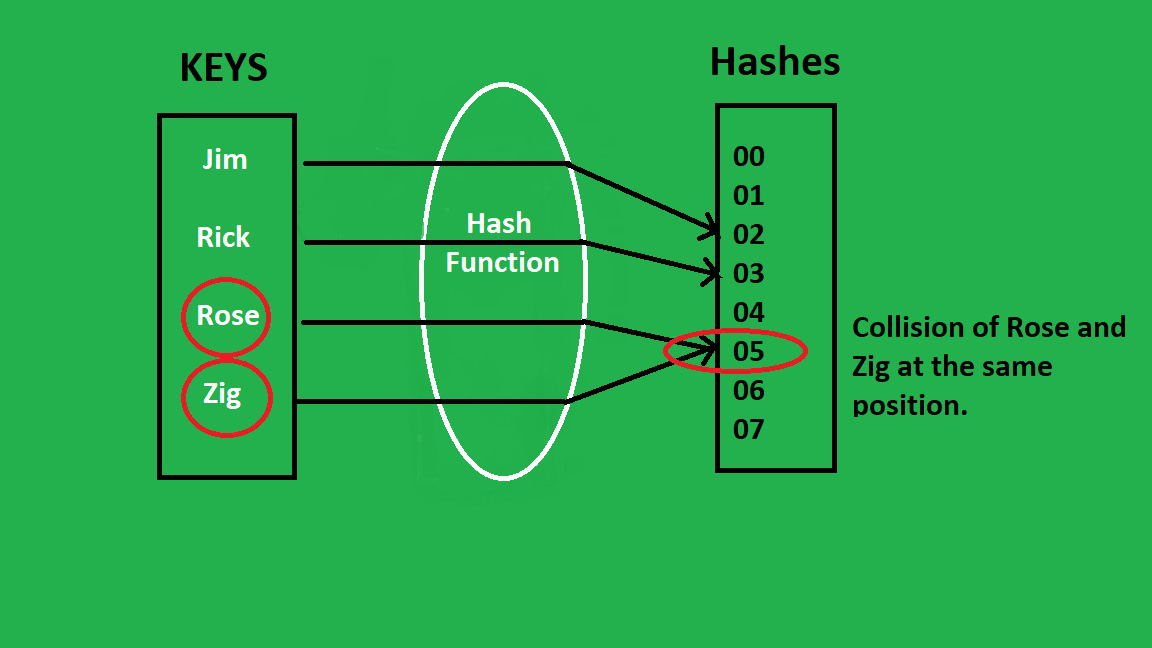
克服这种情况的方法之一是哈希表链。
解决碰撞的链式方法是通过将所有映射到某一槽位的键放在该槽位中,但将它们表示为一个链接列表来处理。
Java中的哈希表链可以通过单链表和双链表实现。虽然实现方式相同,但唯一的区别是,双链表允许双向遍历,即节点包含一个指向下一个节点和上一个节点的指针。因此,与单链表(O(n))相比,在已知位置插入和删除的复杂性降低到O(1)。
示例 :
In Singly Linked List : g -> e -> e -> k -> s
Here, each node contains a pointer to the next node only.
In Doubly Linked List : g <-> e <-> e <-> k <-> s
Each node contains pointer to the next as well as previous node.
步骤 :
1.插入。要插入时,只需对一个键进行哈希处理,以获得表中的位置(这个新键必须插入的列表),然后使用标准的链表程序(在代码中给出)在双链表的头部插入该键。
2.删掉。只需通过哈希函数浏览键映射到的列表,并使用标准的链接列表程序(代码中给出)从该列表中删除键。
下面是上述方法的实现。
// Java implementation of Hashtable chaining
// using doubly linked list
import java.util.*;
class DoublyLinkedListNode {
// Declaration of Nodes
DoublyLinkedListNode next, prev;
int data;
// constructor
DoublyLinkedListNode(int data)
{
this.data = data;
next = null;
prev = null;
}
}
class HashTableChainingDoublyLinkedList {
// Declaration of Hash Table
DoublyLinkedListNode[] hashTable;
// stores the size of HashTable
int size;
// Constructor
HashTableChainingDoublyLinkedList(int hashTableSize)
{
// Creating an empty Hash Table
hashTable = new DoublyLinkedListNode[hashTableSize];
size = 0;
}
// Function to check if hash table is empty
public boolean isEmpty() { return size == 0; }
// Function to clear/delete all elements from Hash table
public void clear()
{
// Capacity of Hash Table
int len = hashTable.length;
// Creating new empty Hash Table
// of same initial capacity
hashTable = new DoublyLinkedListNode[len];
size = 0;
}
// Function that returns size of Hash Table
public int getSize() { return size; }
// Function to insert a value/element
public void insert(int value)
{
size++;
// gets the position/index where the value should be
// stored
int position = hash(value);
// creates a node for storing value
DoublyLinkedListNode node
= new DoublyLinkedListNode(value);
DoublyLinkedListNode start = hashTable[position];
if (hashTable[position] == null)
hashTable[position] = node;
else {
node.next = start;
start.prev = node;
hashTable[position] = node;
}
}
// Function to remove an element
public void remove(int value)
{
try {
// gets the position where the value to
// be deleted exists
int position = hash(value);
DoublyLinkedListNode start
= hashTable[position];
DoublyLinkedListNode end = start;
// if value is found at start
if (start.data == value) {
size--;
if (start.next == null) {
// removing the value
hashTable[position] = null;
return;
}
start = start.next;
start.prev = null;
hashTable[position] = start;
return;
}
// traversing the list
// until the value is found
while (end.next != null
&& end.next.data != value)
end = end.next;
// if reached at the end without finding the
// value
if (end.next == null) {
System.out.println("\nElement not found\n");
return;
}
size--;
if (end.next.next == null) {
end.next = null;
return;
}
end.next.next.prev = end;
end.next = end.next.next;
hashTable[position] = start;
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("\nElement not found\n");
}
}
// Definition of Hash function
private int hash(Integer x)
{
int hashValue = x.hashCode();
hashValue %= hashTable.length;
if (hashValue < 0)
hashValue += hashTable.length;
return hashValue;
}
// Function to print hash table
public void printHashTable()
{
System.out.println();
for (int i = 0; i < hashTable.length; i++) {
System.out.print("At " + i + ": ");
DoublyLinkedListNode start = hashTable[i];
while (start != null) {
System.out.print(start.data + " ");
start = start.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
HashTableChainingDoublyLinkedList hashTab
= new HashTableChainingDoublyLinkedList(5);
hashTab.insert(99);
hashTab.insert(23);
hashTab.insert(36);
hashTab.insert(47);
hashTab.insert(80);
hashTab.printHashTable();
hashTab.insert(92);
hashTab.insert(49);
hashTab.printHashTable();
hashTab.remove(99);
hashTab.printHashTable();
hashTab.clear();
hashTab.printHashTable();
System.out.println(hashTab.isEmpty());
}
}
输出
At 0: 80
At 1: 36
At 2: 47
At 3: 23
At 4: 99
At 0: 80
At 1: 36
At 2: 92 47
At 3: 23
At 4: 49 99
At 0: 80
At 1: 36
At 2: 92 47
At 3: 23
At 4: 49
At 0:
At 1:
At 2:
At 3:
At 4:
true
 极客教程
极客教程