Java HashMap和TreeMap
HashMap和TreeMap是集合框架的一部分。
HashMap
java.util.HashMap类是一个基于Hashing的实现。在HashMap中,我们有一个键和一个值对 。
HashMap<K, V> hmap = new HashMap<K, V>();
让我们考虑以下例子,我们必须计算每个整数在给定的整数阵列中的出现次数。
输入: arr[] = {10, 3, 5, 10, 3, 5, 10};
输出: Frequency of 10 is 3
Frequency of 3 is 2
Frequency of 5 is 2
/* Java program to print frequencies of all elements using
HashMap */
import java.util.*;
class Main
{
// This function prints frequencies of all elements
static void printFreq(int arr[])
{
// Creates an empty HashMap
HashMap<Integer, Integer> hmap =
new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
// Traverse through the given array
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++)
{
Integer c = hmap.get(arr[i]);
// If this is first occurrence of element
if (hmap.get(arr[i]) == null)
hmap.put(arr[i], 1);
// If elements already exists in hash map
else
hmap.put(arr[i], ++c);
}
// Print result
for (Map.Entry m:hmap.entrySet())
System.out.println("Frequency of " + m.getKey() +
" is " + m.getValue());
}
// Driver method to test above method
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int arr[] = {10, 34, 5, 10, 3, 5, 10};
printFreq(arr);
}
}
输出:
Frequency of 34 is 1
Frequency of 3 is 1
Frequency of 5 is 2
Frequency of 10 is 3
关键点
- HashMap既不根据键也不根据值保持任何顺序,如果我们想让键保持一个排序的顺序,我们需要使用TreeMap。
- 复杂性 :get/put/containsKey()操作在平均情况下是O(1),但我们不能保证,因为这完全取决于计算哈希值需要多少时间。
应用:
HashMap基本上是散列的一个实现。因此,只要我们需要用键值对进行散列,我们就可以使用HashMap。例如,在网络应用中,用户名被存储为一个键,用户数据被存储为HashMap中的一个值,以便更快地检索与用户名对应的用户数据。
TreeMap
当我们只需要以排序的方式存储唯一的元素时,TreeMap就会有点方便了。Java.util.TreeMap在后台使用一个红黑树,确保没有重复的元素;此外,它还以排序的方式维护元素。
TreeMap<K, V> hmap = new TreeMap<K, V>();
下面是同一问题的基于TreeMap的实现。这个方案的时间复杂度为O(nLogn),而之前的方案为O(n)。这种方法的优点是,我们可以得到排序后的元素。
推荐实践TreeMap操作 试试吧!
/* Java program to print frequencies of all elements using
TreeMap */
import java.util.*;
class Main
{
// This function prints frequencies of all elements
static void printFreq(int arr[])
{
// Creates an empty TreeMap
TreeMap<Integer, Integer> tmap =
new TreeMap<Integer, Integer>();
// Traverse through the given array
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++)
{
Integer c = tmap.get(arr[i]);
// If this is first occurrence of element
if (tmap.get(arr[i]) == null)
tmap.put(arr[i], 1);
// If elements already exists in hash map
else
tmap.put(arr[i], ++c);
}
// Print result
for (Map.Entry m:tmap.entrySet())
System.out.println("Frequency of " + m.getKey() +
" is " + m.getValue());
}
// Driver method to test above method
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int arr[] = {10, 34, 5, 10, 3, 5, 10};
printFreq(arr);
}
}
输出:
Frequency of 3 is 1
Frequency of 5 is 2
Frequency of 10 is 3
Frequency of 34 is 1
关键点
- 对于添加、删除、包含键等操作,时间复杂度为O(log n,其中n为TreeMap中存在的元素数。
- TreeMap总是保持元素的排序(递增)顺序,而HashMap中的元素没有顺序。TreeMap还提供了一些很酷的方法来处理键的第一个、最后一个、下限和上限。
概述。
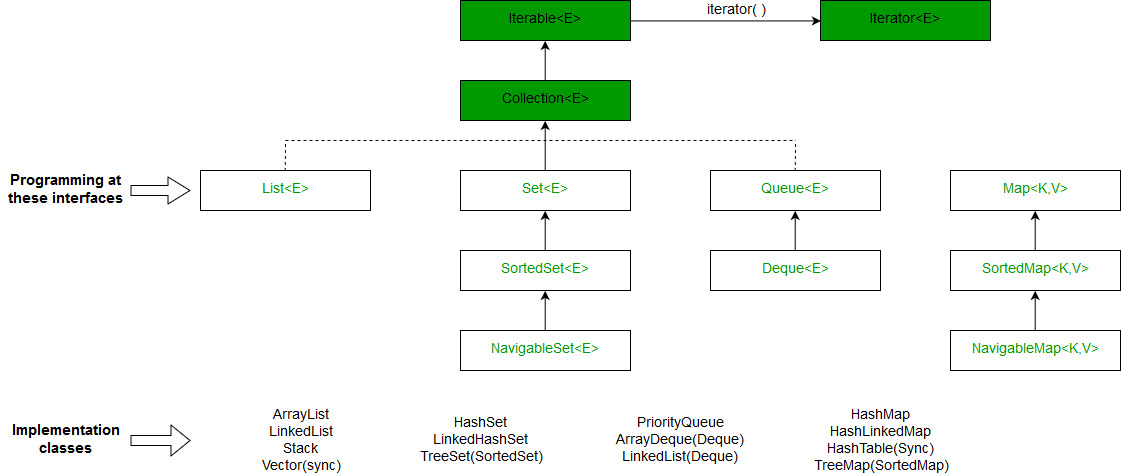
- HashMap实现了Map接口,而TreeMap实现了SortedMap接口。分类地图接口是地图的一个子接口。
- HashMap实现了Hashing,而TreeMap实现了Red-Black Tree(一种自平衡二进制搜索树)。因此,Hashing和平衡二进制搜索树之间的所有区别都适用于此。
- HashMap和TreeMap都有其对应的HashSet和TreeSet。HashSet和TreeSet实现了Set接口。在HashSet和TreeSet中,我们只有键,没有值,这些主要用于查看集合中的存在/不存在。对于上述问题,我们不能使用HashSet(或TreeSet),因为我们不能存储计数。比起HashMap(或TreeMap),我们更喜欢HashSet(或TreeSet)的一个例子是打印一个数组中所有不同的元素。
 极客教程
极客教程