Java DelayQueue类与实例
DelayQueue 类是Java集合框架的一个成员。它属于 java.util.concurrent 包。DelayQueue实现了BlockingQueue接口。DelayQueue是一个专门的优先级队列,它根据元素的延迟时间来排序。这意味着只有那些时间已经过期的元素才能从队列中取出。
DelayQueue head包含了时间过期最少的元素。如果没有延迟过期,那么就没有头部,投票将返回null。DelayQueue只接受那些属于 Delayed 类型的类或实现 java.util.concurrent.Delayed 接口的元素。DelayQueue在内部阻断元素,直到一定的延迟过期。DelayQueue实现了getDelay(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS)方法来返回剩余的延迟时间。传递给getDelay()方法的TimeUnit实例是一个枚举,它告诉我们应该以哪种时间单位返回延迟。TimeUnit枚举可以采取DAYS, HOURS, MINUTES, SECONDS, MILLISECONDS, MICROSECONDS, NANOSECONDS。这个队列不允许出现空元素。这个类和它的迭代器实现了 Collection 和 Iterator 接口的所有可选方法。方法iterator()中提供的迭代器不保证以任何特定的顺序遍历DelayQueue的元素。
// Declaration of Delayed interface
public interface Delayed extends Comparable<Delayed>
{
/**
* Returns the remaining delay associated with this object, in the
* given time unit.
*
* @param unit the time unit
*
* @return the remaining delay; zero or negative values indicate
* that the delay has already elapsed
*/
long getDelay(TimeUnit unit);
}
DelayQueue的层次结构
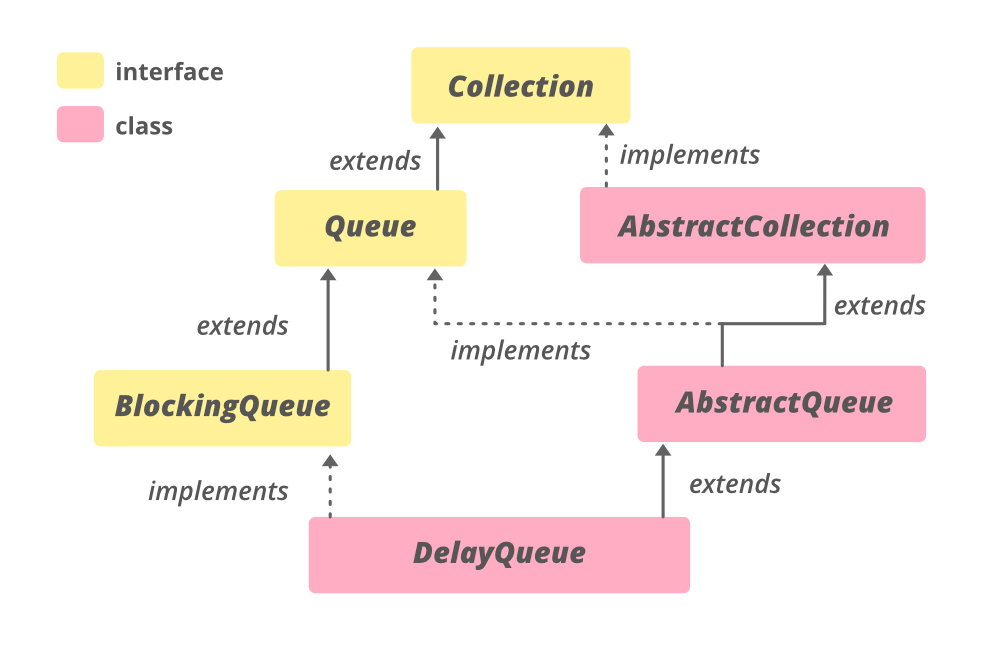
它实现了 **Iterable
类的声明
public class DelayQueue<E extends Delayed> extends AbstractQueue<E> implements BlockingQueue<E>
这里, E 是这个集合所维护的元素的类型。
DelayQueue的构造函数
为了构造一个DelayQueue,我们需要从 java.util.concurrent.DelayQueue 中导入它 。
1.DelayQueue() : 这个构造函数用来构造一个空的DelayQueue。
DelayQueue<E> dq = new DelayQueue<E>()
2.DelayQueue(Collection <E> c): 这个构造函数用来构造一个DelayQueue,其元素是作为参数传递的 Delayed 实例集合。
DelayQueue<E> dq = new DelayQueue(Collection<E> c)
下面是一个示例程序,说明Java中的DelayQueue:
// Java Program Demonstrate DelayQueue
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.*;
// The DelayObject for DelayQueue
// It must implement Delayed and
// its getDelay() and compareTo() method
class DelayObject implements Delayed {
private String name;
private long time;
// Constructor of DelayObject
public DelayObject(String name, long delayTime)
{
this.name = name;
this.time = System.currentTimeMillis()
+ delayTime;
}
// Implementing getDelay() method of Delayed
@Override
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit)
{
long diff = time - System.currentTimeMillis();
return unit.convert(diff, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
// Implementing compareTo() method of Delayed
@Override
public int compareTo(Delayed obj)
{
if (this.time < ((DelayObject)obj).time) {
return -1;
}
if (this.time > ((DelayObject)obj).time) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
// Implementing toString() method of Delayed
@Override
public String toString()
{
return "\n{"
+ "name=" + name
+ ", time=" + time
+ "}";
}
}
// Driver Class
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
throws InterruptedException
{
// create object of DelayQueue
// using DelayQueue() constructor
BlockingQueue<DelayObject> DQ
= new DelayQueue<DelayObject>();
// Add numbers to end of DelayQueue
DQ.add(new DelayObject("A", 1));
DQ.add(new DelayObject("B", 2));
DQ.add(new DelayObject("C", 3));
DQ.add(new DelayObject("D", 4));
// print DelayQueue
System.out.println("DelayQueue: "
+ DQ);
// create object of DelayQueue
// using DelayQueue(Collection c)
// constructor
BlockingQueue<DelayObject> DQ2
= new DelayQueue<DelayObject>(DQ);
// print DelayQueue
System.out.println("DelayQueue: "
+ DQ2);
}
}
输出
DelayQueue: [
{name=A, time=1543472836003},
{name=B, time=1543472836004},
{name=C, time=1543472836005},
{name=D, time=1543472836006}]
DelayQueue: [
{name=A, time=1543472836003},
{name=B, time=1543472836004},
{name=C, time=1543472836005},
{name=D, time=1543472836006}]
下面是一个示例程序,说明Java中的DelayQueue方法。
// Java Program Demonstrate DelayQueue methods
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.*;
// The DelayObject for DelayQueue
// It must implement Delayed and
// its getDelay() and compareTo() method
class DelayObject implements Delayed {
private String name;
private long time;
// Constructor of DelayObject
public DelayObject(String name, long delayTime)
{
this.name = name;
this.time = System.currentTimeMillis()
+ delayTime;
}
// Implementing getDelay() method of Delayed
@Override
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit)
{
long diff = time - System.currentTimeMillis();
return unit.convert(diff, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
// Implementing compareTo() method of Delayed
@Override
public int compareTo(Delayed obj)
{
if (this.time < ((DelayObject)obj).time) {
return -1;
}
if (this.time > ((DelayObject)obj).time) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
// Implementing toString()
// method of Delayed
@Override
public String toString()
{
return "\n{"
+ "name=" + name
+ ", time=" + time
+ "}";
}
}
// Driver Class
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
throws InterruptedException
{
// create object of DelayQueue
// using DelayQueue() constructor
BlockingQueue<DelayObject> DQ
= new DelayQueue<DelayObject>();
// Add numbers to end of DelayQueue
// using add() method
DQ.add(new DelayObject("A", 1));
DQ.add(new DelayObject("B", 2));
DQ.add(new DelayObject("C", 3));
DQ.add(new DelayObject("D", 4));
// print queue
System.out.println("DelayQueue: "
+ DQ);
// print the head using peek() method
System.out.println("Head of DelayQueue: "
+ DQ.peek());
// print the size using size() method
System.out.println("Size of DelayQueue: "
+ DQ.size());
// remove the head using poll() method
System.out.println("Head of DelayQueue: "
+ DQ.poll());
// print the size using size() method
System.out.println("Size of DelayQueue: "
+ DQ.size());
// clear the DelayQueue using clear() method
DQ.clear();
System.out.println("Size of DelayQueue"
+ " after clear: "
+ DQ.size());
}
}
输出
DelayQueue: [
{name=A, time=1543472845012},
{name=B, time=1543472845013},
{name=C, time=1543472845014},
{name=D, time=1543472845015}]
Head of DelayQueue:
{name=A, time=1543472845012}
Size of DelayQueue: 4
Head of DelayQueue:
{name=A, time=1543472845012}
Size of DelayQueue: 3
Size of DelayQueue after clear: 0
基本操作
1.添加元素
Java中DelayQueue类的add(E e)方法用于将给定的元素插入DelayQueue中,如果元素被成功插入,则返回true。
// Java program to illustrate the adding
// elements to the DelayQueue
import java.util.concurrent.DelayQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.Delayed;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class AddingElementsExample {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Create a DelayQueue instance
DelayQueue<Delayed> queue
= new DelayQueue<Delayed>();
// Create an instance of Delayed
Delayed obj = new Delayed() {
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit)
{
return 24; // some value is returned
}
public int compareTo(Delayed o)
{
if (o.getDelay(TimeUnit.DAYS)
> this.getDelay(TimeUnit.DAYS))
return 1;
else if (o.getDelay(TimeUnit.DAYS)
== this.getDelay(TimeUnit.DAYS))
return 0;
return -1;
}
};
// Use the add() method to add obj to
// the empty DelayQueue instance
queue.add(obj);
// printing size of the queue to the console
System.out.println("Size of the queue : "
+ queue.size());
}
}
输出
Size of the queue : 1
2.移除元素
Java中DelayQueue类的remove()方法是用来从这个DelayQueue中移除给定对象的单个实例说obj,如果它存在的话。如果给定的元素被成功移除,它将返回true,否则将返回false。
// Java Program to illustrate the removing
// elements of DelayQueue class
import java.util.concurrent.DelayQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.Delayed;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class RemovingElementsExample {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Create a DelayQueue instance
DelayQueue<Delayed> queue = new DelayQueue<Delayed>();
// Create an object of type Delayed
Delayed ob = new Delayed() {
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit)
{
return 24; // some value is returned
}
public int compareTo(Delayed o)
{
if (o.getDelay(TimeUnit.DAYS)
> this.getDelay(TimeUnit.DAYS))
return 1;
else if (o.getDelay(TimeUnit.DAYS)
== this.getDelay(TimeUnit.DAYS))
return 0;
return -1;
}
};
// Add the object to DelayQueue
queue.add(ob);
// Print initial size of Queue
System.out.println("Initial Size : " + queue.size());
// Remove the object ob from
// this DelayQueue
queue.remove(ob);
// Print the final size of the DelayQueue
System.out.println("Size after removing : " + queue.size());
}
}
输出
Initial Size : 1
Size after removing : 0
3.访问元素
DelayQueue的peek()方法用于检索DelayQueue的头部,但并不像poll()方法那样将头部从DelayQueue中移除。
// Java Program Demonstrate accessing
// elements of DelayQueue
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.*;
// The DelayObject for DelayQueue
// It must implement Delayed and
// its getDelay() and compareTo() method
class DelayObject implements Delayed {
private String name;
private long time;
// Constructor of DelayObject
public DelayObject(String name, long delayTime)
{
this.name = name;
this.time = System.currentTimeMillis() + delayTime;
}
// Implementing getDelay() method of Delayed
@Override public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit)
{
long diff = time - System.currentTimeMillis();
return unit.convert(diff, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
// Implementing compareTo() method of Delayed
@Override public int compareTo(Delayed obj)
{
if (this.time < ((DelayObject)obj).time) {
return -1;
}
if (this.time > ((DelayObject)obj).time) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
// Implementing toString() method of Delayed
@Override public String toString()
{
return "\n{"
+ " " + name + ", time=" + time + "}";
}
}
// Driver Class
public class AccessingElementsExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
throws InterruptedException
{
// create object of DelayQueue
// using DelayQueue() constructor
BlockingQueue<DelayObject> DQ = new DelayQueue<DelayObject>();
// Add numbers to end of DelayQueue
// using add() method
DQ.add(new DelayObject("A", 1));
DQ.add(new DelayObject("B", 2));
// Print delayqueue
System.out.println("Original DelayQueue: " + DQ + "\n");
// removing all elements
DQ.clear();
// peek() method for returning head of the
// DelayQueue
System.out.println("Head of the DelayQueue: " + DQ.peek());
}
}
输出
Original DelayQueue: [
{ A, time=1600770273132},
{ B, time=1600770273134}]
Head of the DelayQueue: null
4.遍历
DelayQueue的iterator()方法被用来返回DelayQueue中所有元素的迭代器。
// Java Program Demonstrate iterating
// over DelayQueue
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.*;
// The DelayObject for DelayQueue
// It must implement Delayed and
// its getDelay() and compareTo() method
class DelayObject implements Delayed {
private String name;
private long time;
// Constructor of DelayObject
public DelayObject(String name, long delayTime)
{
this.name = name;
this.time = System.currentTimeMillis() + delayTime;
}
// Implementing getDelay() method of Delayed
@Override public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit)
{
long diff = time - System.currentTimeMillis();
return unit.convert(diff, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
// Implementing compareTo() method of Delayed
@Override public int compareTo(Delayed obj)
{
if (this.time < ((DelayObject)obj).time) {
return -1;
}
if (this.time > ((DelayObject)obj).time) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
// Implementing toString() method of Delayed
@Override public String toString()
{
return "\n{"
+ " " + name + ", time=" + time + "}";
}
}
// Driver Class
public class IteratingExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
throws InterruptedException
{
// create object of DelayQueue
// using DelayQueue() constructor
BlockingQueue<DelayObject> DQ = new DelayQueue<DelayObject>();
// Add numbers to end of DelayQueue
// using add() method
DQ.add(new DelayObject("A", 1));
DQ.add(new DelayObject("B", 2));
DQ.add(new DelayObject("C", 3));
DQ.add(new DelayObject("D", 4));
// Creating an iterator
Iterator val = DQ.iterator();
// print the value after iterating DelayQueue
System.out.println("The iterator values are: ");
while (val.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(val.next());
}
}
}
输出
The iterator values are:
{ A, time=1600770415898}
{ B, time=1600770415900}
{ C, time=1600770415901}
{ D, time=1600770415902}
DelayQueue的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| add(E e) | 将指定的元素插入这个DelayQueue中。 |
| clear() | 原子化地删除这个DelayQueue中的所有元素。 |
| drainTo(Collection c) | 从这个队列中移除所有可用的元素,并将它们添加到给定的集合中。 drainTo(Collection c, int maxElements) | 从这个队列中最多移除给定数量的可用元素,并将它们添加到给定的集合中。 iterator() | 返回这个队列中所有元素(包括过期的和未过期的)的一个迭代器。 offer(E e) | 将指定的元素插入到这个DelayQueue中。 offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) | 将指定的元素插入到这个DelayQueue中。 peek() | 检索,但不删除这个队列的头部,如果这个队列是空的,则返回null。 poll() | 检索并删除这个队列的头部,如果这个队列没有过期延迟的元素,则返回null。 poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) | 检索并删除这个队列的头部,如果有必要的话,可以等待,直到这个队列上有过期延迟的元素,或者指定的等待时间结束。 put(E e) | 将指定的元素插入到这个DelayQueue中。 remainingCapacity() | 总是返回Integer.MAX_VALUE,因为DelayQueue没有容量限制。 remove(Object o) | 从这个队列中删除指定元素的一个实例,如果它存在的话,不管它是否已经过期。 take() | 检索并删除这个队列的头部,如果有必要的话,可以等待,直到这个队列上有一个过期的延迟的元素。 toArray() | 返回一个包含此队列中所有元素的数组。 toArray(T[] a) | 返回一个包含此队列中所有元素的数组;返回的数组的运行时类型是指定数组的类型。 ### java.util.AbstractQueue类中声明的方法 方法 | 描述 ### java.util.AbstractCollection类中声明的方法 方法 | 描述 |
如果这个集合包含了指定集合中的所有元素,则返回true。 |
| isEmpty() | 如果这个集合不包含任何元素,则返回true。 |
| removeAll(Collection c) | 删除这个集合中也包含在指定集合中的所有元素(可选操作)。 retainAll(Collection c) |
只保留本集合中包含在指定集合中的元素(可选操作)。 |
| toString() | 返回这个集合的一个字符串表示。 |
在接口java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue中声明的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| contains(Object o) | 如果这个队列包含指定的元素,返回true。 |
在接口java.util.Collection中声明的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| addAll(Collection c) | 将指定集合中的所有元素添加到这个集合中(可选操作)。 containsAll(Collection c) |
如果这个集合包含了指定集合中的所有元素,返回true。 |
| equals(Object o) | 将指定的对象与这个集合进行比较,看是否相等。 |
| 哈希代码() | 返回这个集合的哈希代码值。 |
| isEmpty() | 如果这个集合不包含任何元素,返回true。 |
| parallelStream() | 返回一个以该集合为源的可能的并行流。 |
| removeAll(Collection c) | 删除这个集合的所有元素,这些元素也包含在指定的集合中(可选操作)。 removeIf(Predicate filter) | 删除此集合中满足给定谓词的所有元素。 retainAll(Collection c) |
只保留此集合中包含在指定集合中的元素(可选操作)。 |
| size() | 返回这个集合中元素的数量。 |
| spliterator() | 在这个集合中的元素上创建一个Spliterator。 |
| stream() | 返回一个以这个集合为源的顺序流。 |
| toArray(IntFunction<T[]> generator) | 返回一个包含此集合中所有元素的数组,使用提供的生成器函数来分配返回的数组。 |
java.lang.Iterable接口中声明的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| forEach(Consumer<? super T> action) | 对Iterable中的每个元素执行给定的操作,直到所有的元素都被处理完,或者该操作抛出一个异常。 |
接口java.util.Queue中声明的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 元素() | 检索,但不删除该队列的头部。 |
| remove() | 检索并删除该队列的头部。 |
参考 :https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/javase/11/docs/api/java.base/java/util/concurrent/DelayQueue.html
 极客教程
极客教程