Java ConcurrentHashMap
ConcurrentHashMap 类是在JDK 1.5中引入的,属于 java.util.concurrent 包,它实现了ConcurrentMap,也实现了Serializable接口。ConcurrentHashMap是对HashMap的增强,因为我们知道在我们的应用程序中处理线程时,HashMap不是一个好的选择,因为从性能上来说,HashMap是不合格的。
ConcurrentHashMap的关键点
- ConcurrentHashMap的下划线数据结构是Hashtable。
- ConcurrentHashMap类是线程安全的,即多个线程可以对一个对象进行操作而不会产生任何问题。
- 在同一时间,任何数量的线程都可以进行读操作,而不需要锁定ConcurrentHashMap对象,这在HashMap中是不存在的。
- 在ConcurrentHashMap中,对象根据并发级别被划分为若干段。
- ConcurrentHashMap的默认并发级别是16。
- 在ConcurrentHashMap中,任何数量的线程都可以在同一时间进行检索操作,但是为了更新对象,线程必须锁定该线程想要操作的特定段。这种类型的锁定机制被称为 段锁定或桶锁定。 因此,在同一时间,线程可以进行16次更新操作。
- 在ConcurrentHashMap中不可能插入空对象作为键或值。
声明
public class ConcurrentHashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements ConcurrentMap<K,V>, Serializable
这里, K 是键的对象类型, V 是值的对象类型。
ConcurrentHashMap的层次结构
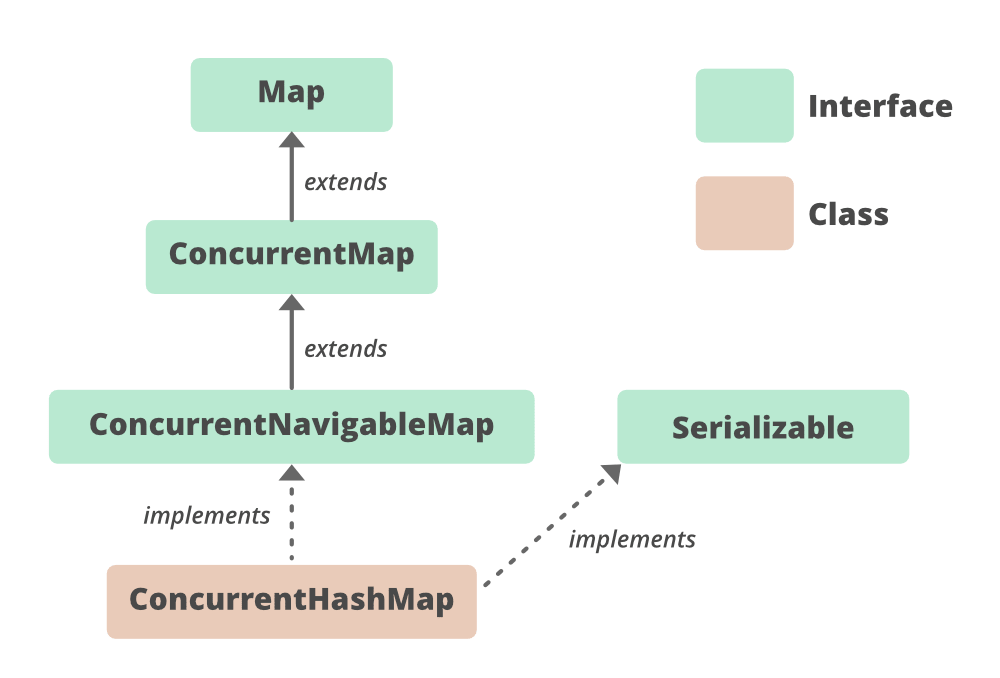
它实现了 Serializable 、ConcurrentMap<K, V>、Map<K, V>接口并扩展了 **AbstractMap <K, V> **类。
ConcurrentHashMap的构造函数
- Concurrency-Level: 它是并发更新Map的线程数。实现会执行内部大小,以尝试容纳这么多线程。
- Load-Factor: 这是一个阈值,用于控制大小的调整。
- 初始容量: 最初由实现提供的一定数量元素的容纳量。如果这个Map的容量是10。这意味着它可以存储10个条目。
1.ConcurrentHashMap() : 创建一个新的、空的Map,具有默认的初始容量(16)、负载系数(0.75)和并发级别(16)。
ConcurrentHashMap<K, V> chm = new ConcurrentHashMap<>()
2.ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity) : 用指定的初始容量创建一个新的空Map,并使用默认的负载因子(0.75)和并发级别(16)。
ConcurrentHashMap<K, V> chm = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(int initialCapacity)
3.ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) : 创建一个新的、空的Map,具有指定的初始容量和负载因子,并具有默认的并发级别(16)。
ConcurrentHashMap<K, V> chm = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor)
4.ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) : 以指定的初始容量、负载因子和并发级别创建一个新的、空的Map。
ConcurrentHashMap<K, V> chm = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel)
5.ConcurrentHashMap(Map m) : 创建一个新的Map,其映射关系与给定的Map相同。
ConcurrentHashMap<K, V> chm = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(Map m)
例子
// Java program to demonstrate working of ConcurrentHashMap
import java.util.concurrent.*;
class ConcurrentHashMapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// create an instance of
// ConcurrentHashMap
ConcurrentHashMap<Integer, String> m
= new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// Insert mappings using
// put method
m.put(100, "Hello");
m.put(101, "Geeks");
m.put(102, "Geeks");
// Here we cant add Hello because 101 key
// is already present in ConcurrentHashMap object
m.putIfAbsent(101, "Hello");
// We can remove entry because 101 key
// is associated with For value
m.remove(101, "Geeks");
// Now we can add Hello
m.putIfAbsent(103, "Hello");
// We cant replace Hello with For
m.replace(101, "Hello", "For");
System.out.println(m);
}
}
输出
{100=Hello, 102=Geeks, 103=Hello}
对ConcurrentHashMap的基本操作
1.添加元素
要向ConcurrentHashMap插入映射,我们可以使用put()或putAll()方法。下面的示例代码解释了这两个方法。
// Java program to demonstrate adding
// elements to the ConcurrentHashMap
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
public class AddingElementsToConcuurentHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating ConcurrentHashMap
ConcurrentHashMap<String, String> my_cmmap
= new ConcurrentHashMap<String, String>();
// Adding elements to the map
// using put() method
my_cmmap.put("1", "1");
my_cmmap.put("2", "1");
my_cmmap.put("3", "1");
my_cmmap.put("4", "1");
my_cmmap.put("5", "1");
my_cmmap.put("6", "1");
// Printing the map
System.out.println("Mappings of my_cmmap : "
+ my_cmmap);
// create another concurrentHashMap
ConcurrentHashMap<String, String> new_chm
= new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// copy mappings from my_cmmap to new_chm
new_chm.putAll(my_cmmap);
// Displaying the new map
System.out.println("New mappings are: " + new_chm);
}
}
输出
Mappings of my_cmmap : {1=1, 2=1, 3=1, 4=1, 5=1, 6=1}
New mappings are: {1=1, 2=1, 3=1, 4=1, 5=1, 6=1}
2.移除元素
要删除一个映射,我们可以使用ConcurrentHashmap类的remove(Object key)方法。如果键在映射中不存在,那么这个函数就没有任何作用。要清除整个映射,我们可以使用clear()方法。
// Java program to demonstrate removing
// elements from ConcurrentHashMap
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
public class RemoveElementsFromConcurrentHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating ConcurrentHashMap
Map<String, String> my_cmmap
= new ConcurrentHashMap<String, String>();
// Adding elements to the map
// using put() method
my_cmmap.put("1", "1");
my_cmmap.put("2", "1");
my_cmmap.put("3", "1");
my_cmmap.put("4", "1");
my_cmmap.put("5", "1");
my_cmmap.put("6", "1");
// Printing the map
System.out.println("Map: " + my_cmmap);
System.out.println();
// Removing the mapping
// with existing key 6
// using remove() method
String valueRemoved = my_cmmap.remove("6");
// Printing the map after remove()
System.out.println(
"After removing mapping with key 6:");
System.out.println("Map: " + my_cmmap);
System.out.println("Value removed: "
+ valueRemoved);
System.out.println();
// Removing the mapping
// with non-existing key 10
// using remove() method
valueRemoved = my_cmmap.remove("10");
// Printing the map after remove()
System.out.println(
"After removing mapping with key 10:");
System.out.println("Map: " + my_cmmap);
System.out.println("Value removed: "
+ valueRemoved);
System.out.println();
// Now clear the map using clear()
my_cmmap.clear();
// Print the clea Map
System.out.println("Map after use of clear(): "
+ my_cmmap);
}
}
输出
Map: {1=1, 2=1, 3=1, 4=1, 5=1, 6=1}
After removing mapping with key 6:
Map: {1=1, 2=1, 3=1, 4=1, 5=1}
Value removed: 1
After removing mapping with key 10:
Map: {1=1, 2=1, 3=1, 4=1, 5=1}
Value removed: null
Map after use of clear(): {}
3.访问元素
我们可以使用get()方法访问ConcurrentHashMap的元素,下面给出了这个例子。
// Java Program Demonstrate accessing
// elements of ConcurrentHashMap
import java.util.concurrent.*;
class AccessingElementsOfConcurrentHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// create an instance of ConcurrentHashMap
ConcurrentHashMap<Integer, String> chm
= new ConcurrentHashMap<Integer, String>();
// insert mappings using put method
chm.put(100, "Geeks");
chm.put(101, "for");
chm.put(102, "Geeks");
chm.put(103, "Contribute");
// Displaying the HashMap
System.out.println("The Mappings are: ");
System.out.println(chm);
// Display the value of 100
System.out.println("The Value associated to "
+ "100 is : " + chm.get(100));
// Getting the value of 103
System.out.println("The Value associated to "
+ "103 is : " + chm.get(103));
}
}
输出
The Mappings are:
{100=Geeks, 101=for, 102=Geeks, 103=Contribute}
The Value associated to 100 is : Geeks
The Value associated to 103 is : Contribute
4.遍历
我们可以使用Iterator接口来遍历集合框架的任何结构。由于迭代器只处理一种类型的数据,我们使用Entry< ?, ? >来将两种不同的类型解析成一种兼容的格式。然后使用 next() 方法打印 ConcurrentHashMap 的元素。
// Java Program for traversing a
// ConcurrentHashMap
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class TraversingConcurrentHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// create an instance of ConcurrentHashMap
ConcurrentHashMap<Integer, String> chmap
= new ConcurrentHashMap<Integer, String>();
// Add elements using put()
chmap.put(8, "Third");
chmap.put(6, "Second");
chmap.put(3, "First");
chmap.put(11, "Fourth");
// Create an Iterator over the
// ConcurrentHashMap
Iterator<ConcurrentHashMap.Entry<Integer, String> >
itr = chmap.entrySet().iterator();
// The hasNext() method is used to check if there is
// a next element The next() method is used to
// retrieve the next element
while (itr.hasNext()) {
ConcurrentHashMap.Entry<Integer, String> entry
= itr.next();
System.out.println("Key = " + entry.getKey()
+ ", Value = "
+ entry.getValue());
}
}
}
输出
Key = 3, Value = First
Key = 6, Value = Second
Key = 8, Value = Third
Key = 11, Value = Fourth
ConcurrentHashMap的方法
- K – Map上的键的类型。
- V – 在Map中映射的值的类型。
java.util.AbstractMap类中声明的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| clone() | 返回这个AbstractMap实例的一个浅层拷贝:键和值本身没有被克隆。 |
| isEmpty() | 如果该Map不包含键值映射,则返回true。 |
| size() | 返回该Map中键值映射的数量。 |
java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentMap接口中声明的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
forEach(BiConsumer<? super K,? super V> action) |
对该Map中的每个条目执行给定的操作,直到所有条目都被处理完或该操作抛出一个异常。 |
replaceAll(BiFunction<? super K,? super V,? extends V> function) |
用对该条目调用给定函数的结果替换每个条目的值,直到所有条目都被处理完或该函数抛出一个异常。 |
必读: HashMap和ConcurrentHashMap的区别
并发哈希图与哈希表
HashTable
- Hashtable 是Map数据结构的一个实现。
- 这是一个传统的类,其中所有的方法都使用synchronized关键字对Hashtable实例进行同步。
- 由于它的方法是同步的,所以是线程安全的。
并发哈希图(ConcurrentHashMap
- ConcurrentHashMap 实现了Map数据结构,也像Hashtable一样提供了线程安全。
- 它的工作原理是将完整的Hashtable数组划分为片段或部分,并允许对这些片段进行并行访问。
- 锁定是在哈希图桶级别的更精细的粒度。
- 当你的应用程序需要非常高的并发性时,使用 ConcurrentHashMap 。
- 它是一个线程安全的,无需同步整个Map。
- 读取可以发生得非常快,而写入则是在段级或桶级的锁下完成。
- 在对象层面上没有锁。
- 如果一个线程试图修改它,而另一个线程正在迭代它,ConcurrentHashMap不会抛出一个 ConcurrentModificationException 。
- ConcurrentHashMap不允许NULL值,所以在 ConcurrentHashMap 中键不能为空。
- 如果一个线程试图修改 ConcurrentHashMap ,而另一个线程正在迭代它,那么ConcurrentHashMap就不会抛出 ConcurrentModificationException 。
总结
如果需要一个线程安全的高并发实现,那么建议使用 ConcurrentHashMap 来代替 Hashtable 。
参考资料 :https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/javase/11/docs/api/java.base/java/util/concurrent/ConcurrentHashMap.html
 极客教程
极客教程