Java ArrayBlockingQueue类
ArrayBlockingQueue 类是一个由数组支持的有界阻塞队列。所谓有界,是指队列的大小是固定的。一旦创建,其容量就不能改变。试图将一个元素放入一个满的队列将导致操作被阻塞。同样,试图从一个空队列中取出一个元素也会被阻塞。ArrayBlockingQueue的边界可以在ArrayBlockingQueue的构造函数中绕过容量作为参数来实现。这个队列对元素进行 FIFO(先进先出) 排序 。 这意味着这个队列的头部是这个队列中存在的元素中最古老的元素。
这个队列的尾部是这个队列的元素中最新的元素。新插入的元素总是插在队列的尾部,而队列的检索操作则在队列的头部获得元素。
这个类和它的迭代器实现了 Collection 和 Iterator 接口的所有可选方法。该类是Java集合框架的一个成员。
ArrayBlockingQueue的层次结构
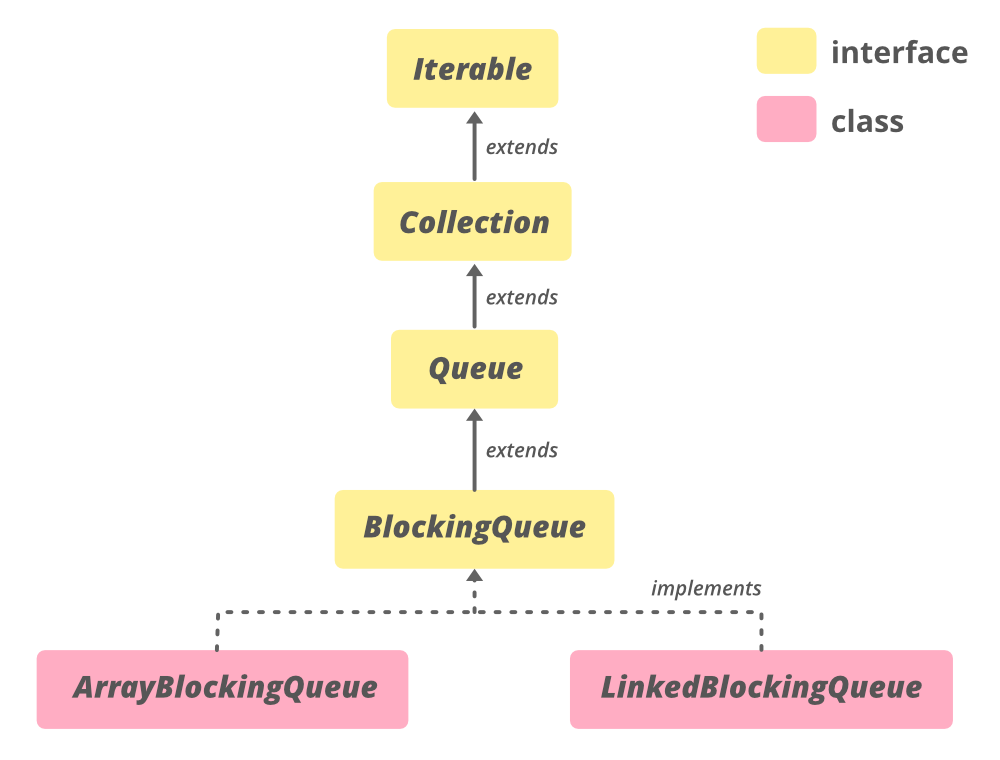
该类扩展了AbstractQueue
声明
public class ArrayBlockingQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E> implements BlockingQueue<E>, Serializable
这里, E 是存储在集合中的元素的类型。
ArrayBlockingQueue的构造函数
这里, 容量 是 **** 阵列阻塞队列的大小。
1.ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity): 创建一个具有给定(固定)容量和默认访问策略的ArrayBlockingQueue。
ArrayBlockingQueue<E> abq = new ArrayBlockingQueue<E>(int capacity)
2.ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair): 创建一个具有给定(固定)容量和指定访问策略的ArrayBlockingQueue。如果fair值为true,那么在插入或移除时被阻塞的线程的队列访问将按FIFO顺序处理;如果false,访问顺序未被指定。
ArrayBlockingQueue<E> abq = new ArrayBlockingQueue<E>(int capacity, boolean fair)
3.ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair, Collection c): 创建一个ArrayBlockingQueue,具有给定(固定)的容量和指定的访问策略,最初包含给定集合的元素,按照集合的迭代器的遍历顺序添加。如果公平值为true,那么插入或移除时被阻塞的线程的队列访问将以FIFO顺序处理;如果为false,访问顺序未被指定。
ArrayBlockingQueue<E> abq = new ArrayBlockingQueue<E>(int capacity, boolean fair, Collection c)
例子
// Java program to demonstrate
// ArrayBlockingQueue(int initialCapacity)
// constructor
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
public class ArrayBlockingQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// define capacity of ArrayBlockingQueue
int capacity = 15;
// create object of ArrayBlockingQueue
// using ArrayBlockingQueue(int initialCapacity) constructor
ArrayBlockingQueue<Integer> abq = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Integer>(capacity);
// add numbers
abq.add(1);
abq.add(2);
abq.add(3);
// print queue
System.out.println("ArrayBlockingQueue:" + abq);
}
}
输出
ArrayBlockingQueue:[1, 2, 3]
基本操作
1.添加元素
add(E e)方法在这个队列的尾部插入作为参数传递给该方法的元素。如果添加的元素超过了队列的容量,那么这个方法将抛出一个 IllegalStateException。 如果添加元素成功,该方法返回true,否则将抛出一个IllegalStateException。
// Java Program to Demonstrate adding
// elements to an ArrayBlockingQueue.
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
public class AddingElementsExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// define capacity of ArrayBlockingQueue
int capacity = 15;
// create object of ArrayBlockingQueue
ArrayBlockingQueue<Integer> abq = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Integer>(capacity);
// add numbers
abq.add(1);
abq.add(2);
abq.add(3);
// print queue
System.out.println("ArrayBlockingQueue:" + abq);
}
}
输出
ArrayBlockingQueue:[1, 2, 3]
2.移除元素
remove(Object o)方法从这个队列中移除指定元素的一个实例,如果它存在的话。我们可以说,如果这个队列包含一个或多个这样的元素,那么该方法就会移除一个元素e,即o.e equals(e)。如果这个队列包含我们想要移除的指定元素,Remove()方法返回真。
// Java program to demonstrate removal of
// elements from an AbstractQueue
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
public class RemovingElementsExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// define capacity of ArrayBlockingQueue
int capacity = 15;
// create object of ArrayBlockingQueue
ArrayBlockingQueue<Integer> abq = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Integer>(capacity);
// add numbers
abq.add(1);
abq.add(2);
abq.add(3);
// print queue
System.out.println("ArrayBlockingQueue:" + abq);
// remove 223
boolean response = abq.remove(2);
// print Queue
System.out.println("Removal of 2 :" + response);
// print Queue
System.out.println("queue contains " + abq);
// remove all the elements
abq.clear();
// print queue
System.out.println("ArrayBlockingQueue:" + abq);
}
}
输出
ArrayBlockingQueue:[1, 2, 3]
Removal of 2 :true
queue contains [1, 3]
ArrayBlockingQueue:[]
3.访问元素
Queue 接口提供的peek()方法被用来返回队列的头部。它检索但不删除,这个队列的头部。如果队列是空的,那么这个方法返回null。
// Java program to demonstrate accessing
// elements of ArrayBlockingQueue
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
public class AccessingElementsExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Define capacity of ArrayBlockingQueue
int capacity = 5;
// Create object of ArrayBlockingQueue
ArrayBlockingQueue<Integer> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Integer>(capacity);
// Add element to ArrayBlockingQueue
queue.add(23);
queue.add(32);
queue.add(45);
queue.add(12);
// Print queue after adding numbers
System.out.println("After adding numbers queue is ");
System.out.println(queue);
// Print head of queue using peek() method
System.out.println("Head of queue " + queue.peek());
}
}
输出
After adding numbers queue is
[23, 32, 45, 12]
Head of queue 23
4.遍历
ArrayBlockingQueue 类的iterator()方法是用来返回一个与该队列相同的元素的迭代器,并以适当的顺序排列。从这个方法返回的元素包含了从第一个(head)到最后一个(tail)的顺序。返回的迭代器是弱一致性的。
// Java Program to Demonstrate iterating
// over ArrayBlockingQueue.
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.*;
public class TraversingExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Define capacity of ArrayBlockingQueue
int capacity = 5;
// Create object of ArrayBlockingQueue
ArrayBlockingQueue<String> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<String>(capacity);
// Add 5 elements to ArrayBlockingQueue
queue.offer("User");
queue.offer("Employee");
queue.offer("Manager");
queue.offer("Analyst");
queue.offer("HR");
// Print queue
System.out.println("Queue is " + queue);
// Call iterator() method and Create an iterator
Iterator iteratorValues = queue.iterator();
// Print elements of iterator
System.out.println("\nThe iterator values:");
while (iteratorValues.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iteratorValues.next());
}
}
}
输出
Queue is [User, Employee, Manager, Analyst, HR]
The iterator values:
User
Employee
Manager
Analyst
HR
ArrayBlockingQueue的方法
这里, E 是这个集合中持有的元素的类型
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| add(E e) | 如果有可能在不超过队列容量的情况下立即插入指定的元素在这个队列的尾部,成功后返回true,如果这个队列已满,则抛出IllegalStateException。 |
| 清除() | 原子化地删除这个队列中的所有元素。 |
| contains(Object o) | 如果这个队列包含指定的元素,返回真。 |
| drainTo(Collection c) | 从这个队列中移除所有可用的元素,并将它们添加到给定的集合中。 drainTo(Collection c, int maxElements) | 从这个队列中最多移除给定数量的可用元素,并将它们添加到给定的集合中。 forEach(Consumer action) | 对Iterable的每个元素执行给定的动作,直到所有的元素都被处理完,或者该动作抛出一个异常。 iterator() | 按照适当的顺序返回这个队列中的元素的迭代器。 offer(E e) | 如果有可能在不超过队列容量的情况下立即插入指定的元素到这个队列的尾部,成功后返回 true,如果这个队列已满则返回 false。 offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) | 在这个队列的尾部插入指定的元素,如果队列已满,最多等待指定的等待时间来获得空间。 put(E e) | 在这个队列的尾部插入指定的元素,如果队列已满,则等待空间的出现。 remainingCapacity() | 返回这个队列在理想情况下(在没有内存或资源限制的情况下)可以接受的额外元素的数量,而不会出现阻塞。 remove(Object o) | 从这个队列中删除指定元素的一个实例,如果它存在的话。 removeAll(Collection c) |
删除此集合中也包含在指定集合中的所有元素(可选操作)。 |
| removeIf(Predicate filter) | 删除此集合中满足给定谓词的所有元素。 retainAll(Collection c) |
只保留此集合中包含在指定集合中的元素(可选操作)。 |
| size() | 返回这个队列中元素的数量。 |
| spliterator() | 返回这个队列中的元素的Spliterator。 |
| toArray() | 返回一个包含该队列中所有元素的数组,并以适当的顺序排列。 |
| toArray(T[] a) | 返回一个包含队列中所有元素的数组,并以适当的顺序排列;返回的数组的运行时类型是指定数组的类型。 |
java.util.AbstractQueue类中声明的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| addAll(Collection c) | 将指定集合中的所有元素添加到这个队列中。 element() | 检索,但不删除这个队列的头部。 remove() | 检索并删除此队列的头部。 ### java.util.AbstractCollection类中声明的方法 方法 | 描述 |
如果这个集合包含了指定集合中的所有元素,返回true。 |
| isEmpty() | 如果这个集合不包含任何元素,则返回true。 |
| toString() | 返回这个集合的一个字符串表示。 |
在接口java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue中声明的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) | 检索并删除这个队列的头部,如果有必要,可以等待指定的等待时间,让元素变得可用。 |
| take() | 检索并移除这个队列的头部,如果需要的话,等待一个元素变得可用。 |
java.util.Collection接口中声明的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| addAll(Collection c) | 将指定集合中的所有元素添加到这个集合中(可选操作)。 containsAll(Collection c) |
如果这个集合包含了指定集合中的所有元素,返回true。 |
| equals(Object o) | 将指定的对象与这个集合进行比较,看是否相等。 |
| 哈希代码() | 返回这个集合的哈希代码值。 |
| isEmpty() | 如果这个集合不包含任何元素,返回true。 |
| parallelStream() | 返回一个以该集合为源的可能的并行流。 |
| stream() | 返回一个以这个集合为源的顺序流。 |
| toArray(IntFunction<T[]> generator) | 返回一个包含此集合中所有元素的数组,使用提供的生成器函数来分配返回的数组。 |
java.util.Queue中声明的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 元素() | 检索,但不删除这个队列的头部。 |
| peek() | 检索但不删除此队列的头部,如果此队列为空,则返回null。 |
| poll() | 检索并删除这个队列的头部,如果这个队列是空的,则返回null。 |
| remove() | 检索并删除这个队列的头部。 |
结论: ArrayBlockingQueue 通常用于 线程安全的 环境中,你想在一个资源上阻塞两个或更多的操作,只允许一个线程。同时,我们可以使用容量约束因子来阻塞一个线程。
参考资料: https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/javase/11/docs/api/java.base/java/util/concurrent/ArrayBlockingQueue.html
 极客教程
极客教程