Java AbstractSequentialList与实例
Java中的 AbstractSequentialList 类是Java集合框架的一部分,实现了 集合接口 和 AbstractCollection类。 它被用来实现一个不可修改的列表,为此人们只需要扩展这个AbstractList类,并只实现get()和size()方法。
这个类提供了一个List接口的骨架实现,以最大限度地减少实现这个接口所需的努力,该接口由一个 “顺序访问 “数据存储(如一个链接列表)支持。对于随机访问的数据(如数组),应该优先使用AbstractList而不是这个类。
类的层次结构
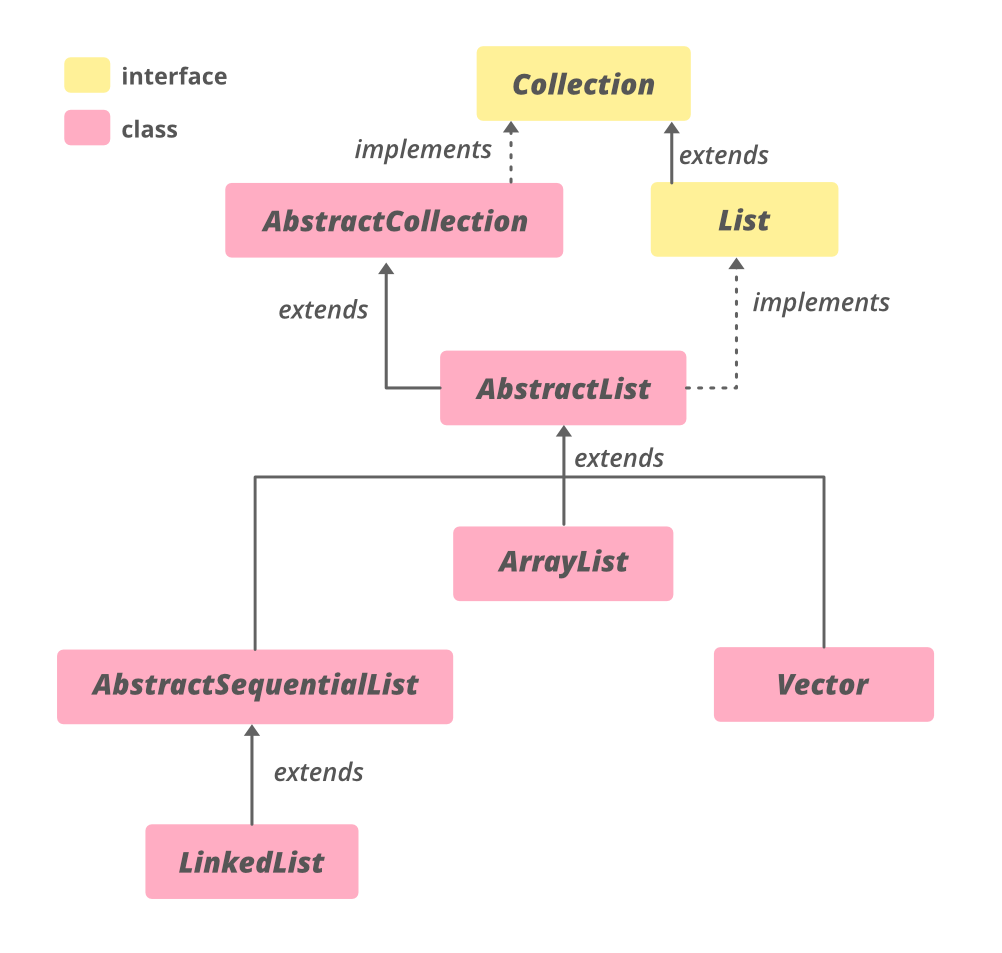
声明 。
public abstract class AbstractSequentialList<E>
extends AbstractList<E>
其中E是该清单所维护的元素类型。
它实现了Iterable <E>, Collection <E> , List<E>接口。LinkedList是AbstractSequentialList的唯一直接子类。
构造函数: protected AbstractSequentialList() 默认的构造函数,但是由于被保护,它不允许创建一个AbstractSequentialList对象。
AbstractSequentialList<E> asl = new LinkedList<E>()
例子1: AbstractSequentialList是一个抽象类,所以应该给它分配一个子类的实例,比如LinkedList .
// Java code to illustrate AbstractSequentialList
import java.util.*;
public class GfG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an instance of
// the AbstractSequentialList
AbstractSequentialList<Integer> absl
= new LinkedList<>();
// adding elements to absl
absl.add(5);
absl.add(6);
absl.add(7);
// Printing the list
System.out.println(absl);
}
}
输出
[5, 6, 7]
例2:
// Java code to illustrate
// methods of AbstractSequentialList
import java.util.*;
import java.util.AbstractSequentialList;
public class AbstractSequentialListDemo {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating an empty AbstractSequentialList
AbstractSequentialList<String>
absqlist = new LinkedList<String>();
// Using add() method to
// add elements in the list
absqlist.add("Geeks");
absqlist.add("for");
absqlist.add("Geeks");
absqlist.add("10");
absqlist.add("20");
// Output the list
System.out.println("AbstractSequentialList: "
+ absqlist);
// Remove the head using remove()
absqlist.remove(3);
// Print the final list
System.out.println("Final List: "
+ absqlist);
// Fetching the specific
// element from the list
// using get() method
System.out.println("The element is: "
+ absqlist.get(2));
}
}
输出
AbstractSequentialList: [Geeks, for, Geeks, 10, 20]
Final List: [Geeks, for, Geeks, 20]
The element is: Geeks
AbstractSequentialList的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| add(int index, E element) | 在这个列表的指定位置上插入指定的元素(可选操作)。 |
| addAll(int index, Collection c) | 将指定集合中的所有元素插入到这个列表的指定位置(可选操作)。 get(int index) | 返回这个列表中指定位置上的元素。 iterator() | 返回这个列表中的元素的迭代器(按适当的顺序)。 listIterator(int index) | 返回这个列表中的元素的迭代器(按适当的顺序)。 remove(int index) | 移除这个列表中指定位置的元素(可选操作)。 set(int index, E element) | 用指定的元素替换这个列表中指定位置的元素(可选操作)。 ### 从java.util.AbstractList类继承的方法 方法 | 描述 ### 从java.util.AbstractCollection类继承的方法 方法 | 描述 |
如果这个集合包含了指定集合中的所有元素,返回真。 |
| isEmpty() | 如果这个集合不包含任何元素,则返回真。 |
| remove(Object o) | 从这个集合中删除指定元素的一个实例,如果它存在的话(可选操作)。 |
| removeAll(Collection c) | 移除这个集合中所有也包含在指定集合中的元素(可选操作)。 retainAll(Collection c) |
只保留本集合中包含在指定集合中的元素(可选操作)。 |
| toArray() | 返回一个包含此集合中所有元素的数组。 |
| toArray(T[] a) | 返回一个包含此集合中所有元素的数组;返回的数组的运行时类型是指定数组的类型。 |
| toString() | 返回这个集合的字符串表示。 |
从java.util.Collection接口继承的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| parallelStream() | 返回一个以该集合为源的可能的并行流。 |
| removeIf(Predicate filter) | 删除这个集合中满足给定谓词的所有元素。 stream() | 返回一个以这个集合为源的顺序流。 toArray(IntFunction ### 从 java.lang.Iterable 接口继承的方法 方法 | 描述 ### 从 java.util.List 接口继承的方法 方法 | 描述 |
如果这个列表包含指定集合的所有元素,返回 true。 |
| isEmpty() | 如果这个列表不包含任何元素,则返回 true。 |
| remove(Object o) | 如果指定的元素存在,从这个列表中移除它的第一次出现(可选操作)。 |
| removeAll(Collection c) | 从这个列表中移除所有包含在指定集合中的元素(可选操作)。 replaceAll(UnaryOperator retainAll(Collection c) |
只保留这个列表中包含在指定集合中的元素(可选操作)。 |
| size() | 返回这个列表中元素的数量。 |
| sort(Comparator<? super E> c) | 根据指定的比较器引起的顺序对这个列表进行排序。 |
| spliterator() | 在这个列表中的元素上创建一个Spliterator。 |
| toArray() | 返回一个包含这个列表中所有元素的数组,并以适当的顺序(从第一个元素到最后一个元素)。 |
| toArray(T[] a) | 返回一个包含列表中所有元素的数组(从第一个元素到最后一个元素);返回的数组的运行时类型是指定数组的类型。 |
参考资料 : https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/javase/11/docs/api/java.base/java/util/AbstractSequentialList.html
 极客教程
极客教程