Java AbstractQueue与实例
Java中的 AbstractQueue 类是Java Collection框架的一部分,实现了 Collection 接口和AbstractCollection类。它提供了一些 队列 操作的骨架式实现。当基础实现不允许空元素时,这个类中的实现是合适的。方法add、remove和element分别基于offer、poll和peek,但抛出异常,而不是通过false或null返回表示失败。
类的层次结构
java.lang.Object
↳ java.util.AbstractCollection<E>
↳ Class AbstractQueue<E>
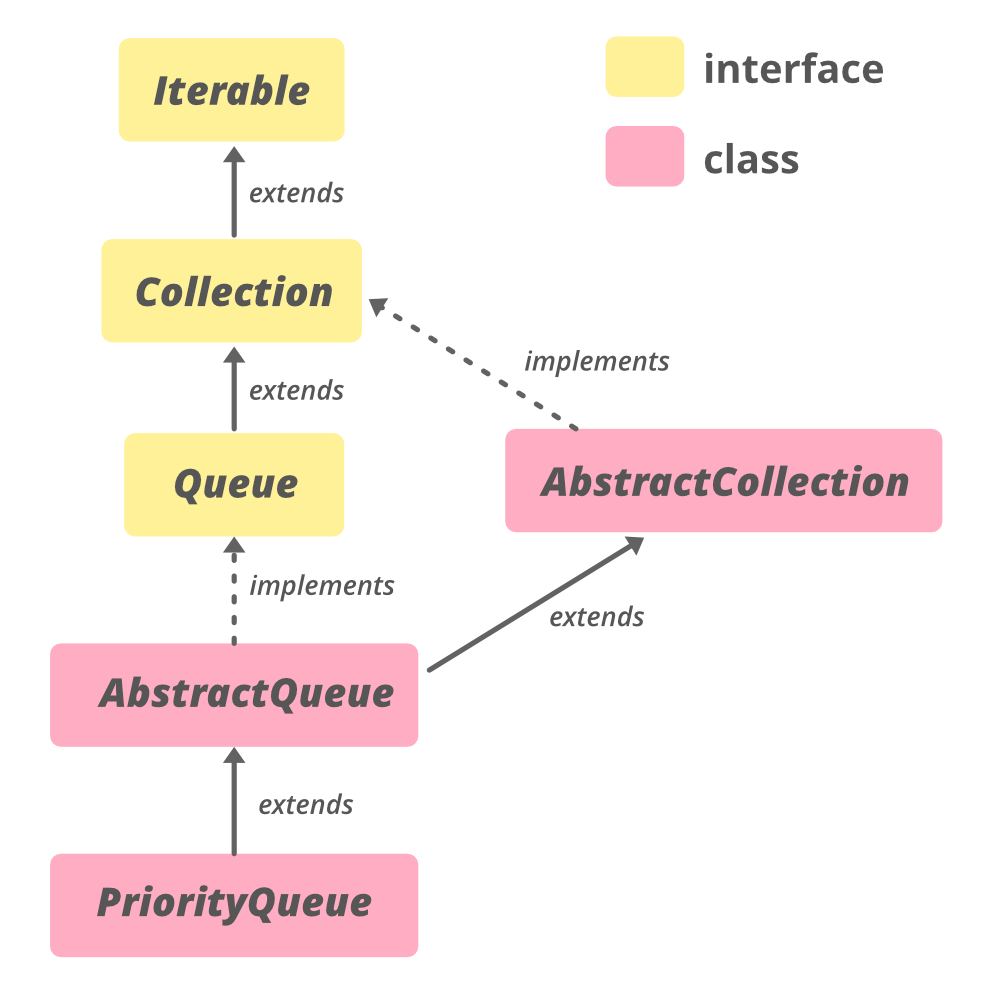
该类实现了 **Iterable
声明
public abstract class AbstractQueue<E> extends AbstractCollection<E> implements Queue<E>
E – 由集合框架类或接口维护的元素类型。
Java中的构造函数 AbstractQueue
由于AbstractQueue是一个抽象类,它的实现是由其子类提供的。下面是可以提供实现的类的列表。要创建它,我们需要从 java.util.AbstractQueue 中获取 。
protected AbstractQueue() : 默认构造函数,但由于是抽象的,它不允许创建一个AbstractQueue对象。实现应该由它的一个子类提供,比如ArrayBlockingQueue、ConcurrentLinkedQueue、DelayQueue、LinkedBlockingDeque、LinkedBlockingQueue、LinkedTransferQueue、PriorityBlockingQueue、PriorityQueue、 SynchronousQueue。
AbstractQueue<E> objName = new ArrayBlockingQueue<E>();
下面是一个说明Java中AbstractQueue的示例程序:
// Java code to illustrate AbstractQueue
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
public class AbstractQueueExample {
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception
{
// Creating object of AbstractQueue<Integer>
AbstractQueue<Integer> AQ = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Integer>();
// Adding elements to the Queue
AQ.add(10);
AQ.add(20);
AQ.add(30);
AQ.add(40);
AQ.add(50);
// print the queue contents to the console
System.out.println("AbstractQueue contains: " + AQ);
}
}
输出
AbstractQueue contains: [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
基本操作
1.添加元素
为了向AbstractQueue添加元素,它提供了两个方法。add(E e)方法将指定的元素插入这个队列,如果有可能立即这样做而不违反容量限制的话。它在成功后返回真,如果当前没有可用空间,则抛出一个 IllegalStateException 。addAll(E e)方法将指定集合中的所有元素添加到这个队列中。
// Java program to illustrate the
// adding elements to the AbstractQueue
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
public class AddingElementsExample {
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception
{
// Since AbstractQueue is an abstract class
// create object using LinkedBlockingQueue
AbstractQueue<Integer> AQ1 = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Integer>();
// Populating AQ
AQ1.add(10);
AQ1.add(20);
AQ1.add(30);
AQ1.add(40);
AQ1.add(50);
// print AQ
System.out.println("AbstractQueue contains : "
+ AQ1);
// Since AbstractQueue is an abstract class
// create object using LinkedBlockingQueue
AbstractQueue<Integer> AQ2 = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Integer>();
// print AQ2 initially
System.out.println("AbstractQueue2 initially contains : " + AQ2);
// adds elements of AQ1 in AQ2
AQ2.addAll(AQ1);
System.out.println( "AbstractQueue1 after addition contains : " + AQ2);
}
}
输出
AbstractQueue contains : [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
AbstractQueue2 initially contains : []
AbstractQueue1 after addition contains : [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
2.移除元素
为了从AbstractQueue中删除元素,它提供了remove()和clear()方法。
- remove()方法返回并删除该队列的头部。
- clear()方法从这个队列中删除所有的元素。这个调用返回后,队列将是空的。
// Java program to illustrate the
// removal of elements from AbstractQueue
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
public class RemovingElementsExample {
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception
{
// Since AbstractQueue is an abstract class
// create object using LinkedBlockingQueue
AbstractQueue<Integer> AQ1 = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Integer>();
// Add elements using add method
AQ1.add(10);
AQ1.add(20);
AQ1.add(30);
AQ1.add(40);
AQ1.add(50);
// print the queue contents to the console
System.out.println("AbstractQueue1 contains : " + AQ1);
// Retrieves the head
int head = AQ1.remove();
// print the head element to the console
System.out.println("head : " + head);
// print the modified queue
System.out.println("AbstractQueue1 after removal of head : " + AQ1);
// remove all the elements
AQ1.clear();
// print the modified queue
System.out.println("AbstractQueue1 : " + AQ1);
}
}
输出
AbstractQueue1 contains : [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
head : 10
AbstractQueue1 after removal of head : [20, 30, 40, 50]
AbstractQueue1 : []
3.访问元素
AbstractQueue的element()方法检索但不删除,这个队列的头。
// Java program to illustrate the
// accessing element from AbstractQueue
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
public class AccessingElementExample {
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception
{
// Since AbstractQueue is an abstract class
// create object using LinkedBlockingQueue
AbstractQueue<Integer> AQ1 = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Integer>();
// Populating AQ1 using add method
AQ1.add(10);
AQ1.add(20);
AQ1.add(30);
AQ1.add(40);
AQ1.add(50);
// print AQ to the console
System.out.println("AbstractQueue1 contains : " + AQ1);
// access the head element
System.out.println("head : " + AQ1.element());
}
}
输出
AbstractQueue1 contains : [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
head : 10
AbstractQueue的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| add(E e) | 如果可以在不违反容量限制的情况下立即插入指定的元素到这个队列中,成功后返回true,如果当前没有可用空间,则抛出IllegalStateException。 |
| addAll(Collection c) | 将指定集合中的所有元素添加到这个队列中。 clear() | 从这个队列中移除所有的元素。 element() | 检索,但不删除这个队列的头部。 remove() | 检索并删除此队列的头部。 ### java.util.AbstractCollection类中声明的方法 方法 | 描述 |
如果这个集合包含了指定集合中的所有元素,则返回true。 |
| isEmpty() | 如果这个集合不包含任何元素,则返回真。 |
| iterator() | 返回这个集合中所包含的元素的迭代器。 |
| remove(Object o) | 从这个集合中移除指定元素的一个实例,如果它存在的话(可选操作)。 |
| removeAll(Collection c) | 删除这个集合中也包含在指定集合中的所有元素(可选操作)。 retainAll(Collection c) |
只保留本集合中包含在指定集合中的元素(可选操作)。 |
| toArray() | 返回一个包含此集合中所有元素的数组。 |
| toArray(T[] a) | 返回一个包含此集合中所有元素的数组;返回的数组的运行时类型是指定数组的类型。 |
| toString() | 返回这个集合的字符串表示。 |
java.util.Collection接口中声明的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| contains(Object o) | 如果这个集合包含指定的元素,返回true。 |
| containsAll(Collection c) | 如果这个集合包含指定集合中的所有元素,则返回true。 equals(Object o) | 将指定的对象与这个集合进行比较,看是否相等。 hashCode() | 返回此集合的哈希代码值。 isEmpty() | 如果这个集合不包含任何元素,返回true。 iterator() | 返回这个集合中的元素的迭代器。 parallelStream() | 返回一个以这个集合为源的可能的并行流。 remove(Object o) | 从这个集合中移除指定元素的一个实例,如果它存在的话(可选操作)。 removeAll(Collection c) |
删除这个集合中也包含在指定集合中的所有元素(可选操作)。 |
| removeIf(Predicate filter) | 移除此集合中满足给定谓词的所有元素。 retainAll(Collection c) |
只保留此集合中包含在指定集合中的元素(可选操作)。 |
| size() | 返回这个集合中元素的数量。 |
| spliterator() | 在这个集合中的元素上创建一个Spliterator。 |
| stream() | 返回一个以这个集合为源的顺序流。 |
| toArray() | 返回一个包含此集合中所有元素的数组。 |
| toArray(IntFunction<T[]> generator) | 返回一个包含此集合中所有元素的数组,使用提供的生成器函数来分配返回的数组。 |
| toArray(T[] a) | 返回一个包含此集合中所有元素的数组;返回的数组的运行时类型是指定数组的类型。 |
java.lang.Iterable接口中声明的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| forEach(Consumer<? super T> action) | 对Iterable中的每个元素执行给定的动作,直到所有元素都被处理完或者该动作抛出一个异常。 |
接口java.util.Queue中声明的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| offer(E e) | 如果有可能在不违反容量限制的情况下立即插入指定的元素到这个队列中。 |
| peek() | 检索但不删除此队列的头部,如果此队列为空,则返回null。 |
| poll() | 检索并删除这个队列的头部,如果这个队列是空的,则返回null。 |
参考: https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/javase/11/docs/api/java.base/java/util/AbstractQueue.html
 极客教程
极客教程