Java中的反向优先队列
当对象需要根据优先级进行处理时,会使用PriorityQueue。通常队列遵循先入先出原则,但有时需要按照优先级处理队列元素,此时就可使用PriorityQueue。PriorityQueue基于Priority Heap构建,队列元素按照自然排序或在构建队列时提供的比较器排序(取决于使用哪个构造函数)。
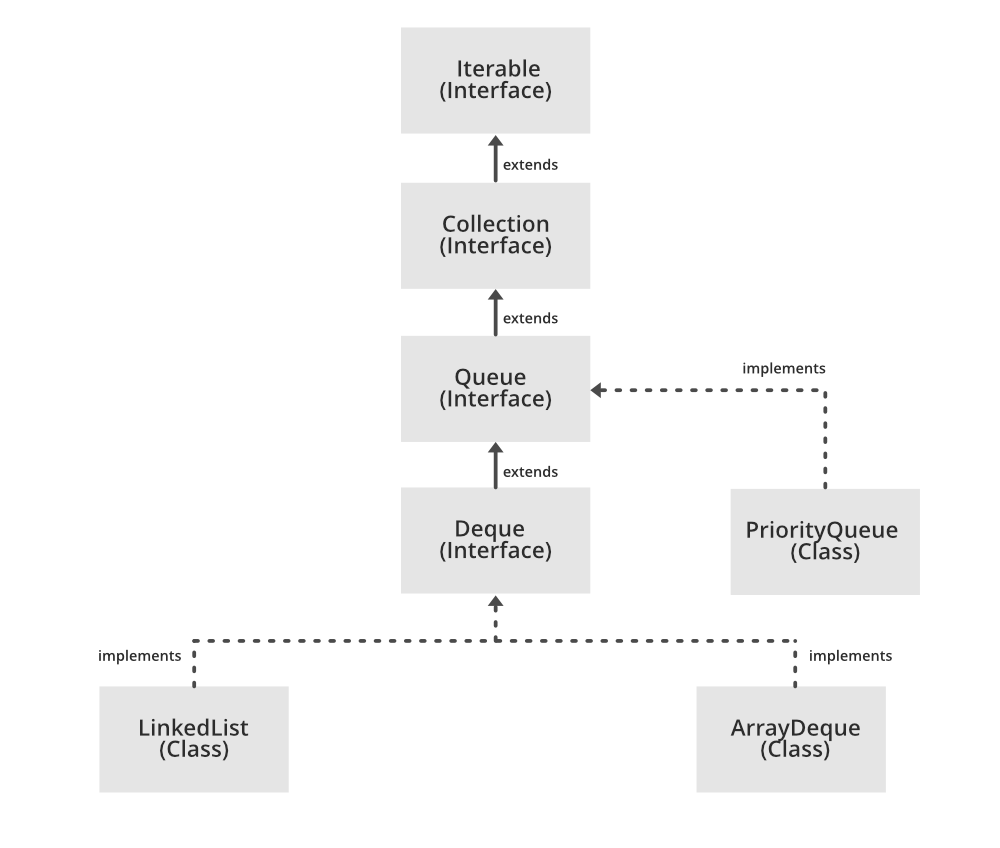
声明:
public class PriorityQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E> implements Serializable
其中 E 表示该队列中保存的元素类型
PriorityQueue的类型
- Max Priority Queue (最大优先队列)
- Min Priority Queue (最小优先队列)
默认优先队列示例
//默认PriorityQueue演示的Java程序
import java.util.*;
class PriorityQueueDemo {
// 主方法
public static void main(String args[])
{
// 创建空的优先级队列
PriorityQueue<Integer> pQueue
= new PriorityQueue<Integer>();
// 使用add()方法向pQueue添加元素
pQueue.add(10);
pQueue.add(20);
pQueue.add(15);
pQueue.add(5);
// 输出优先级队列的顶部元素
System.out.println(pQueue.peek());
// 输出并从PriorityQueue容器中删除顶部元素
System.out.println(pQueue.poll());
// 再次输出顶部元素
System.out.println(pQueue.peek());
}
}
输出
5
5
10
在Java中,PriorityQueue默认实现为min Priority Queue。如果需要从min到max Priority Queue更改Priority Queue的顺序,则可以使用以下方法:
- 使用默认Comparator Collections.reverseOrder()
- 使用自定义比较器
- 使用 lambda表达式
方法1: 使用默认Comparator Collections.reverseOrder()
使用Collections.reverseOrder()方法来获取默认比较器的相反行为。这是java.util包中的默认比较器。
示例:
// Java program to demonstrate the
// working of PriorityQueue in reverse order
import java.util.*;
class PriorityQueueDemo {
// Main Method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating empty priority queue
PriorityQueue<Integer> pQueue
= new PriorityQueue<Integer>(
Collections.reverseOrder());
// Adding items to the pQueue using add()
pQueue.add(10);
pQueue.add(20);
pQueue.add(15);
pQueue.add(5);
// Printing the top element of PriorityQueue
System.out.println(pQueue.peek());
// Printing the top element and removing it
// from the PriorityQueue container
System.out.println(pQueue.poll());
// Printing the top element again
System.out.println(pQueue.peek());
}
}
输出
20
20
15
方法二:使用自定义比较器
The java.util.PriorityQueue.comparator() 方法共享了一个重要的作用,即设置并返回可用于对 PriorityQueue 中的元素进行排序的比较器。如果队列遵循元素的自然排序模式,则该方法返回 null 值。
示例:
// Java program to demonstrate the
// working of PriorityQueue in reverse order
import java.util.*;
public class PriorityQueueDemo {
// Main Method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating empty priority queue
// with custom Comparator
PriorityQueue pQueue
= new PriorityQueue(
new Comparator() {
// Compare method for place element in
// reverse order
public int compare(Integer a, Integer b)
{
if (a < b)
return 1;
if (a > b)
return -1;
return 0;
}
});
// Adding items to the pQueue using add()
pQueue.add(10);
pQueue.add(15);
pQueue.add(20);
pQueue.add(5);
// Printing the top element of PriorityQueue
System.out.println(pQueue.peek());
// Printing the top element and removing it
// from the PriorityQueue container
System.out.println(pQueue.poll());
// Printing the top element again
System.out.println(pQueue.peek());
}
}
输出:
20
20
15
方法三:使用 lambda 表达式
Lambda 表达式自 Java 8 以来就开始使用,lambda 函数将其输入参数命名为 a 和 b,并返回(b-a),这基本上就是 int 比较器类所做的,只不过它返回 a-b。
示例:
// Java program to demonstrate the
// working of PriorityQueue in reverse order
import java.util.*;
class PriorityQueueDemo {
// Main Method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating empty priority queue
PriorityQueue pQueue
= new PriorityQueue((a, b) -> b - a);
// Adding items to the pQueue using add()
pQueue.add(10);
pQueue.add(20);
pQueue.add(15);
pQueue.add(5);
// Printing the top element of PriorityQueue
System.out.println(pQueue.peek());
// Printing the top element and removing it
// from the PriorityQueue container
System.out.println(pQueue.poll());
// Printing the top element again
System.out.println(pQueue.peek());
}
}
输出:
20
20
15
 极客教程
极客教程