NavigableMap接口在Java中的使用示例
NavigableMap接口 是Java集合框架成员之一,属于 java.util 包的扩展排序映射(SortedMap),提供方便的导航方法,如lowerKey、floorKey、ceilingKey和higherKey,还提供了从现有Map中创建子Map的方法,例如headMap(其键小于指定键)、tailMap(其键大于指定键)和subMap(其键在toKey和fromKey之间)。
实现NavigableMap的一个示例类是TreeMap。
声明:
public interface NavigableMap<K, V> extends SortedMap<K, V>
这里, K 是键对象类型, V 是值对象类型。
NavigableMap 的层次结构:
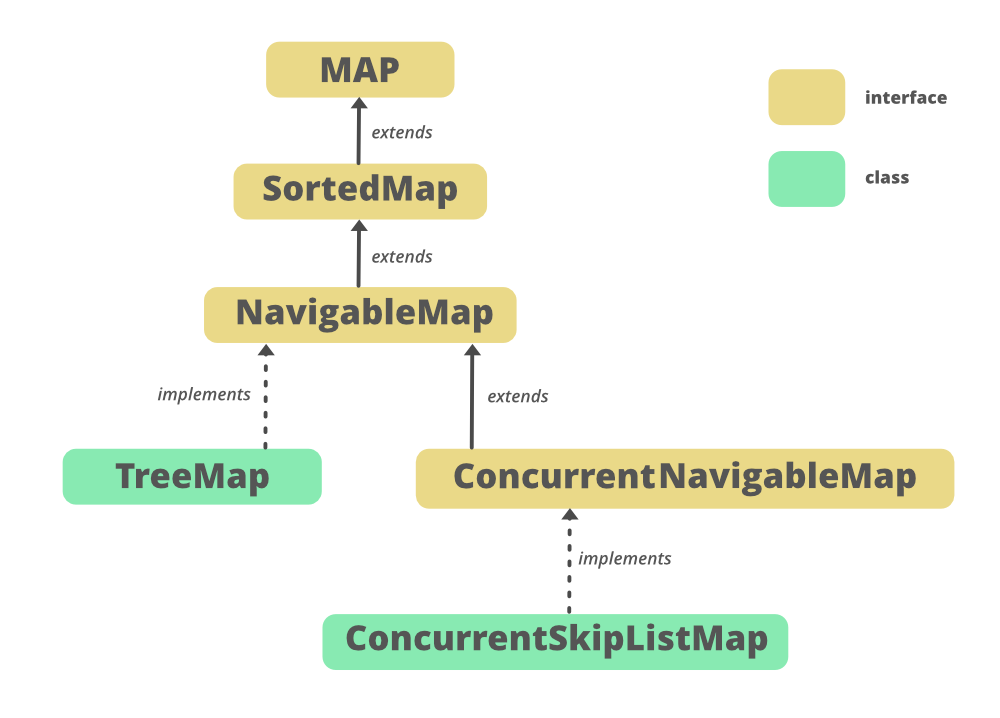
它实现了Map<K,V>和SortedMap<K,V>接口,ConcurrentNavigableMap<K,V>扩展NavigableMap,ConcurrentSkipListMap和TreeMap实现NavigableMap。
示例:
// Java program to demonstrate
// the NavigableMap interface
import java.util.NavigableMap;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class NavigableMapExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Instantiate an object
// Since NavigableMap
// is an interface so we
// use TreeMap
NavigableMap<String, Integer> nm
= new TreeMap<String, Integer>();
// Add elements using put() method
nm.put("C", 888);
nm.put("Y", 999);
nm.put("A", 444);
nm.put("T", 555);
nm.put("B", 666);
nm.put("A", 555);
// Print the contents on the console
System.out.println("Mappings of NavigableMap : "
+ nm);
System.out.printf("Descending Set : %s%n",
nm.descendingKeySet());
System.out.printf("Floor Entry : %s%n",
nm.floorEntry("L"));
System.out.printf("First Entry : %s%n",
nm.firstEntry());
System.out.printf("Last Key : %s%n", nm.lastKey());
System.out.printf("First Key : %s%n",
nm.firstKey());
System.out.printf("Original Map : %s%n", nm);
System.out.printf("Reverse Map : %s%n",
nm.descendingMap());
}
}
输出:
Mappings of NavigableMap : {A=555, B=666, C=888, T=555, Y=999}
Descending Set : [Y, T, C, B, A]
Floor Entry : C=888
First Entry : A=555
Last Key : Y
First Key : A
Original Map : {A=555, B=666, C=888, T=555, Y=999}
Reverse Map : {Y=999, T=555, C=888, B=666, A=555}
实现类
NavigableMap有两个实现类,分别是 ConcurrentSkipListMap 和 TreeMap ,TreeMap是基于红黑树的NavigableMap实现,它根据其键的自然顺序排序,或者根据提供的比较器在创建映射时进行排序,这取决于使用哪种构造方法。TreeMap在插入、删除和访问操作方面的时间复杂度为 log(n) 。TreeMap不是同步的,需要外部完成。
语法:
NavigableMap<K, V> objectName = new TreeMap<K, V>();
基本操作
1. 添加元素
要向NavigableMap添加元素,可以使用Map接口的任何方法。下面的代码展示了如何使用它们。可以观察到,代码中未保留插入顺序。当在构建时未提供Comparator时,将遵循自然顺序。
// Java program for adding elements
// to a NavigableMap
import java.util.*;
class AddingElementsExample {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Instantiate an object
// Since NavigableMap is an interface
// We use TreeMap
NavigableMap<Integer, String> nmap
= new TreeMap<Integer, String>();
// Add elements using put()
nmap.put(3, "Geeks");
nmap.put(2, "For");
nmap.put(1, "Geeks");
// Print the contents on the console
System.out.println("Mappings of NavigableMap : "
+ nmap);
}
}
输出结果:
Mappings of NavigableMap : {1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}
2. 移除元素
要移除元素,我们可以使用Map接口的方法,因为NavigableMap是Map的子类。我们可以使用 remove() 方法,该方法取键值并从该treemap中删除键的映射(如果存在于该地图上)。我们可以使用clear()方法删除地图的所有元素。
// Java Program for deleting
// elements from NavigableMap
import java.util.*;
class RemovingElementsExample {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Instantiate an object
// Since NavigableMap
// is an interface
// We use TreeMap
NavigableMap<Integer, String> nmap
= new TreeMap<Integer, String>();
// Add elements using put()
nmap.put(3, "Geeks");
nmap.put(2, "Geeks");
nmap.put(1, "Geeks");
nmap.put(4, "For");
// Print the contents on the console
System.out.println("Mappings of NavigableMap : "
+ nmap);
// Remove elements using remove()
nmap.remove(4);
// Print the contents on the console
System.out.println(
"\nNavigableMap, after remove operation : "
+ nmap);
// Clear the entire map using clear()
nmap.clear();
System.out.println(
"\nNavigableMap, after clear operation : "
+ nmap);
}
}
输出结果:
Mappings of NavigableMap : {1=Geeks, 2=Geeks, 3=Geeks, 4=For}
NavigableMap, after remove operation : {1=Geeks, 2=Geeks, 3=Geeks}
NavigableMap, after clear operation : {}
3. 访问元素
我们可以使用get()方法来访问NavigableMap的元素,以下是一个示例。
//用 Java 来访问 NavigableMap 中的元素的程序
import java.util.*;
public class AccessingElementsExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//实例化一个对象
//由于 NavigableMap 是一个接口
//所以我们使用 TreeMap
NavigableMap<Integer, String> nmap
= new TreeMap<Integer, String>();
//使用 put() 添加元素
nmap.put(8, "第三个");
nmap.put(6, "第二个");
nmap.put(3, "第一个");
nmap.put(11, "第四个");
//使用 get() 并将 key 作为参数来访问元素
System.out.println(nmap.get(3));
System.out.println(nmap.get(6));
System.out.println(nmap.get(8));
System.out.println(nmap.get(11));
//使用 keySet() 显示键的集合
System.out.println("\nNavigableMap 的键集合: "
+ nmap.keySet());
}
}
输出:
第一个
第二个
第三个
第四个
NavigableMap 的键集合: [3, 6, 8, 11]
4. 遍历
我们可以使用 Iterator 接口来遍历集合框架中的任何结构。由于迭代器与一种数据类型一起工作,因此我们使用 Entry< ? , ? > 将两种分离的类型解析为兼容格式。然后使用 next() 方法打印 NavigableMap 的元素。另一种常用的方法是使用 for-each 循环并获取键。通过使用 getValue() 方法找到键的值。
//用 Java 来遍历 NavigableMap 的程序
import java.util.*;
class TraversalExample {
public static void main(String args[])
{
//实例化一个对象
//由于 NavigableMap 是一个接口
//所以我们使用 TreeMap
NavigableMap<Integer, String> nmap
= new TreeMap<Integer, String>();
//使用 put() 添加元素
nmap.put(3, "极客们");
nmap.put(2, "为了");
nmap.put(1, "极客们");
//创建一个迭代器
Iterator<NavigableMap.Entry<Integer, String> > itr
= nmap.entrySet().iterator();
System.out.println("使用 Iterator 遍历: ");
//使用 hasNext() 方法检查是否有下一个元素
//使用 next() 方法检索下一个元素
while (itr.hasNext()) {
NavigableMap.Entry<Integer, String> entry
= itr.next();
System.out.println("Key = " + entry.getKey()
+ ", Value = "
+ entry.getValue());
}
System.out.println("使用 for-each 遍历: ");
//使用 for-each 循环遍历
for (Map.Entry mapElement : nmap.entrySet()) {
//使用 getKey() 获取键
int key = (int)mapElement.getKey();
//查找值
String value = (String)mapElement.getValue();
System.out.println("Key = " + key
+ ", Value = " + value);
}
}
}
输出:
使用 Iterator 遍历:
Key = 1, Value = 极客们
Key = 2, Value = 为了
Key = 3, Value = 极客们
使用 for-each 遍历:
Key = 1, Value = 极客们
Key = 2, Value = 为了
Key = 3, Value = 极客们
注意: 每次我们说“NavigableMap 的元素”时,必须注意这些元素实际上存储在 NavigableMap 实现类的对象中,在本例中为 TreeMap。
NavigableMap 的方法
NavigableMap 继承了 Map 接口和 SortedMap 接口的方法。父接口提供了添加元素、删除元素和遍历的基本方法。NavigableMap 的方法在下表中给出。这里,
- K - 映射中键的类型。
- V - 映射中值的类型。
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| ceilingEntry(K key) | 返回与给定键大于或等于最小键相关联的键值对映射,如果没有这样的键,则返回null。 |
| ceilingKey(K key) | 返回大于或等于给定键的最小键,如果没有这样的键,则返回null。 |
| descendingKeySet() | 返回包含此映射中的键的反向顺序NavigableSet视图。 |
| descendingMap() | 返回包含此映射中的映射的反向排序视图。 |
| firstEntry() | 返回与此映射中最小键相关联的键值对映射,如果映射为空,则返回null。 |
| floorEntry(K key) | 返回与小于或等于给定键的最大键相关联的键值对映射,如果没有这样的键,则返回null。 |
| floorKey(K key) | 返回小于或等于给定键的最大键,如果没有这样的键,则返回null。 |
| headMap(K toKey) | 返回键严格小于toKey的此映射部分的视图。 |
| headMap(K toKey, boolean inclusive) | 返回键小于(如果inclusive为true,则为小于或等于)toKey的此映射部分的视图。 |
| higherEntry(K key) | 返回与给定键严格大于的最小键相关联的键值对映射,如果没有这样的键,则返回null。 |
| higherKey(K key) | 返回严格大于给定键的最小键,如果没有这样的键,则返回null。 |
| lastEntry() | 返回与此映射中最大键相关联的键值对映射,如果映射为空,则返回null。 |
| lowerEntry(K key) | 返回与给定键严格小于的最大键相关联的键值对映射,如果没有这样的键,则返回null。 |
| lowerKey(K key) | 返回严格小于给定键的最大键,如果没有这样的键,则返回null。 |
| navigableKeySet() | 返回此映射中包含的键的NavigableSet视图。 |
| pollFirstEntry() | 移除并返回与此映射中最小键相关联的键值对映射,如果映射为空,则返回null。 |
| pollLastEntry() | 移除并返回与此映射中最大键相关联的键值对映射,如果映射为空,则返回null。 |
| subMap(K fromKey, boolean fromInclusive, K toKey, boolean toInclusive) | 返回键范围从fromKey到toKey的此映射部分的视图。 |
| subMap(K fromKey,K toKey) | 返回键范围从fromKey(包含)到toKey(不包含)的此映射部分的视图。 |
| tailMap(K fromKey) | 返回键大于或等于fromKey的此映射部分的视图。 |
| tailMap(K fromKey, boolean inclusive) | 返回键大于(如果inclusive为true,则为大于或等于)fromKey的此映射部分的视图。 |
从接口java.util.SortedMap继承的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| comparator() | 返回用于按照此映射中键的顺序排序的比较器,如果该映射使用其键的自然排序,则返回 null。 |
| entrySet() | 返回此映射所包含的映射的 Set 视图。 |
| firstKey() | 返回此映射当前所有键中的第一个(最低)键。 |
| keySet() | 返回此映射中键的 Set 视图。 |
| lastKey() | 返回此映射当前所有键中的最后一个(最高)键。 |
| values() | 返回此映射中值的 Collection 视图。 |
继承自 java.util.Map 的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| clear() | 从这个映射中删除所有映射(可选操作)。 |
| compute(K key, BiFunction<? super K,? super V,? extends V> remappingFunction) | 尝试为指定的键及其当前映射值(如果没有当前映射,则为null)计算映射。 |
| computeIfAbsent(K key, Function<? super K,? extends V> mappingFunction) | 如果指定的键尚未与值关联(或映射到null),则尝试使用给定的映射函数计算其值,并将其输入到此映射中,除非为null。 |
| computeIfPresent(K key, BiFunction<? super K,? super V,? extends V> remappingFunction) | 如果指定键的值存在且非null,则尝试计算给定键及其当前映射值的新映射。 |
| containsKey(Object key) | 如果此映射包含指定键的映射,则返回true。 |
| containsValue(Object value) | 如果此映射将一个或多个键映射到指定值,则返回true。 |
| equals(Object o) | 将指定对象与此映射进行比较以测试是否相等。 |
| forEach(BiConsumer<? super K,? super V> action) | 对此映射中的每个条目执行给定操作,直到所有条目都已处理或操作抛出异常。 |
| get(Object key) | 返回指定键映射到的值,如果此映射不包含键的映射,则返回null。 |
| getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) | 返回指定键映射到的值,如果此映射不包含key的映射,则返回defaultValue。 |
| hashCode() | 返回此Map的哈希码值。 |
| isEmpty() | 如果此映射不包含键值映射,则返回true。 |
| merge(K key, V value, BiFunction<? super V,? super V,? extends V> remappingFunction) | 如果指定的键尚未与值相关联或与null相关联,则将其与给定的非null值相关联。 |
| put(K key, V value) | 将指定值与指定键在此映射中关联(可选操作)。 |
| putAll(Map<? extends K,? extends V> m) | 从指定映射复制所有的映射到此映射(可选操作)。 |
| putIfAbsent(K key, V value) | 如果指定键尚未与值相关联(或与null相关联),则将其与给定值相关联并返回null,否则返回当前值。 |
| remove(Object key) | 如果存在,则从此映射中删除一个键的映射(可选操作)。 |
| remove(Object key, Object value) | 仅当当前将该键映射到指定值时,才从此映射中删除指定键的条目。 |
| replace(K key, V value) | 仅当将该键映射到某个值时才替换该键的条目。 |
| replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) | 如果当前将该键映射到指定值时,则将该键的项替换为指定新值。 |
| replaceAll(BiFunction<? super K,? super V,? extends V> function) | 对此映射中的每个条目执行给定的操作,以替换每个与该键关联的值,直到所有条目都已处理或该操作引发异常。 |
| replaceAll(Function function) | 对map中的每个键值对执行给定的函数,并用函数的结果替换该键值对中的值,直到所有键值对都被处理或函数抛出异常为止。 |
| size() | 返回此Map中键值映射的数量。 |
参考: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/NavigableMap.html
 极客教程
极客教程