Java中的Map接口
在Java中,Map接口位于java.util包中,代表着键和值之间的映射关系。Java的Map接口不是Collection接口的子类型,因此与其他集合类型的行为有所不同。Map包含唯一的键。
Geeks,头脑风暴者应该思考 为什么和何时应该使用Maps。
Maps非常适合用于键-值关联映射,例如字典。Maps用于通过键执行查找,或当某人想要检索和更新元素时使用键。一些常见的场景如下:
- 错误代码和其描述的Map。
- 邮政编码和城市的Map。
- 经理和员工的Map。每个经理(键)都与他管理的员工列表(值)相关联。
- 班级和学生的Map。每个班级(键)都与其学生列表(值)相关联。
创建Map对象
由于Map是一个接口,因此不能创建Map类型的对象。我们总是需要一个扩展此Map的类才能创建对象。还有,在Java 1.5引入泛型之后,可以限制可以存储在Map中的对象的类型。
语法: 定义类型安全的Map
Map hm = new HashMap();
//Obj是要存储在Map中的对象的类型
Map接口的特征
- Map不能包含重复的键,每个键最多只能映射到一个值。一些实现允许null键和null值,例如HashMap和LinkedHashMap,但有些实现不允许,例如TreeMap。
- Map的顺序取决于具体的实现方式。例如TreeMap和LinkedHashMap具有可预测的顺序,而HashMap则没有。
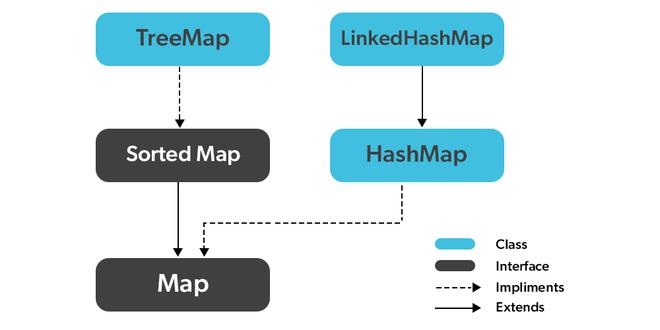
- 实现Map接口的类有两个接口,即Map和SortedMap,以及三个类:HashMap、TreeMap和LinkedHashMap。
Java Map接口的方法
| 方法 | 执行的操作 |
|---|---|
| clear() | 该方法用于Java Map接口,用于清除并删除指定Map集合中的所有元素或映射。 |
| containsKey(Object) | 该方法用于Java Map接口,用于检查特定的键是否被映射到Map中。它以键元素作为参数,如果该元素被映射到Map中,则返回True。 |
| containsValue(Object) | 该方法用于Java Map接口,用于检查特定的值是否被一个或多个键映射到Map中。它以值为参数,如果该值被任何一个键映射到Map中,则返回True。 |
| entrySet() | 该方法用于Java Map接口,用于根据Map中包含的相同元素创建一个集合。它基本上返回Map的集合视图,也可以创建一个新集合并将Map元素存储到其中。 |
| equals(Object) | 该方法用于Java Map接口,用于检查两个Map之间的相等性。它验证以另一个Map作为参数的元素是否等于此Map的元素。 |
| get(Object) | 该方法用于检索或获取参数中指定的 key 所映射的值。当Map不包含该键的映射关系时,返回Null。 |
| hashCode() | 该方法用于Java Map接口,用于生成给定包含键和值的Map的哈希码。 |
| isEmpty() | 该方法用于检查Map是否具有键和值对的条目。如果不存在映射,则返回True。 |
| keySet() | 该方法用于Java Map接口,用于返回此Map中包含的键的Set视图。该Set由Map支持,因此对Map的更改会反映在集合中,反之亦然。 |
| put(Object, Object) | 该方法用于Java Map接口,用于在Map中将指定的值与指定的键关联。 |
| putAll(Map) | 该方法用于Java Map接口,将指定Map中的所有映射复制到此Map中。 |
| remove(Object) | 该方法用于Java Map接口,用于从Map中删除一个键的映射(如果它存在于Map中)。 |
| size() | 该方法用于返回Map中可用的键/值对数。 |
| values() | 该方法用于Java Map接口,用于将Map的值创建成一个集合。它基本上返回HashMap中值的集合视图。 |
| getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) | 返回指定键映射到的值,如果此映射不包含键的映射,则返回defaultValue。 |
| merge(K key, V value, BiFunction<? super V,? super V,? extends V> remappingFunction) | 如果指定的键还没有与值关联,或者与null关联,则将其与给定的非null值相对应。 |
| putIfAbsent(K key, V value) | 如果指定的键还没有与值相关联(或映射到null),则将其与给定的值相关联并返回null,否则返回当前相关联的值。 |
示例:
// Java Program to illustrate the LinkedHashMap Class
// Importing required classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating a Map of Integer keys and String values
Map<Integer, String> lhm
= new LinkedHashMap<>();
// Adding elements to the Map
lhm.put(100, "Amit");
lhm.put(105, "Vijay");
lhm.put(101, "Rahul");
// Displaying the contents of the map
System.out.println("Initial list of elements:");
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> me :
lhm.entrySet()) {
System.out.println("Key: " + me.getKey()
+ " Value: " + me.getValue());
}
// Removing an element with key "105"
lhm.remove(105);
System.out.println("\nAfter invoking remove() method:");
System.out.println("Updated list of elements:");
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> me :
lhm.entrySet()) {
System.out.println("Key: " + me.getKey()
+ " Value: " + me.getValue());
}
// Removing all elements
lhm.clear();
System.out.println("\nAfter invoking clear() method:");
System.out.println("Updated list of elements:");
System.out.println("Size of Map: " + lhm.size());
}
}
输出:
Initial list of elements:
Key: 100 Value: Amit
Key: 105 Value: Vijay
Key: 101 Value: Rahul
After invoking remove() method:
Updated list of elements:
Key: 100 Value: Amit
Key: 101 Value: Rahul
After invoking clear() method:
Updated list of elements:
Size of Map: 0
3. TreeMap
Java TreeMap contains values based on the key. It implements the NavigableMap interface and extends AbstractMap class. Java TreeMap contains only unique elements. Java TreeMap is not synchronized. Java TreeMap cannot have null key but can have multiple null values. Let’s see how to create a map object using this class.
示例
// Java Program to illustrate
// Java TreeMap Class
// Importing required classes
import java.util.TreeMap;
import java.util.Map;
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an empty TreeMap
TreeMap tmap
= new TreeMap();
// Adding values to TreeMap
tmap.put(1, "Data1");
tmap.put(23, "Data2");
tmap.put(70, "Data3");
tmap.put(4, "Data4");
// Displaying the TreeMap
for (Map.Entry entry :
tmap.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey()
+ " "
+ entry.getValue());
}
}
}
输出:
1 Data1
4 Data4
23 Data2
70 Data3
// Java Program to demonstrate adding elements to HashMap
// Importing required classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an empty HashMap
HashMap<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>();
// Adding elements to the map
map.put(1, "Geeks");
map.put(2, "for");
map.put(3, "Geeks");
// Iterating over Map using for each loop
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> e : map.entrySet())
// Printing key-value pairs
System.out.println(e.getKey() + " "
+ e.getValue());
}
}
输出
1 Geeks
2 for
3 Geeks
2. Removing Elements
In order to remove an element from the map, we can use the remove() method. This method takes in a key as an argument and removes the key-value pair associated with that key from the map.
示例
// Java Program to demonstrate removing elements from HashMap
// Importing required classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating a HashMap
HashMap<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>();
// Adding elements to the map
map.put(1, "Geeks");
map.put(2, "for");
map.put(3, "Geeks");
// Removing elements from Map
map.remove(2);
// Iterating over Map using for each loop
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> e : map.entrySet())
// Printing key-value pairs
System.out.println(e.getKey() + " "
+ e.getValue());
}
}
输出
1 Geeks
3 Geeks
3. Updating Elements
In order to update an element in the map, we can use the put() method again with the same key and new value. This will replace the previous value associated with the key with the new value.
示例
// Java Program to demonstrate updating elements in HashMap
// Importing required classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating a HashMap
HashMap<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>();
// Adding elements to the map
map.put(1, "Geeks");
map.put(2, "for");
map.put(3, "Geeks");
// Updating elements in Map
map.put(2, "GEEKS");
// Iterating over Map using for each loop
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> e : map.entrySet())
// Printing key-value pairs
System.out.println(e.getKey() + " "
+ e.getValue());
}
}
输出
1 Geeks
2 GEEKS
3 Geeks
// 演示 Map 接口的工作的 Java 程序
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Map 的默认初始化
Map<Integer, String> hm1 = new HashMap<>();
// 使用泛型初始化 Map
Map<Integer, String> hm2
= new HashMap<Integer, String>();
// 插入元素
hm1.put(1, "Geeks");
hm1.put(2, "For");
hm1.put(3, "Geeks");
hm2.put(new Integer(1), "Geeks");
hm2.put(new Integer(2), "For");
hm2.put(new Integer(3), "Geeks");
System.out.println(hm1);
System.out.println(hm2);
}
}
输出
{1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}
{1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}
2. 修改元素
在添加元素后,如果我们希望改变元素,则可以通过再次使用 put() 方法添加元素来实现。由于 Map 中的元素是使用键进行索引的,因此可以通过为我们希望更改的键插入更新的值来更改键的值。
示例
// 演示 Map 接口的工作的 Java 程序
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// 使用泛型初始化 Map
Map<Integer, String> hm1
= new HashMap<Integer, String>();
// 插入元素
hm1.put(new Integer(1), "Geeks");
hm1.put(new Integer(2), "Geeks");
hm1.put(new Integer(3), "Geeks");
System.out.println("初始 Map " + hm1);
hm1.put(new Integer(2), "For");
System.out.println("更新后的 Map " + hm1);
}
}
输出
初始 Map {1=Geeks, 2=Geeks, 3=Geeks}
更新后的 Map {1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}
3. 删除元素
要从 Map 中删除元素,可以使用 remove() 方法。此方法获取键值并从 Map 中删除具有此键的映射(如果存在)。
示例
// 演示 Map 接口的工作的 Java 程序
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// 使用泛型初始化 Map
Map<Integer, String> hm1
= new HashMap<Integer, String>();
// 插入元素
hm1.put(new Integer(1), "Geeks");
hm1.put(new Integer(2), "For");
hm1.put(new Integer(3), "Geeks");
hm1.put(new Integer(4), "For");
// 初始 Map
System.out.println(hm1);
hm1.remove(new Integer(4));
// 最终 Map
System.out.println(hm1);
}
}
输出
{1=Geeks,2=For, 3=Geeks, 4=For}
{1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}
4. 遍历 Map
遍历 Map 的方法有多种。最常用的方法是使用 for-each 循环并获取键。可以使用 getValue() 方法找到键的值。
示例
// Java程序演示Map接口的工作
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
//使用泛型初始化Map
Map<Integer, String> hm1
= new HashMap<Integer, String>();
//插入元素
hm1.put(new Integer(1), "Geeks");
hm1.put(new Integer(2), "For");
hm1.put(new Integer(3), "Geeks");
for (Map.Entry mapElement : hm1.entrySet()) {
int key = (int)mapElement.getKey();
//查找值
String value = (String)mapElement.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " : " + value);
}
}
}
输出
1 : Geeks
2 : For
3 : Geeks
5.使用HashMap计算数字出现的次数
在此代码中,我们使用 putIfAbsent() 与 Collections.frequency() 一起计算数字的确切出现次数。在许多程序中,需要计数特定数字或字母的出现次数。使用以下方法解决这些类型的问题
// Java程序计算HashMap中数字的出现次数
import java.util.*;
class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a[] = { 1, 13, 4, 1, 41, 31, 31, 4, 13, 2 };
//将所有元素放入ArrayList
ArrayList<Integer> aa = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
aa.add(a[i]);
}
HashMap<Integer, Integer> h = new HashMap();
//计算数字的出现次数
for (int i = 0; i < aa.size(); i++) {
h.putIfAbsent(aa.get(i), Collections.frequency(
aa, aa.get(i)));
}
System.out.println(h);
}
}
输出
{1=2, 2=1, 4=2, 41=1, 13=2, 31=2}
Java Map接口常见问题解答
Q1. Java中的Map接口是什么?
答:
Map包含键值对,通过键值访问Map中的元素。
Q2. Java中的Map接口有哪些类型?
答:
有3种Map接口实现:HashMap、LinkedHashMap和TreeMap。
 极客教程
极客教程