Java中的IdentityHashMap类
IdentityHashMap 使用Hashtable实现Map接口,在比较键(和值)时使用引用相等性而不是对象相等性。这个类不是通用的Map实现。虽然这个类实现了Map接口,但它故意违反了Map的一般契约,该契约规定在比较对象时要使用equals()方法。当用户需要通过引用比较对象时,需要使用这个类。它属于 java.util 包。
IdentityHashMap的特点
- 它遵循引用相等性,而不是使用equals()方法,它使用==操作符。
- 它不是同步的,必须在外部同步。
- 迭代器是快速失败的,在迭代时尝试修改会抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常。
- 对于基本操作(get和put),该类提供常数时间性能,假设系统标识哈希函数(System.identityHashCode(Object))在桶之间正确地分散元素。IdentityHashMap不使用hashCode()方法,而是使用System.identityHashCode()方法。这是一个重要的区别,因为现在可以使用可变对象作为映射中的键,当映射存储在IdentityHashMap中时,它的哈希代码可能会改变。
声明:
public class IdentityHashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>, Serializable, Cloneable
这里, K 是键对象类型, V 是值对象类型。
在Java中,IdentityHashMap是实现Map接口的类。它类似于HashMap类,主要区别在于IdentityHashMap在比较键时使用引用相等性而不是对象相等性。
虽然HashMap使用equals()方法来比较键,但IdentityHashMap使用==操作符来比较键。这意味着在IdentityHashMap中,仅当两个键是同一对象时才认为它们相等,而不是在内容方面相等。
下面是如何在Java中使用IdentityHashMap的示例:
import java.util.IdentityHashMap;
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IdentityHashMap<String, Integer> identityHashMap = new IdentityHashMap<>();
identityHashMap.put("A", 1);
identityHashMap.put(new String("A"), 2);
System.out.println(identityHashMap.size()); // 2
System.out.println(identityHashMap.get("A")); // 1
}
}
输出结果:
2
1
Java中的IdentityHashMap类是一个基于哈希表的Map接口实现,它在比较键(和值)时使用引用相等性而不是对象相等性。
使用IdentityHashMap的优点:
- 查找速度更快:由于IdentityHashMap使用引用相等性进行比较,因此在查找方面比使用对象相等性的HashMap更快。
- 有用于比较对象实例:IdentityHashMap在您想比较对象实例而不是对象值的情况下非常有用。
使用IdentityHashMap的不足之处:
- 使用更多的内存:与HashMap相比,IdentityHashMap使用更多的内存,因为它需要存储对象的引用。
- 不适用于所有用例:IdentityHashMap并不适用于所有用例,应谨慎使用,因为在某些情况下可能会导致意外行为。
IdentityHashMap的层次结构
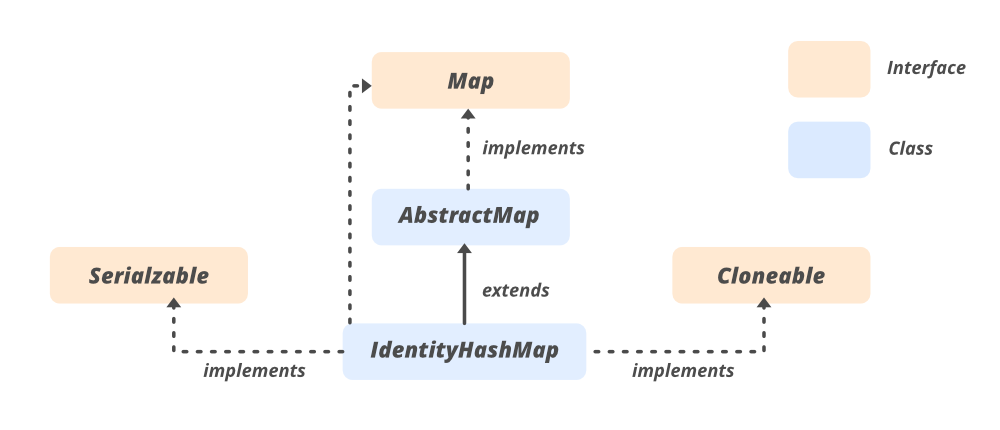
它实现了 Serializable , Cloneable , Map <K,V> 接口并扩展 **AbstractMap <K,V> ** 类。
示例:
// Java代码演示IdentityHashMap
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.IdentityHashMap;
public class IdentityHashMapExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// 创建IdentityHashMap的实例
Map<String,String> ihm = new IdentityHashMap<>();
// 将键值对放入IdentityHashMap对象中
ihm.put("ihmkey","ihmvalue");
ihm.put(new String("ihmkey"),"ihmvalue1");
// 由于它通过引用比较对象,因此ihm.size()将打印2
System.out.println("IdentityHashMap 的大小--"+ihm.size());
}
}
结果
IdentityHashMap 的大小--2
IdentityHashMap 的构造方法
我们可以通过两种方式来创建 IdentityHashMap 的实例:
IdentityHashMap<K,V> ihm = new IdentityHashMap<K,V>();
(或)
Map<K,V> hm = new IdentityHashMap<K,V>();
1. IdentityHashMap(): 使用默认的预期最大大小构造一个新的空标识哈希映射。
IdentityHashMap<K,V> ihm = new IdentityHashMap<K,V>();
2. IdentityHashMap(int expectedMaxSize): 使用指定的预期最大大小构造一个新的空映射。
IdentityHashMap<K,V> ihm = new IdentityHashMap(int expectedMaxSize);
3. IdentityHashMap(Map m): 使用指定映射中的键值映射构造一个新的标识哈希映射。
IdentityHashMap<K,V> ihm = new IdentityHashMap(Map m);
IdentityHashMap 的基本操作
1. 添加元素
要将映射插入或添加到IdentityHashMap中,我们有put()和putAll()方法。 put()可以将特定的键及其映射的值插入特定的映射中。如果传递了现有键,则前一个值将被新值替换。 putAll()将所有元素,即映射从一个映射复制到另一个映射。
// Java代码演示
//向IdentityHashMap添加元素
import java.util.*;
public class AddingElementsToIdentityHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// 创建一个空的IdentityHashMap
Map identity_hash
= new IdentityHashMap();
// 使用put()方法将字符串值映射到int键
identity_hash.put(10, "Geeks");
identity_hash.put(15, "4");
identity_hash.put(20, "Geeks");
identity_hash.put(25, "Welcomes");
identity_hash.put(30, "You");
// 显示IdentityHashMap
System.out.println("初始映射为:" + identity_hash);
// 插入现有键与新值
// 返回先前的值并存储在returned_value中
String returned_value
= (String)identity_hash.put(20, "All");
// 验证返回值
System.out.println("返回的值是:" + returned_value);
// 显示新map
System.out.println("新map为:" + identity_hash);
// 创建一个新的Identityhash map并复制
Map new_Identityhash_map
= new IdentityHashMap();
new_Identityhash_map.putAll(identity_hash);
// 显示最终的IdentityHashMap
System.out.println("新map为:" + new_Identityhash_map);
}
}
输出
初始映射为:{30=You, 10=Geeks, 15=4, 25=Welcomes, 20=Geeks}
返回的值是:Geeks
新map为:{30=You, 10=Geeks, 15=4, 25=Welcomes, 20=All}
新map为:{30=You, 10=Geeks, 15=4, 25=Welcomes, 20=All}
2. 删除元素
要删除映射,我们使用IdentityHashMap类的内置方法remove(),用于从map中删除任何特定键的映射。
// Java代码演示
//从IdentityHashMap中删除元素
import java.util.*;
public class RemovingMappingsFromIdentityHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// 创建一个空的IdentityHashMap
Map Identity_hash = new
IdentityHashMap();
// 将字符串值映射到int键
Identity_hash.put(10, "Geeks");
Identity_hash.put(15, "4");
Identity_hash.put(20, "Geeks");
Identity_hash.put(25, "Welcomes");
Identity_hash.put(30, "You");
// 显示IdentityHashMap
System.out.println("初始映射为:" +
Identity_hash);
// 删除现有键映射
String returned_value =
(String)Identity_hash.remove(20);
// 验证返回值
System.out.println("返回的值是:" +
returned_value);
// 显示新map
System.out.println("新map为:" + Identity_hash);
}
}
输出
初始映射为:{30=You, 10=Geeks, 15=4, 25=Welcomes, 20=Geeks}
返回的值是:Geeks
新map为:{30=You, 10=Geeks, 15=4, 25=Welcomes}
3. 访问元素
我们可以使用get()方法访问IdentityHashMap中的元素,示例如下。
// Java代码演示
//访问IdentityHashMap中的元素
import java.util.*;
public class AccessingElementsOfIdentityHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args){
// 创建一个空的IdentityHashMap
IdentityHashMap Identity_hash = new IdentityHashMap();
// 将字符串值映射到int键
Identity_hash.put(10, "Geeks");
Identity_hash.put(15, "4");
Identity_hash.put(20, "Geeks");
Identity_hash.put(25, "Welcomes");
Identity_hash.put(30, "You");
// 使用get()方法访问特定键的值
System.out.println("key = 10 的值为:" + Identity_hash.get(10));
// 显示IdentityHashMap
System.out.println("IdentityHashMap中的所有元素:" + Identity_hash);
}
}
输出
key = 10 的值为:Geeks
IdentityHashMap中的所有元素:{30=You, 10=Geeks, 15=4, 25=Welcomes, 20=Geeks}
// Java代码示例说明从IdentityHashMap访问元素
import java.util.*;
public class AccessingElementsFromIdentityHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// 创建一个空的IdentityHashMap
Map<Integer, String> identity_hash
= new IdentityHashMap<Integer, String>();
// 将字符串值映射到整数键
identity_hash.put(10, "Geeks");
identity_hash.put(15, "4");
identity_hash.put(20, "Geeks");
identity_hash.put(25, "Welcomes");
identity_hash.put(30, "You");
// 显示IdentityHashMap
System.out.println("Initial Mappings are: "
+ identity_hash);
// 获取25的值
System.out.println("The Value is: "
+ identity_hash.get(25));
// 获取10的值
System.out.println("The Value is: "
+ identity_hash.get(10));
// 使用keySet()获取键的集合视图
System.out.println("The set is: " + identity_hash.keySet());
// 使用entrySet()获取集合视图
System.out.println("The set is: " +
identity_hash.entrySet());
}
}
输出
Initial Mappings are: {30=You, 10=Geeks, 15=4, 25=Welcomes, 20=Geeks}
The Value is: Welcomes
The Value is: Geeks
The set is: [30, 10, 15, 25, 20]
The set is: [30=You, 10=Geeks, 15=4, 25=Welcomes, 20=Geeks]
4. Traversing
我们可以使用Iterator接口来遍历集合框架中的任何结构。由于迭代器只能按一种数据类型处理数据,我们将Entry用于将两种不同的类型解决为兼容格式。然后使用next()方法打印IdentityHashMap的元素。
// Java代码示例演示如何遍历IdentityHashmap
import java.util.*;
public class IteratingIdentityHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// 创建一个空的IdentityHashMap
IdentityHashMap<Integer, String> identity_hash
= new IdentityHashMap<Integer, String>();
// 将字符串值映射到整数键
identity_hash.put(10, "Geeks");
identity_hash.put(15, "4");
identity_hash.put(20, "Geeks");
identity_hash.put(25, "Welcomes");
identity_hash.put(30, "You");
// 显示IdentityHashMap
System.out.println("Initial Mappings are: "
+ identity_hash);
// 创建一个IdentityHashMap的迭代器
Iterator<IdentityHashMap.Entry<Integer, String> >
itr = identity_hash.entrySet().iterator();
// hasNext()方法用于检查是否有下一个元素
// next()方法用于检索下一个元素
while (itr.hasNext()) {
IdentityHashMap.Entry<Integer, String> entry
= itr.next();
System.out.println("Key = " + entry.getKey()
+ ", Value = "
+ entry.getValue());
}
}
}
输出
Initial Mappings are: {30=You, 10=Geeks, 15=4, 25=Welcomes, 20=Geeks}
Key = 30, Value = You
Key= 10, Value = Geeks
Key = 15, Value = 4
Key = 25, Value = Welcomes
Key = 20, Value = Geeks
同步IdentityHashMap
如果多个线程同时访问身份哈希映射,并且其中至少一个线程进行了结构性修改,则必须在外部进行同步。(结构性修改是任何添加或删除一个或多个映射的操作;仅更改实例已经包含的键的关联值不是结构性修改。)通常,这是通过在自然封装映射的某个对象上进行同步来实现的。如果不存在这样的对象,则应使用 Collections.synchronizedMap 方法“包装”地图。最好在创建时完成此操作,以防止意外的不同步访问地图。
Map m = Collections.synchronizedMap(new IdentityHashMap (…));
IdentityHashMap的方法
- K - 地图中键的类型。
- V - 映射在地图中的值的类型。
| METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| clear() | 从此地图中删除所有映射。 |
| clone() | 返回此身份哈希映射的浅层副本:不克隆键和值本身。 |
| containsKey(Object key) | 测试指定的对象引用是否为此身份哈希映射中的键。 |
| containsValue(Object value) | 测试指定的对象引用是否为此身份哈希映射中的值。 |
| entrySet() | 返回此地图中包含的映射的Set视图。 |
| equals(Object o) | 将指定的对象与此映射进行比较以检查相等性。 |
| get(Object key) | 返回指定键映射到的值;如果此地图不包含键的映射,则返回null。 |
| hashCode() | 返回此映射的哈希代码值。 |
| isEmpty() | 如果此身份哈希映射不包含键值映射,则返回true。 |
| keySet() | 返回此地图中包含的键的基于标识的集视图。 |
| put(K key, V value) | 在此身份哈希映射中将指定的值与指定的键关联。 |
| putAll(Map<? extends K,? extends V> m) | 将指定地图中的所有映射复制到此地图中。 |
| remove(Object key) | 如果存在,则从此地图中删除此键的映射。 |
| size() | 返回此身份哈希映射中的键值映射数。 |
| values() | 返回此地图中包含的值的Collection视图。 |
在类java.util.AbstractMap中声明的方法
| METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| toString() | 返回此地图的字符串表示形式。 |
在接口java.util.Map中声明的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| compute(K key, BiFunction<? super K,? super V,? extends V> remappingFunction) | 尝试为指定的键和其当前的映射值(如果没有当前的映射值则为null)计算映射。 |
| computeIfAbsent(K key, Function<? super K,? extends V> mappingFunction) | 如果指定的键还没有与值关联(或映射到null),则尝试使用给定的映射函数计算它的值并将其输入到此映射中,除非null。 |
| computeIfPresent(K key, BiFunction<? super K,? super V,? extends V> remappingFunction) | 如果指定键的值存在且非null,则尝试根据键和其当前映射值计算新映射。 |
| forEach(BiConsumer<? super K,? super V> action) | 对此映射中的每个条目执行给定的操作,直到所有条目都已处理完或操作引发异常。 |
| getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) | 返回指定键所映射的值,如果此映射不包含该键的映射,则返回defaultValue。 |
| merge(K key, V value, BiFunction<? super V,? super V,? extends V> remappingFunction) | 如果指定键还没有与值关联或已关联到null,则将其与给定的非null值关联。 |
| putIfAbsent(K key, V value) | 如果指定的键还没有与值关联(或映射到null),则将其与给定值关联,并返回null,否则返回当前值。 |
| remove(Object key, Object value) | 仅当指定键当前已映射到指定值时才删除该键入口。 |
| replace(K key, V value) | 仅当指定键入口当前已映射到某个值时才替换该键入口。 |
| replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) | 仅当指定键入口当前映射到指定值时才替换该键入口。 |
| replaceAll(BiFunction<? super K,? super V,? extends V> function) | 将每个键入口的值替换为在该键入口上调用给定函数的结果,直到所有条目都已处理完或函数引发异常。 |
IdentityHashMap vs HashMap
- IdentityHashMap使用等号运算符“==”比较键和值,而HashMap使用equals方法比较Map内的键和值。
- 由于IdentityHashMap不使用equals(),对于具有昂贵的equals()的对象,比HashMap快。
- IdentityHashMap不要求键是不可变的,因为它不依赖于equals()。
下面的程序说明了IdentityHashMap和HashMap实现之间的区别。
// Java code to demonstrate IdentityHashMap and
// illustration of how it is different from HashMap
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.IdentityHashMap;
public class IdentityHashMapExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating HashMap and IdentityHashMap objects
Map<String, String> hm = new HashMap<>();
Map<String, String> ihm = new IdentityHashMap<>();
// Putting key and value in HashMap and IdentityHashMap Object
hm.put("hmkey","hmvalue");
hm.put(new String("hmkey"),"hmvalue1");
ihm.put("ihmkey","ihmvalue");
ihm.put(new String("ihmkey"),"ihmvalue1");
// Print Size of HashMap and WeakHashMap Object
// hm.size() will print 1 since it compares the objects logically
// and both the keys are same
System.out.println("Size of HashMap is : "+hm.size());
// ihm.size() will print 2 since it compares the objects by reference
System.out.println("Size of IdentityHashMap is : "+ihm.size());
}
}
输出
Size of HashMap is : 1
Size of IdentityHashMap is : 2
IdentityHashMap是Java中实现Map接口的类,它使用引用相等性来比较键。它类似于一个常规的HashMap,但它使用==运算符来比较键,而不是equals()方法。这意味着具有相同内容但不同对象引用的两个键将在IdentityHashMap中被视为不同的键。
下面是Java中使用IdentityHashMap的示例:
import java.util.IdentityHashMap;
public class IdentityHashMapExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IdentityHashMap<String, Integer> map = new IdentityHashMap<>();
// Add key-value pairs to the map
String key1 = new String("key");
String key2 = new String("key");
map.put(key1, 1);
map.put(key2, 2);
// Get values from the map using the same and different keys
System.out.println(map.get(key1)); // Output: 1
System.out.println(map.get(key2)); // Output: 2
System.out.println(map.get(new String("key"))); // Output: null
}
}
输出
1
2
null
在这个例子中,我们创建了一个IdentityHashMap,将String键映射到Integer值。我们使用两个具有相同内容但不同String对象将两个键值对添加到映射中。然后,我们使用相同和不同的String对象从映射中检索值。我们发现可以使用具有相同内容但是不同对象引用的两个键从映射中检索值,但是无法使用具有相同内容但是不同对象引用的String对象检索值。
请注意,IdentityHashMap的行为与常规的HashMap略有不同,并且通常仅在引用相等性很重要的某些情况下有用。在大多数情况下,常规的HashMap足够并更适合使用。
 极客教程
极客教程