Java中聚合和组合的区别
聚合和组合描述对象之间相互通信时的关系类型,这可能在低级设计中用于描述对象之间的关联。在本文中,我们将讨论Java编程语言中聚合和组合之间的区别。
聚合
它是一种特殊的协会形式:
- 它代表Has-A的关系。
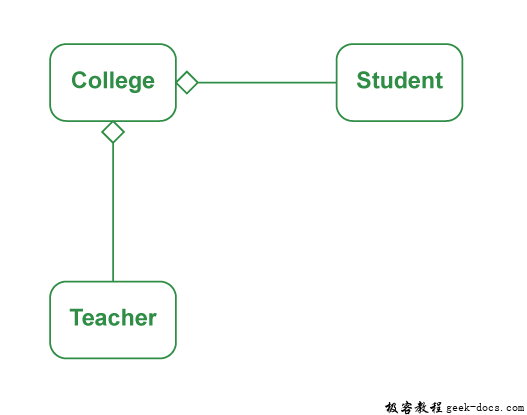
- 这是一种单向关联,即单向关系。例如,一个系可以有学生,但反过来是不可能的,因此是单向的。
- 在聚合中,两个条目都可以单独存在,这意味着结束一个实体不会影响另一个实体。
示例:
// Java program to illustrate the
// Concept of Aggregation
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Class 1
// Student class
class Student {
// Attributes of student
String name;
int id;
String dept;
// Constructor of student class
Student(String name, int id, String dept)
{
// This keyword refers to current instance itself
this.name = name;
this.id = id;
this.dept = dept;
}
}
// Class 2
// Department class contains list of student objects
// It is associated with student class through its Objects
class Department {
// Attributes of Department class
String name;
private List<Student> students;
Department(String name, List<Student> students)
{
// this keyword refers to current instance itself
this.name = name;
this.students = students;
}
// Method of Department class
public List<Student> getStudents()
{
// Returning list of user defined type
// Student type
return students;
}
}
// Class 3
// Institute class contains list of Department
// Objects. It is associated with Department
// class through its Objects
class Institute {
// Attributes of Institute
String instituteName;
private List<Department> departments;
// Constructor of institute class
Institute(String instituteName,List<Department> departments)
{
// This keyword refers to current instance itself
this.instituteName = instituteName;
this.departments = departments;
}
// Method of Institute class
// Counting total students of all departments
// in a given institute
public int getTotalStudentsInInstitute()
{
int noOfStudents = 0;
List<Student> students;
for (Department dept : departments) {
students = dept.getStudents();
for (Student s : students) {
noOfStudents++;
}
}
return noOfStudents;
}
}
// Class 4
// main class
class GFG {
// main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating object of Student class inside main()
Student s1 = new Student("Mia", 1, "CSE");
Student s2 = new Student("Priya", 2, "CSE");
Student s3 = new Student("John", 1, "EE");
Student s4 = new Student("Rahul", 2, "EE");
// Creating a List of CSE Students
List<Student> cse_students = new ArrayList<Student>();
// Adding CSE students
cse_students.add(s1);
cse_students.add(s2);
// Creating a List of EE Students
List<Student> ee_students
= new ArrayList<Student>();
// Adding EE students
ee_students.add(s3);
ee_students.add(s4);
// Creating objects of EE and CSE class inside
// main()
Department CSE = new Department("CSE", cse_students);
Department EE = new Department("EE", ee_students);
List<Department> departments = new ArrayList<Department>();
departments.add(CSE);
departments.add(EE);
// Lastly creating an instance of Institute
Institute institute = new Institute("BITS", departments);
// Display message for better readability
System.out.print("Total students in institute: ");
// Calling method to get total number of students
// in institute and printing on console
System.out.print(institute.getTotalStudentsInInstitute());
}
}
输出:
Total students in institute: 4
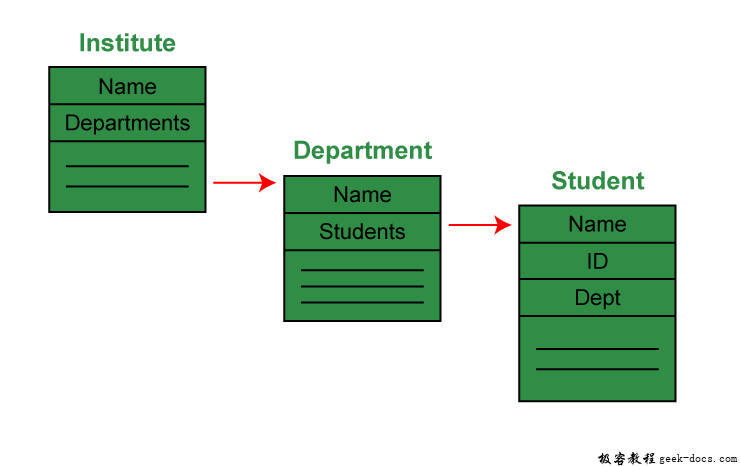
输出解释: 在这个例子中,有一个研究所,它有许多部门,如CSE和EE。每个部门都没有。的学生。因此,我们创建了一个Institute类,它有一个Object或no的引用。Department类的object(即List of Objects)。这意味着Institute类通过它的Object与Department类相关联。Department类也引用了Student类的一个或多个对象(即对象列表),这意味着它通过它的对象与Student类相关联。它表示Has-A关系。在上面的例子中:Student has a name。学生有一个ID。优等生系优等生系优等生如下图所示。
我们什么时候使用聚合?
代码重用最好通过聚合来实现。
组合
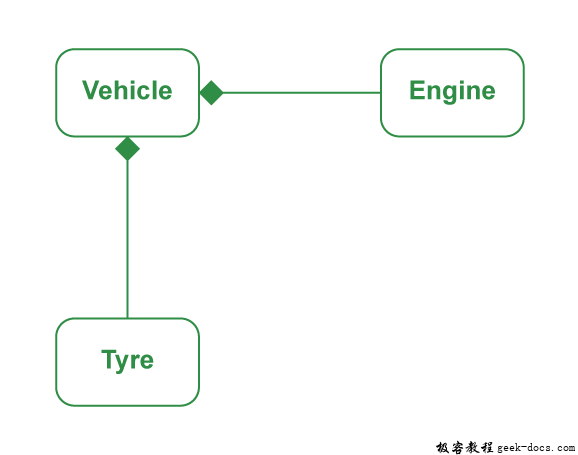
组合是一种限制形式的聚合,其中两个实体高度依赖彼此。
- 它代表了关系的一部分。
- 在组合中,两个实体相互依赖。
- 当两个实体之间存在组合时,组合的对象不能离开另一个实体而存在。
示例:
// Java program to illustrate
// the concept of Composition
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Class 1
// Book
class Book {
// Attributes of book
public String title;
public String author;
// Constructor of Book class
Book(String title, String author)
{
// This keyword refers to current instance itself
this.title = title;
this.author = author;
}
}
// Class 2
class Library {
// Reference to refer to list of books
private final List<Book> books;
// Library class contains list of books
Library(List<Book> books)
{
// Referring to same book as
// this keyword refers to same instance itself
this.books = books;
}
// Method
// To get total number of books in library
public List<Book> getTotalBooksInLibrary()
{
return books;
}
}
// Class 3
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating objects of Book class inside main()
// method Custom inputs
Book b1
= new Book("EffectiveJ Java", "Joshua Bloch");
Book b2
= new Book("Thinking in Java", "Bruce Eckel");
Book b3 = new Book("Java: The Complete Reference",
"Herbert Schildt");
// Creating the list which contains number of books
List<Book> books = new ArrayList<Book>();
// Adding books
// using add() method
books.add(b1);
books.add(b2);
books.add(b3);
Library library = new Library(books);
// Calling method to get total books in library
// and storing it in list of user0defined type -
// Books
List<Book> bks = library.getTotalBooksInLibrary();
// Iterating over books using for each loop
for (Book bk : bks) {
// Printing the title and author name of book on
// console
System.out.println("Title : " + bk.title
+ " and "
+ " Author : " + bk.author);
}
}
}
输出:
Title : EffectiveJ Java and Author : Joshua Bloch
Title : Thinking in Java and Author : Bruce Eckel
Title : Java: The Complete Reference and Author : Herbert Schildt
输出解释: 在上面的例子中,一个图书馆可以有许多关于相同或不同主题的书。所以,如果图书馆被毁了,那么这个图书馆里的所有书都会被毁。也就是说,书不能没有图书馆。这就是构成的原因。书是图书馆的一部分。
Java中聚合和组合的区别
| 聚合 | 组合 |
|---|---|
| 聚合可以被描述为“Has-a”关系,它表示对象之间的关联。 | 复合意味着一个对象包含在另一个对象中。它是一种特殊类型的聚合(即Has-a关系),这意味着一个对象是另一个对象的所有者,这可以称为所有权关联。 |
| 对象之间存在相互依赖关系。 | 有一种单向的关系,这也叫“部分”关系。 |
| 它是一种弱类型的关联,两个对象都有自己独立的生命周期。 | 它是一种强类型的关联(聚合),子对象没有自己的生命周期。 |
| 关联对象可以独立存在,并且有自己的生命周期。 | 孩子的生命取决于父母的生命。只有父对象有独立的生命周期。 |
| White Diamond的UML表示表示聚合。 | 黑钻石的UML表示表示组合。 |
| 例如,学生和部门之间的关系。学生可能没有一个系。 | 例如,一个包含在文件夹中的文件,如果删除了文件夹内的所有文件就会被删除。如果没有文件夹,文件就不能存在。 |
 极客教程
极客教程