与 Java 中的数组类似,LinkedList是线性数据结构。但是,LinkedList元素不存储在像数组这样的连续位置中,它们使用指针相互链接。LinkedList的每个元素都具有指向LinkedList的下一个元素的引用(地址/指针)。
LinkedList表示
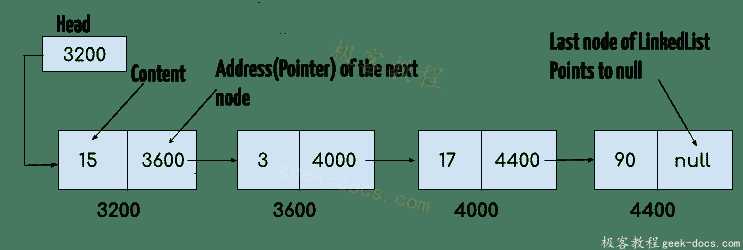
LinkedList中的每个元素称为节点。LinkedList的每个节点包含两个项目:1)元素的内容 2)指向链表中的下一节点的指针/地址/引用。
这就是LinkedList的样子:
注意:
LinkedList的头仅包含List的第一个元素的地址。LinkedList的最后一个元素在节点的指针部分包含null,因为它是List的结尾,因此它不指向任何内容,如上图所示。- 上图所示的图表示单链表。
LinkedList的另一种复杂类型变体称为双向链表,双向链表的节点包含三部分:1)指向链表的前一节点的指针,2)元素的内容,3)指向链表的下一个节点的指针。
为什么我们需要链表?
你必须知道数组也是一个线性数据结构,但**数组有一些限制,如:
1)数组的大小是固定的**这是我们决定的创建一个数组,因此很难预先预测元素的数量,如果声明的大小不足,那么我们就不能增加数组的大小,如果我们声明一个大型数组并且不需要存储那么多的元素那么它是浪费记忆。
2)数组元素需要连续的存储单元来存储它们的值。
3)在数组中插入一个元素是性能上昂贵的,因为我们必须移动几个元素来为新元素腾出空间。例如:
假设我们有一个具有以下元素的数组:10,12,15,20,4,5,100,现在如果我们想要在具有值 12 的元素之后插入新元素 99 那么我们必须将 12 之后的所有元素移到右边,为新元素腾出空间。
类似地,从数组中删除元素也是性能上昂贵的操作,因为删除元素之后的所有元素都必须向左移位。
通过提供以下功能在链表中处理这些限制:
- 链表允许动态内存分配,这意味着内存分配在运行时由编译器完成在链表声明中我们不需要提及列表的大小。
-
链表元素不需要连续的存储单元,因为元素使用包含列表的下一个节点的地址的节点的引用部分相互链接。
-
在链表中插入和删除操作的性能并不昂贵,因为从链表中添加和删除元素不需要元素移位,只需要更改前一个节点和下一个节点的指针。
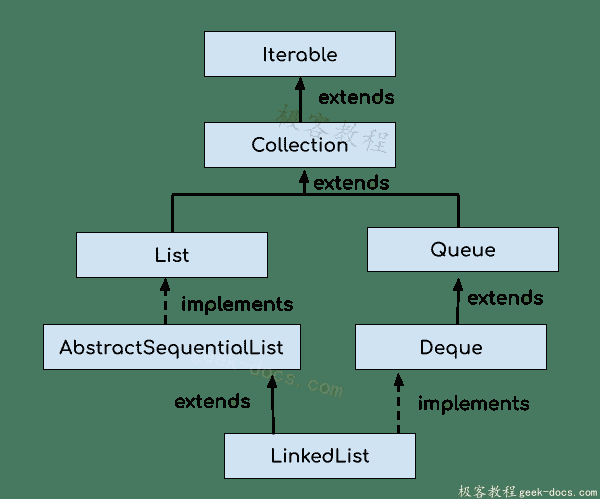
Java 中的LinkedList类的层次结构
Java LinkedList添加元素的示例
在下面的例子中,我们使用add(),addFirst()和addLast()方法在LinkedList中的所需位置添加元素,LinkedList类中有几个这样有用的方法,我在本文末尾提到过文章。
package com.beginnersbook;
import java.util.*;
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
LinkedList<String> list=new LinkedList<String>();
//Adding elements to the Linked list
list.add("Steve");
list.add("Carl");
list.add("Raj");
//Adding an element to the first position
list.addFirst("Negan");
//Adding an element to the last position
list.addLast("Rick");
//Adding an element to the 3rd position
list.add(2, "Glenn");
//Iterating LinkedList
Iterator<String> iterator=list.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
}
输出:

从LinkedList中删除元素的 Java 示例
在下面的示例中,我们将检查LinkedList中用于从LinkedList中的某些位置删除元素的几个流行的删除方法。这些方法的详细说明以及示例将在单独的教程中介绍,本文末尾提供了链接。
package com.beginnersbook;
import java.util.*;
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
LinkedList<String> list=new LinkedList<String>();
//Adding elements to the Linked list
list.add("Steve");
list.add("Carl");
list.add("Raj");
list.add("Negan");
list.add("Rick");
//Removing First element
//Same as list.remove(0);
list.removeFirst();
//Removing Last element
list.removeLast();
//Iterating LinkedList
Iterator<String> iterator=list.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.print(iterator.next()+" ");
}
//removing 2nd element, index starts with 0
list.remove(1);
System.out.print("\nAfter removing second element: ");
//Iterating LinkedList again
Iterator<String> iterator2=list.iterator();
while(iterator2.hasNext()){
System.out.print(iterator2.next()+" ");
}
}
}
输出:
Java 中的LinkedList示例
import java.util.*;
public class LinkedListExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
/* Linked List Declaration */
LinkedList<String> linkedlist = new LinkedList<String>();
/*add(String Element) is used for adding
* the elements to the linked list*/
linkedlist.add("Item1");
linkedlist.add("Item5");
linkedlist.add("Item3");
linkedlist.add("Item6");
linkedlist.add("Item2");
/*Display Linked List Content*/
System.out.println("Linked List Content: " +linkedlist);
/*Add First and Last Element*/
linkedlist.addFirst("First Item");
linkedlist.addLast("Last Item");
System.out.println("LinkedList Content after addition: " +linkedlist);
/*This is how to get and set Values*/
Object firstvar = linkedlist.get(0);
System.out.println("First element: " +firstvar);
linkedlist.set(0, "Changed first item");
Object firstvar2 = linkedlist.get(0);
System.out.println("First element after update by set method: " +firstvar2);
/*Remove first and last element*/
linkedlist.removeFirst();
linkedlist.removeLast();
System.out.println("LinkedList after deletion of first and last element: " +linkedlist);
/* Add to a Position and remove from a position*/
linkedlist.add(0, "Newly added item");
linkedlist.remove(2);
System.out.println("Final Content: " +linkedlist);
}
}
输出:
Linked List Content: [Item1, Item5, Item3, Item6, Item2]
LinkedList Content after addition: [First Item, Item1, Item5, Item3, Item6, Item2, Last Item]
First element: First Item
First element after update by set method: Changed first item
LinkedList after deletion of first and last element: [Item1, Item5, Item3, Item6, Item2]
Final Content: [Newly added item, Item1, Item3, Item6, Item2]
LinkedList类的方法:
这里我已经提到了
LinkedList方法的简要说明,我已经在单独的教程中介绍了这些方法中的每一个,本文末尾提供了链接。
对于以下方法中的所有示例,请将llistobj视为LinkedList<String>的参考。
LinkedList<String> llistobj = new LinkedList<String>();
1) boolean add(Object item):它在列表的末尾添加项目。
llistobj.add("Hello");
它会在链表的末尾添加字符串"Hello"。
2) void add(int index, Object item):它在列表的给定索引处添加一个项目。
llistobj.add(2, "bye");
这将在第 3 个位置添加字符串"bye"(索引 2 是第 3 个位置,因为索引从 0 开始)。
3) boolean addAll(Collection c):它将指定集合c的所有元素添加到列表中。如果指定的集合为null,则抛出NullPointerException。考虑下面的例子 –
LinkedList<String> llistobj = new LinkedList<String>();
ArrayList<String> arraylist= new ArrayList<String>();
arraylist.add("String1");
arraylist.add("String2");
llistobj.addAll(arraylist);
这段代码会将ArrayList的所有元素添加到LinkedList中。
4)boolean addAll(int index, Collection c):它将集合c的所有元素从列表中的给定索引开始添加到列表中。如果集合c为null,则抛出NullPointerException;如果指定的索引超出范围,则抛出IndexOutOfBoundsException。
llistobj.add(5, arraylist);
它会将ArrayList的所有元素从位置 6(索引 5)开始添加到LinkedList。
5)void addFirst(Object item):它在列表的第一个位置添加项(或元素)。
llistobj.addFirst("text");
它会在列表的开头添加字符串"text"。
6)void addLast(Object item):它在列表的末尾插入指定的项目。
llistobj.addLast("Chaitanya");
该语句将在链表的末尾添加一个字符串"Chaitanya"。
7) void clear():删除列表中的所有元素。
llistobj.clear();
8)Object clone():返回列表的副本。
对于例如我的linkedList有四个项目:text1,text2,text3和text4。
Object str= llistobj.clone();
System.out.println(str);
输出:上面代码的输出是:
[text1,text2,text3,text4]
9) boolean contains(Object item):它检查给定项是否存在于列表中。如果该项目存在,则返回true,否则返回false。
boolean var = llistobj.contains("TestString");
它将检查列表中是否存在字符串"TestString"。
10) Object get(int index):从列表中返回指定索引的项。
Object var = llistobj.get(2);
它将从列表中获取第 3 个项目。
11) Object getFirst():从列表中取出第一个项目。
Object var = llistobj.getFirst();
12)Object getLast():从列表中取出最后一项。
Object var= llistobj.getLast();
13)int indexOf(Object item):返回指定项的索引。
llistobj.indexOf("bye");
14)int lastIndexOf(Object item):返回指定元素最后一次出现的索引。
int pos = llistobj.lastIndexOf("hello);
整数变量pos将具有最后一次出现的字符串"hello"的索引。
15)Object poll():它返回并删除列表的第一项。
Object o = llistobj.poll();
16)Object pollFirst():与poll()方法相同。删除列表中的第一项。
Object o = llistobj.pollFirst();
17)Object pollLast():返回并删除列表的最后一个元素。
Object o = llistobj.pollLast();
18)Object remove():删除列表的第一个元素。
llistobj.remove();
19)Object remove(int index):它从列表中删除指定索引处的项目。
llistobj.remove(4);
它将从列表中删除第 5 个元素。
20)Object remove(Object obj):从列表中删除指定的对象。
llistobj.remove("Test Item");
21)Object removeFirst():它从列表中删除第一个项目。
llistobj.removeFirst();
22)Object removeLast():删除列表的最后一项。
llistobj.removeLast();
23)Object removeFirstOccurrence(Object item):删除指定项的第一次出现。
llistobj.removeFirstOccurrence("text");
它将从列表中删除第一次出现的字符串"text"。
24)Object removeLastOccurrence(Object item):删除给定元素的最后一次出现。
llistobj.removeLastOccurrence("String1);
它将删除最后一次出现的字符串"String1"。
25)Object set(int index, Object item):用赋值更新指定索引的项。
llistobj.set(2, "Test");
它将使用字符串"Test"更新第 3 个元素。
26) int size():返回列表元素的数量。
llistobj.size();
 极客教程
极客教程